The Utilization of CBD Hand Therapy for Pain Treament
Filed under Uncategorized
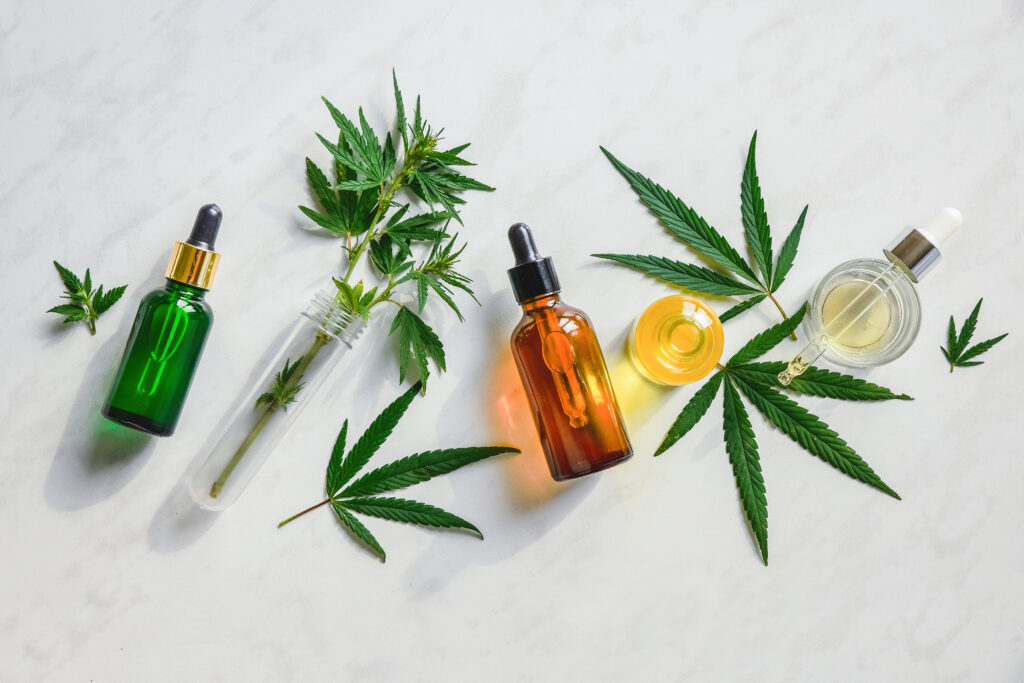

Patients frequently ask for advice on how to alleviate their pain symptoms. It is common for them to ask about the benefits of CBD Therapy. With the expanding holistic treatment market, Cannabis and CBD is at the forefront of holistic pain treatment. This article aims to give an overview of the utilization of CBD in patients who suffer acute and chronic pain.
“All Cannabis has CBD in it, but CBD is not Cannabis.”
What is CBD?
CBD is Cannabidiol, and it is derived from the hemp plant. It is non-psychoactive and legal to use. CBD is reported to help act as an anti-inflammatory pain killer (CBD pain killer) and has the benefits of reducing anxiety. CBD can be utilized alone or in combination with THC.
What is THC?
THC is Tetrahydrocannabinol. This is often associated with medical marijuana and elicits the psychotropic (“high”) effect. This compound can act as an anti-inflammatory and a sleep aid. THC has been legalized in some states, but there remains some legal grey zone when utilizing CBD with THC. However, changes are underway on the federal and state level to clarify the CBD regulation with THC products.
Does it work?
There is a plethora of anecdotal evidence supporting the use of CBD for pain relief in patients with acute and chronic conditions including arthritis, and other pain-causing ailments. Animal studies have suggested CBD is helpful in providing pain relief and reducing inflammation. There are more extensive studies underway studying the efficacy in humans; however, the evidence remains somewhat inconclusive.
How is CBD taken?
CBD can be taken orally, topically, or inhaled. When taken orally, it can come in capsule or liquid form. It is also sold in cookies or gummies; however, the dosing can be unreliable. There is usually a delay in absorption of one to 2 hours if taken in a capsule form. If taken in a tincture or spray, it can be absorbed within 15 to 45 minutes.
Topically CBD comes in a lotion, oil, or balm and can be applied over painful areas. Topicals can contain a combination of menthol, camphor, and other pain-relieving medication, making it difficult to determine which component is beneficial.
CBD can be inhaled. This is not recommended—vaping has been shown to cause an increased hospitalization rate, and many other adverse health effects have been reported.
How will I know if it is a good product?
CBD products are not well regulated in the United States. There are issues with reporting and controlling the strength of CBD, the presence of undeclared THC. Here is a list of common things to look for to ensure you get a quality CBD product.
- Ask, is it manufactured in the US?
- Purchase from companies that test each batch and one that uses independent labs approved by the American Herbal Pharmacopeia and the US Pharmacopeia
- Avoid companies that overpromise
- People manufacturing and producing CBD products are often not healthcare professionals.
What is the bottom line?
While there is some anecdotal evidence supporting CBD, the benefits remain inconclusive. There remains some risk with integration in CBD in your practice, including the lack of standardization and the possible interaction of other treatments or prescribed medications. It is essential to provide clear guidelines on CBD use and not specify or prescribe any medication. It is also important to not oversell and indicate the product will have specific health benefits as this has not been proven. A good idea is to consult with a certified CBD therapist.
1 Comment
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Factors that influence orthosis adherence in patients with acute traumatic tendon injuries to the hand
Savaş, S., & Aydoğan, Ç. (2020). Factors affecting orthosis adherence after acute traumatic hand tendon repairs: A prospective cohort study. Journal of Hand Therapy, S0894113020301848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2020.10.005 World Health Organization. (2003). Adherence to long-term therapies: evidence for action. World Health Organization. The Skinny Adherence to orthosis wear is vital for protecting healing tendons after a traumatic tendon…
How to use Kinesiology Taping for Shoulder Subluxation
How to us Kinesiology Tape for Shoulder Subluxation By: Tayler Roost What is shoulder subluxation? Shoulder subluxation is a dislocation of the glenohumeral joint. This can be classified as traumatic, non-traumatic, or neurological. A traumatic shoulder subluxation can be caused by contact sports or repetitive shoulder movements. A non-traumatic shoulder subluxation can be caused indirectly…
Differential Diagnosis: Trigger Finger vs. Subluxing Sagittal Band Injury vs. Subluxing Lateral Band
Differential Diagnosis: Trigger Finger vs. Subluxing Sagittal Band Injury vs. Subluxing Lateral Band Hand therapists frequently encounter patients presenting with finger pain, clicking, and difficulty with tendon glide. Among the most commonly confused conditions are trigger finger, subluxing sagittal band injury, and subluxing lateral band. Each of these pathologies involves different anatomical structures and biomechanical…
How To Do A Fast but Thorough Hand Therapy Assessment
We don’t get a lot of time. Sometimes new patients come in unexpectedly or someone comes at the wrong time and your 1-hour block for an eval is suddenly only 30 minutes. Do you know how to get the most out of your eval time with the patient? Do you know what things are the…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.




Great article source to read. Thank you for sharing this.