Stretching Alone Can Change P1 Bone Shape in Patients with Camptodactyly
Filed under Reviews
Woo Hong, S. Kim, J., Sang Kwon, O., Ho Lee, M., Sik Gong, H., Hyun Baek, G., (2019). Radiographic Remodeling of the Proximal Phalangeal Head Using a Stretching Exercise in Patients With Camptodactyly. J Hand Surg Am, 1.e1-1.e10
The Skinny – Camptodactyly is a congenital, nontraumatic flexion contracture of the PIP in fingers other than the thumb. Type 1 Camptodactyly ( Isolated anomaly in children <36 months) also includes volarly angulated and beak-shaped flat proximal phalangeal head. This study investigated the impact of a stretching-only camptodactyly treatment plan on restoration of Proximal Phalangeal head angulation as well as joint contracture.
In The Weeds – In a retrospective cohort study using radiographic series, 48 digits in 20 patients <36 months with >12 months of follow up were studies. 2 indexes were created to measure Head Angle (HA) and Head Triangle Ratio, or head shape (HTR).
Camptodactyly Stretches: Parents conducted a minimum of 20 sessions/day of a minimum of 5 minutes/session on affected fingers. Wrist and MCP were held in extension to increase FDS and FDP tension while force was applied to DIP joint flexion crease. This was done for 12 months.
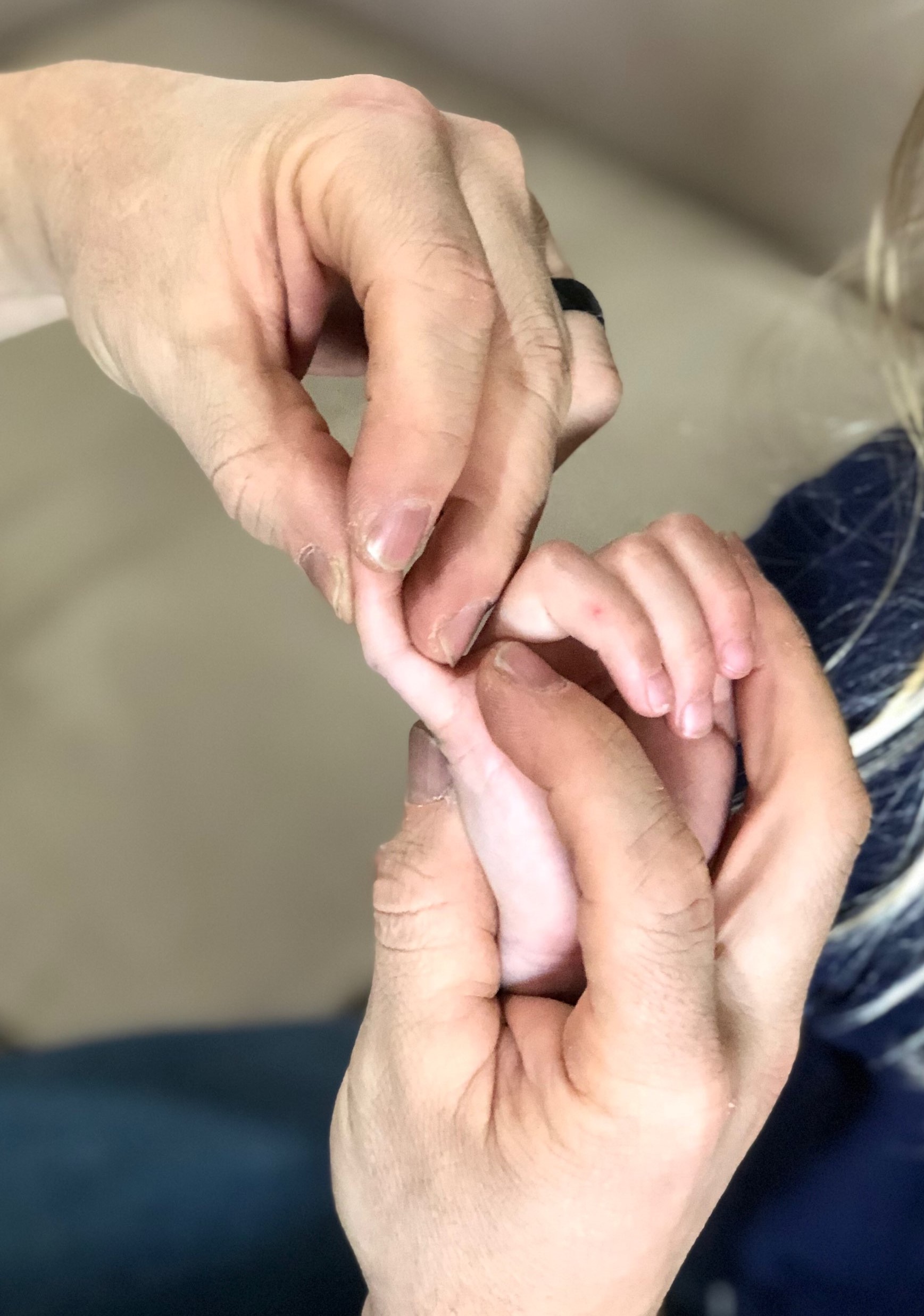

Results: “roundness and concentricity of the proximal phalangeal head was restored in all cases” with statistical significance. Flexion contracture of the PIP decreased from 34 degrees ± 13 to 6 degrees ±7.
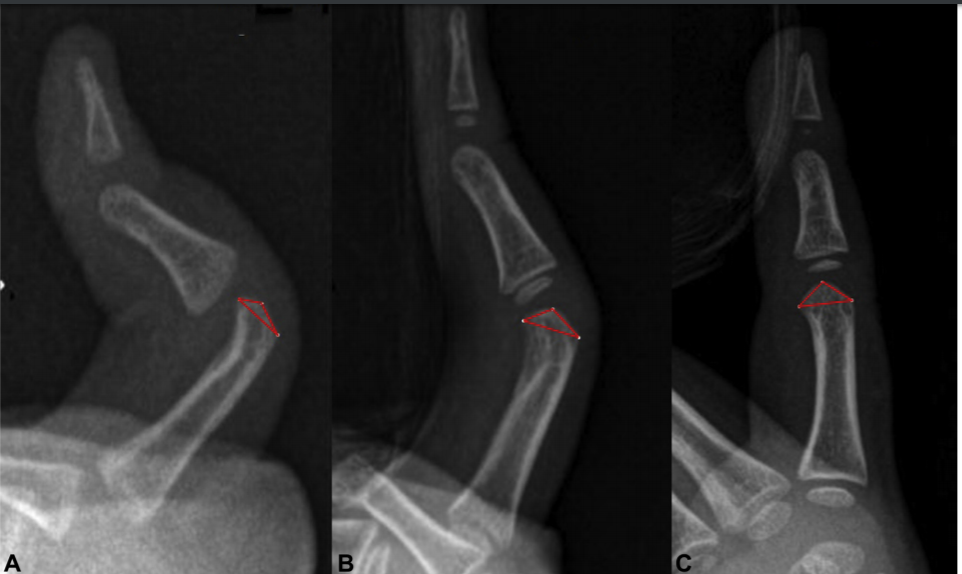
Bring it Home – Radiographic imaging indicates that stretching alone can restore the shape and angulation of the proximal phalangeal head and decrease flexion contracture. There was no correlation between contracture angle and boney shape throughout the study. This study had significant intra and inter-rater reliability for HA and HTR measures and control group illustrated that bone growth alone did not account for change in these parameters.
While other types (i.e. ages) of camptodactyly need to be studied, this study supports the strong value in stretching exercises for this diagnosis (camptodactyly exercises). Younger patients are particularly more receptive due to soft tissues being more extensile and the joint is more flexible. While the stretching protocol in this study is extensive, and may not be maintainable by many families, this approach is highly effective in achieving results non-surgically.
2 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Mirror Therapy
Mirror therapy has many implications for therapy and can be used to treat many diagnoses that commonly involve the upper extremity. These include some of the Neuro Conditions we highlighted last week including, Stroke and Focal Hand Dystonia. Btw, you can download a mirror therapy exercises pdf here for free. How long should the patient…
Upper extremity weight-bearing tolerance
Barlow, S.J., Scholtz, J. & Medeiros (2020). Wrist weight-bearing tolerance in healthy adults. Journal of Hand Therapy, xxx currently in press. The Skinny Wrist pain and instability are common occurrences and can occur with acute or chronic injuries. This leads to significant dysfunction, including the inability to tolerate axial loading through the upper extremity. There is…
What is Chronic Exertional Compartment Syndrome? Overview and Hand Therapy Treatment Ideas
Compartment syndrome is a condition characterized by increased pressure within a compartment of the body, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced tissue perfusion (Barkay et al., 2021; Buerba et al., 2019). It can be either acute or chronic (Barkay et al., 2021). Chronic exertional compartment syndrome (CECS) is a rare type, most commonly observed in…
The effects of cupping therapy as a new approach in the physiotherapeutic management of carpal tunnel syndrome
Article Review By: Rachel Reed Mohammadi, S., Roostayi, M. M., Naimi, S. S., & Baghban, A. A. (2019). The effects of cupping therapy as a new approach in the physiotherapeutic management of carpal tunnel syndrome. Physiotherapy research international : the journal for researchers and clinicians in physical therapy, 24(3), e1770. https://doi.org/10.1002/pri.1770 The Skinny: The purpose of this…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.





Is it possible for me to obtain a copy of the full article?
We can’t distribute the article itself, but the reference is provided so you can still find it. If you have a connection at a local university they may be able to pull it for you. Or Google Scholar will often have articles available in full print for viewing.