Lin, K.M, James, E.W., Spitze, E. & Fabricant, P.D. (2018). Pediatric and adolescent anterior shoulder instability: Clinical management of first-time dislocators. Current opinion in pediatrics, 30, 49-56. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000566.
The Skinny:
- Shoulder instability for pediatric and adolescent patients is fairly common and is often complicated by a high re-dislocation rate. Shoulder instability typically occurs after an acute traumatic event or cumulative repetitive microtrauma (such as baseball pitching) and can be further aggravated by pediatric joint hypermobility. Shoulder instability can occur in many planes of movement: anterior, posterior, or multi-planar however, anterior dislocation and subsequent instability is most common.
- This purpose of this study is to analyze the outcomes of conservative versus surgical management of anterior instability in pediatric and adolescent patients in light of the recent trend towards early surgical stabilization.
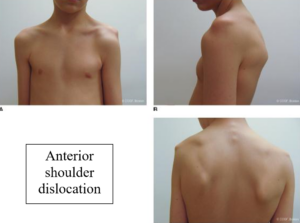
In the Weeds:
- Studies have shown that hypermobility shoulder dislocation per 100,000 people is 0.92 for children ages 0-9 years old, 39.71 for adolescents ages 10-19 years old, and 23.9 for overall ages. This data indicates that shoulder instability after initial dislocation most frequently occurs in adolescents.
- Two factors have been connected with the high recurrence rate of shoulder instability for adolescents. The most dominant being retained collagen elasticity after childhood. Additionally, the authors theorize that patients with closed growth plates are more likely to have a recurrent dislocation (88%) than those with open growth plates (53%).
- These findings assert that children tend to have significantly less recurrence of dislocation than adolescents overall and therefore surgical intervention for younger patients may be unnecessary and may predispose them to undue risk of surgery complications.
- The article further suggests that patients under 25 years of age are likely to have recurrent instability regardless of intervention. These patients have a non-operative recurrent instability rate as high as 90% after an initial dislocation without intervention, and recurrent instability rates after surgery linger around 20%.
Bringing It Home:
- Currently, therapy remains the final form of treatment for 60% of patients under 25-years-of-age. Early implementation of therapy focusing on scapular and rotator cuff strengthening has demonstrated the best outcomes to reduce incidence of recurrent instability. Four to five weeks of therapy following initial dislocation allows pediatric and adolescent patients to regain full motion and strength and decrease apprehension with use.
- Without intervention and strengthening post-dislocation, recurrent instability can cause persistent symptoms that effect quality of life, and lead to chondral damage in the shoulder, placing the patient at risk for developing symptomatic osteoarthritis.
- Limitations: The article does not mention the statistical improvements for patients with recurrent instability who participate in therapy versus those patients who do not complete therapy or undergo surgery.
2 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Which is better for DeQuervain’s: Splinting or Injection?
Rapid Review Cavaleri, R., Schabrun, S. M., Te, M., & Chipchase, L. S. (2016). Hand therapy versus corticosteroid injections in de Quervain’s disease treatment: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of hand therapy: official journal of the American Society of Hand Therapists, 29(1), 3–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2015.10.004 The Skinny: DeQuervain’s Tenosynovitis is a stenosing tenosynovial inflammation affecting the…
5 return-to-cooking activities (that don’t require a kitchen)
Hand therapy can and should be very occupation-based. Every week, we hear comments from patients that back that statement up: “I need to get back to work” “I just want to golf again” “I can’t even open a water bottle” “My spouse has to do all of the cooking” Although standard exercises are helpful, it’s…
Splinting Options for Stiff Finger Joints
Following an injury to the proximal interphalangeal joint, there is often a loss of range of motion, typically in both the flexion and extension planes. Therefore, we have compiled a list of helpful splinting options for stiff finger joints. To Improve PIP Joint Flexion Flexion Wrap with Elastic Tape (Coban): This is a very easy…
Which orthosis design is better for zone 5-6 extensor tendon injuries, a relative motion orthosis compared to a dynamic extension orthosis?
M. Buhler, ˝ D. Gwynne-Jones, M. Chin et al., (2023) Are the outcomes of relative motion extension orthoses noninferior and cost-effective compared with dynamic extension orthoses for management of zones V-VI finger extensor tendon repairs: A randomizedcontrolledtrialJournalofHandTherapy. The Skinny: The aim of this study was to compare the data for two different types of orthoses…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.






good information, I get young adults with shoulder dislocations and many times when I ask if this had happened before it’s like they think I have a crystal ball into their younger days. They say How do you know?
That is funny! Thanks for sharing. Miranda