Preston Lake 的文章评论
Moradi, A.、Sadr, A.、Ebrahimzadeh, MH、Hassankhani, GG 和 Mehrad-Majd, H.
(2020)。糖尿病会改变腕管松解术的疗效吗?证据来自
系统综述和荟萃分析。《手部治疗杂志》,33(3),
394–401。https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2020.01.003
瘦子:
本研究的目的是系统地回顾当前可用的文献,以描述
手术的临床、功能和神经生理结果的差异
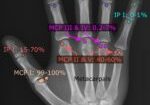
减压 糖尿病患者 和非糖尿病患者 腕管 综合症(CTS)。
作者试图澄清先前关于该主题的研究中所发现的矛盾的结果。
在杂草丛中:
这项荟萃分析回顾了 10 篇符合纳入标准和研究相关性的文章,其中 446
糖尿病患者和 2423 名非糖尿病患者接受腕管综合征手术减压治疗。所有研究
本综述纳入了 2 个回顾性队列研究和 7 个前瞻性队列研究。
糖尿病患者平均年龄为57.8岁,非糖尿病患者平均年龄为54.8岁。所有研究均纳入
使用波士顿腕管问卷 (BCTQ) 报告的结果,快速残疾
手臂、肩部和手部 (QuickDASH) 或神经传导研究。此外,研究
仅当患者接受开放手术或内镜手术松解并接受 6 个月
后续研究。本综述纳入的所有研究均为队列研究,其中 2 项为回顾性研究,7 项为
具有前瞻性。

主要发现
- 非糖尿病患者和糖尿病患者之间没有显著差异
对于使用 Quick DASH 和 BCTQ 报告结果的研究 - 非糖尿病患者和糖尿病患者之间没有显著差异
正中神经和尺神经的运动传导研究 - 非糖尿病患者的感觉传导结果明显更好
手腕至手掌部分和手腕至中指部分。 - 糖尿病患者的手术部位伤口感染率略高
患者,但结果并不具有统计学意义。
把它带回家:
本研究结果发现 CTS 减压手术在以下方面具有同等益处
术后症状和功能。作者发现,糖尿病患者
接受CTS减压手术的患者可以预期获得与无糖尿病患者相同的临床益处。有人提出,糖尿病患者感觉功能障碍水平较高
接受减压手术的患者与先前存在的糖尿病有关
神经病变。
评分:3/5
这是一项高水平的研究设计(荟萃分析),其中包括经过验证的临床结果
测量和出版偏见评估。作者提出了一个明确的临床问题,并
易于理解且无错误的方法论部分。本研究的局限性在于缺乏
随机对照试验、短期随访以及未能解释糖尿病神经病变
对结果的影响。
更多阅读内容
籽骨:它们是什么以及它们有什么作用?
作者:Brittany Carrie 学生的视角 在轮岗的头几周,我接触到了许多在课堂上没有接触过的新的、令人兴奋的事情。我观察并帮助治疗遭受从肌腱撕裂到完全截肢等严重创伤的患者,看到了不同的夹板技术,……
标题:了解 De Quervain 的病理学:特殊测试的综合探索
了解 De Quervain 的病理学:对特殊测试的全面探索 作者:Miranda Materi De Quervain 和特殊测试 De Quervain 腱鞘炎是一种以手腕拇指侧肌腱发炎为特征的疾病,会导致疼痛和不适。这些肌腱包括拇长展肌 (APL) 和拇短伸肌,因为它们穿过……
手部治疗领域的评估
作者:Dalton Busch 下面我列出了手部治疗领域中常见的一些评估。请记住,此列表并不包含您在此设置中可能遇到的所有评估。在每次评估中,我都会描述它是什么、评估是谁……
有伤口吗?作为手部治疗师如何管理它们。
伤口护理很混乱。伤口种类繁多(例如,伤口周围的白色皮肤),产品种类繁多,这可能会让人感到害怕,很难知道该使用什么、何时使用以及如何使用。如果您参加伤口护理会议,您将花费大部分时间……
注册即可直接将更新发送到您的收件箱!
注册我们,我们将定期向您发送有关手部治疗的所有内容的博客文章、每次上传新视频和教程时的通知,以及讲义、协议和其他有用信息。