Therapeutic Interventions and Contraindications of Cupping
Filed under Treatments
By Kaylen Kallander
Cupping therapy is used to apply negative pressure to a localized area of muscular or neurological pain to relieve nerve pressure and increase blood flow to an affected area. This modality is commonly used for athletes, but is also a frequent treatment in physical therapy, occupational therapy, or hand therapy. While cupping can be an effective and beneficial treatment, it should be used in correct circumstances with specific precautions.
Reasons for Use
- Musculoskeletal injuries/tightness
- Myofascial adhesions
- Neurologic pain with doctor’s approval
Cupping along median nerve pathways modified to use smaller cups for this patient whose arms had less surface area for suction.
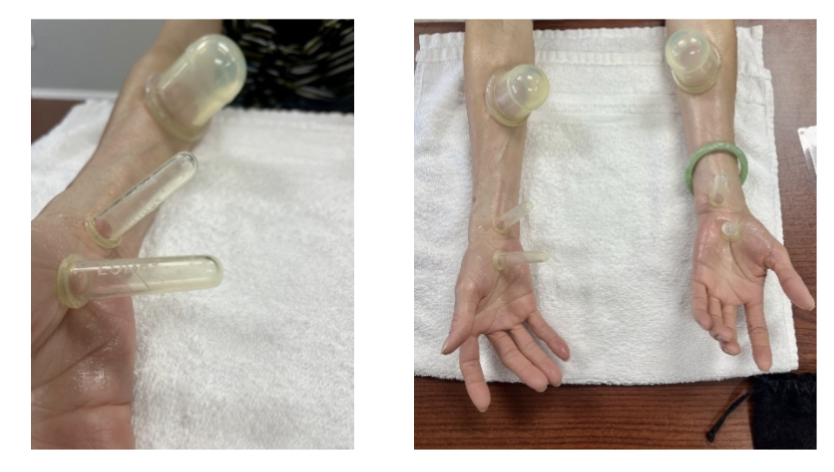
Contraindications & Reasons to Discontinue
- Open wounds or acute injury with 24-72 hours
- Neurovascular compromise
- Cardiac or blood malfunction
- Blisters, lightheadedness, or significant pain during use
Considerations
In addition to the appropriate application of cupping therapy, a thorough explanation of treatment effects must be provided to patients. Patients, or parents of minor patients, should give consent before treatment proceeds. Allergies to cupping material, lotion, or oil should be considered as well. Significant bruises are expected and can last from a few days to two weeks. However, treatment should always be within a patient’s pain tolerance. While soreness is normal, it shouldn’t feel worse than having received a deep tissue massage. Patients who have received multiple treatments often present less discomfort with increased suction and decreased bruising over time. Therapeutic effects of cupping treatment can be seen with as little as 5 minutes but should be no longer than 30 minutes if in a static position.
Key Takeaways
Therapy should always be holistic, purposeful, and patient specific. Cupping may be utilized for various diagnoses and pain relief, but patient experience and preference is equally important. Furthermore, a sufficient background of medical knowledge is required to understand potential contraindications to refrain from, delay, or cease treatment. With professional critical reasoning, cupping can be a great modality to use in hand therapy for decreased muscular or nerve pain.
Cage, A. (2019). Clinical Experts Statement: The definition, Prescription, and application of cupping Therapy. Clinical Practice in Athletic Training, 2(2), 4–11. https://doi.org/10.31622/2019/0002.2
4 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Orthotic Options for Hand Burns
By: Sophia Grimm Hand burns can be very challenging to treat, and successful rehabilitation begins early after acute injury. Following a burn injury, scar contractures are the primary reason for the deformity of the hand. Therefore, proper orthotic intervention is key to preventing joint and ligament contractures (Kelly, Berenz & Williams, 2019). Splinting goals following…
Differentiating Proximal Median Nerve Entrapment from Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
By: Brittany Day Proximal Median Nerve Entrapment, Pronator Syndrome, or Lacertus Syndrome? Pronator syndrome is a term used to describe proximal median nerve entrapment (PMNE) in the forearm. Pronator syndrome and lacertus syndrome are sometimes used interchangeably to describe proximal median nerve entrapment distal to the ligament of Struthers and proximal to the flexor superficialis…
How to use Kinesiology Taping for Shoulder Subluxation
How to us Kinesiology Tape for Shoulder Subluxation By: Tayler Roost What is shoulder subluxation? Shoulder subluxation is a dislocation of the glenohumeral joint. This can be classified as traumatic, non-traumatic, or neurological. A traumatic shoulder subluxation can be caused by contact sports or repetitive shoulder movements. A non-traumatic shoulder subluxation can be caused indirectly…
A Fun Fact from a Hand Therapy Student
By: Ammie Ingwaldson Level 2 Fieldwork at a hand therapy clinic is a fast paced and continuous learning experience. The perfect example of this occurred last week while observing a therapist provide a client with their home CMC arthritis program. The therapist was educating the client on how to oppose their thumb to their small…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.





I love your blog posts. Short and full of little gems.
Thank you for your kind words! We love sharing.
I would add to always include active movement with your cupping treatments for best results.
That is a great tip as well!