Exertional (Chronic) Compartment Syndrome of The Hand
Filed under Treatments
By: Tommi Long
What is it?
Chronic exertional compartment syndrome (CECS) is an exercise-induced condition affecting the muscles and nerves, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced muscle function due to increased pressure and restricted circulation. While most commonly, it impacts the arms and legs, it is rare to happen in the hand(s). CECS is most prevalent in young adult runners and athletes who participate in repetitive activities, although anyone can develop this condition.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Weakness
- Bludging around muscle
- Tightness
- Pain while completing stretches
- Numbness and tingling
- Aching, burning, or cramping pain in the affected muscle
How is CECS diagnosed?
- X-ray to rule out any fractures or bone injuries
- MRI evaluates the compartments’ muscles and structures. Advanced MRIs can also assess the fluid volumes of each compartment during and after exercise.
- Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a newer technique for measuring the amount of oxygen in the blood and tissue of the affected limb. It is performed at rest and after exercise.
- Compartment pressure testing measures the pressure within your muscle compartments by inserting a needle into several different places. This test is the gold standard for diagnosing chronic exertional compartment syndrome.
Treatments:
Surgical and nonsurgical methods are available for this condition, although nonsurgical options must immediately stop or significantly limit activities that cause compartment syndrome. Nonsurgical options typically don’t have long-lasting effects for true CECS.
Nonsurgical options-
- Break from exercise or activity
- Medications for pain and anti-inflammatory
- Therapy (manual therapy, ergonomics, modified environment, strengthening, flexibility)
- Botulinum toxin A injections into affected muscles
- Orthosis
Surgical Options-
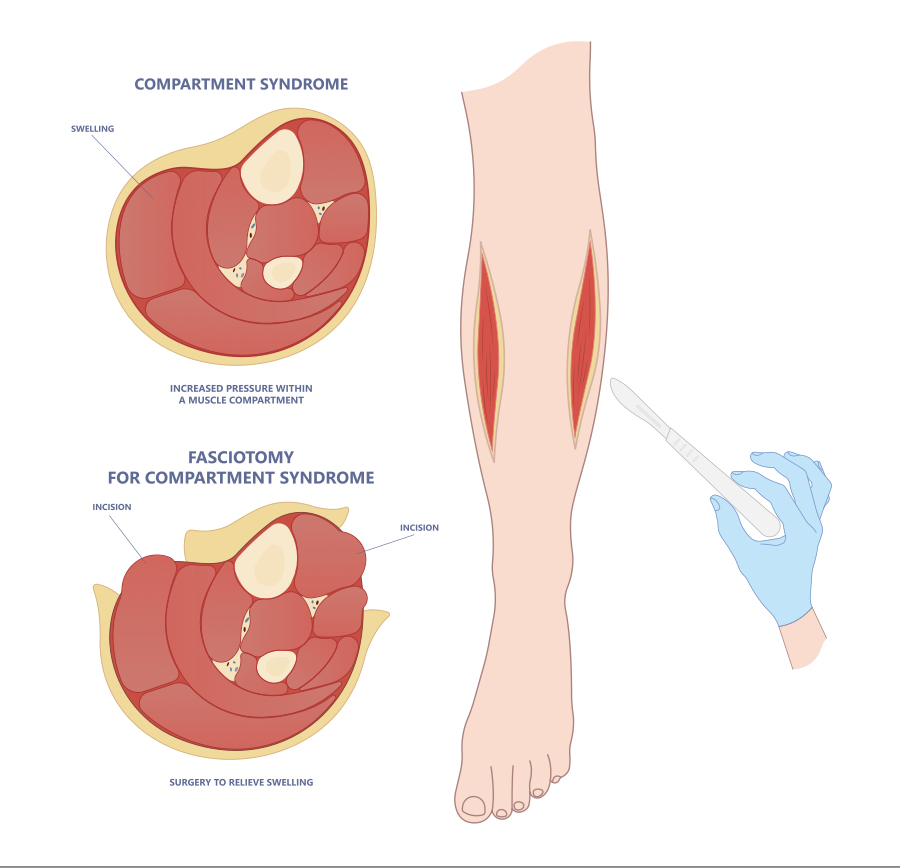
- Research suggests fasciotomies are the most effective treatment (Cutting open tissues encasing affected muscle compartments to relieve pressure) or (small incisions to reduce recovery time)
- Selective releases of the thenar and hypothenar compartments
References:
Dwyer, C. L., Soong, M. C., & Kasparyan, N. G. (2016). Chronic exertional compartment syndrome of the hand: Case report and literature review. HAND, 12(3). https://doi.org/10.1177/1558944716668826
Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (n.d.). Chronic exertional compartmentsyndrome. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/chronic-exertional-compartment-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20350830
Phillips, J. H., Mackinnon, S. E., Murray, J. F., & McMurtry, R. Y. (1986). Exercise-inducedchronic compartment syndrome of the first dorsal interosseous muscle of the hand: A case report. The Journal of Hand Surgery, 11(1), 124–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0363-5023(86)80118-6
What are the main signs of compartment syndrome?. Cleveland Clinic. (2024, August 5).https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15315-compartment-syndrome
More To Read
The effects of cupping therapy as a new approach in the physiotherapeutic management of carpal tunnel syndrome
Article Review By: Rachel Reed Mohammadi, S., Roostayi, M. M., Naimi, S. S., & Baghban, A. A. (2019). The effects of cupping therapy as a new approach in the physiotherapeutic management of carpal tunnel syndrome. Physiotherapy research international : the journal for researchers and clinicians in physical therapy, 24(3), e1770. https://doi.org/10.1002/pri.1770 The Skinny: The purpose of this…
Do you know the difference between an Electromyography (EMG) and a Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV) Study?
Do you know the difference between EMG and NCV (an Electromyography and a Nerve Conduction Velocity Study? The term nerve test is usually a broad term that typically indicates both an Electromyography (EMG) and a Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV) study (EMG vs NCV). An EMG looks at the electrical signals your muscle makes when at…
Brachial Plexopathy Case Example in Hand Therapy
Brachial Plexopathy Case Example in Hand Therapy (plexopathy examples) One of the recent cases we have seen is a 13-year old with a brachial plexus injury. We are seeing the patient post-surgery for tendon transfers to increase functional use of his left upper extremity (LUE). Before the surgery, he could not extend the wrist and…
Rapid Review: Is Finger Splinting Necessary after Flexor Tendon Repair?
Outcome of Flexor Tendon Repair Using Eight-Strand Core Stitch Without Postoperative Finger Splinting Reference: El-Gammal, T. A., Kotb, M. M., Ragheb, Y. F., El-Gammal, Y. T., & Anwar, M. M. (2024). Outcome of Flexor Tendon Repair Using Eight-Strand Core Stitch Without Postoperative Finger Splinting. HAND. https://doi.org/10.1177/15589447231220686 The Skinny: The purpose of this study was to…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.