J. F. Goubau, L. Goubau, A. Van Tongel, P. Van Hoonacker, D. Kerckhove, B. Berghs (2013).The wrist hyperflexion and abduction of the thumb (WHAT) test: a more specific and sensitive test to diagnose de Quervain tenosynovitis than the Eichhoff’s Test. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2014 Mar; 39(3): 286–292. Published online 2013 Jan 22. doi: 10.1177/1753193412475043
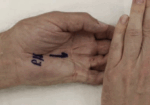
“The WHAT test is performed as follows: the wrist is hyperflexed and the thumb abducted in full MP and IP extension, resisted against the therapist’s index finger. Exacerbation of the symptomatology is considered a positive test result”.
The Skinny- When choosing a provocative test for De Quervain’s disease (De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis Test), therapists in the past have typically chosen from two popular tests; Eichoff’s test and Finkelstein’s test. The latter often being confused with the first. This study compares Eichoff’s test to a new test called The Wrist Hyperflexion and Abduction of the Thumb test (wrist hyperabduction test – WHAT). The study included 100 patients experiencing de Quervain tendinopathy between the years 2007-2010.
In The Weeds-Each patient underwent the Eichoff’s test and the WHAT test in random order by two experienced hand surgeons (test for de quervain’s tenosynovitis). Each provocative testing procedure was carried out in the same sequence to ensure consistency. Patients who tested positive under either test were sent for X-ray and ultrasonography to confirm the diagnosis of de Quervains.
Results: Ninety-three ultrasounds were positive and seven were negative. The accuracy of Eichoff’s test was .84 while the accuracy of the WHAT test was .94, suggesting that the latter performs better overall in establishing the correct diagnosis. The WHAT test also produced a better sensitivity at .99 and specificity at .29.
Bring it Home- A new test known as the WHAT test was developed due to the controversy associated with the accuracy of Eichoff’s test, and also the need for a more patient-friendly test for use in daily practice. This study found the WHAT test to be superior in all categories. This may be due in part to the specific mechanics of the WHAT test, positioning the anatomy in a way to accurately detect even the earliest symptoms.
This study was transparent about their methodology and had well thought out methods including sequence protocols for each provocative test for consistency, random order, and a large sample size. Using ultrasound technology to confirm the results of the in-clinic provocative testing provides a reliable diagnosis for comparison. Detailed explanations of the WHAT test were also provided along with pictures and illustrations of the anatomy, showing the superior mechanism of the test.
2 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
How Weather Changes Affect Joint Pain
By: Lucas Godwin How Weather Changes Affect Joint Pain Numerous potential factors can cause weather-related joint pain, including humidity, temperature, precipitation, and changes in barometric pressure. Scientists have performed many studies on joint pain and weather over the years, but so far, none can say for sure what the connection is. Timmermans et al., 2015…
Discovering Connections Between Trigger Finger and Dupuytren’s
Discovering Connections Between Trigger Finger and Dupuytren’s By: Tayer Roost Reference: Yang, Gehring, M., Bou Zein Eddine, S., & Hettinger, P. (2019). Association between stenosing tenosynovitis and dupuytren’s contracture in the hand. Plastic and reconstructive surgery. Global open, 7(1), e2088–e2088. https://doi.org/10.1097/GOX.0000000000002088 The Skinny: This retrospective chart review discussed the possibility of a correlation between stenosing…
Tommy John Injury: Journey Back to Throwing after a UCL Injury
Anatomy of Ulnar Collateral Ligament (UCL) Originating on the anteroinferior surface of the medial epicondyle of the humerus and inserting onto the sublime tubercle of the ulna, the ulnar collateral ligament (UCL), also known as the medial collateral ligament (MCL), is crucial in providing support to the medial aspect of the elbow by restraining valgus…
Effectiveness of Conservative Therapy and Splinting for 1st CMC OA
Tsehaie, J., Sprekraijse, K., Wouters, R., Slijper, H., Feitz, R., Hovious, S., & Selles, R. (2018). Outcome of a Hand Orthosis and Hand Therapy for Carpometacarpal Osteoarthritis in Daily Practice: A Prospective Cohort Study. American Society for Surgery of the Hand, 1-11. The skinny: Non-surgical approaches (hand therapy & orthotics) are typically the go-to for…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.






I am looking forward to performing this test along with the Eichoff’s test. I think that if both are positive then it provides the physician with more information at their next MD appointment. I find that this diagnosis is often missed with my wrist sprain/strain patients.
Thank you for this information.
Nice post, I really appreciate you for sharing this informative post. Thanks