Pillar Pain After Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
Carpal tunnel release (CTR) surgery is a common procedure, with the majority of patients experiencing satisfaction with its outcomes. However, for some individuals, a temporary complication known as “pillar pain” may arise, affecting approximately 13% of those undergoing CTR.
Pillar pain manifests in the thenar eminence and hypothenar eminence due to their proximity to the transverse carpal ligament. It is characterized by wrist pain that causes tenderness and discomfort upon touch, distinct from the incision pain typical of surgical recovery, which usually subsides within a few days to weeks.
Although pillar pain symptoms typically resolve within three months, they can persist longer, even up to 9-12 months. While the exact cause of pillar pain remains elusive, several theories have been proposed, including tender scar tissue, muscle alignment alterations, joint inflammation, injury to small nerve fiber branches, and nerve irritation. Notably, a neurogenic component is suggested, indicating that nerve tissue damage from carpal tunnel surgery may play a significant role.
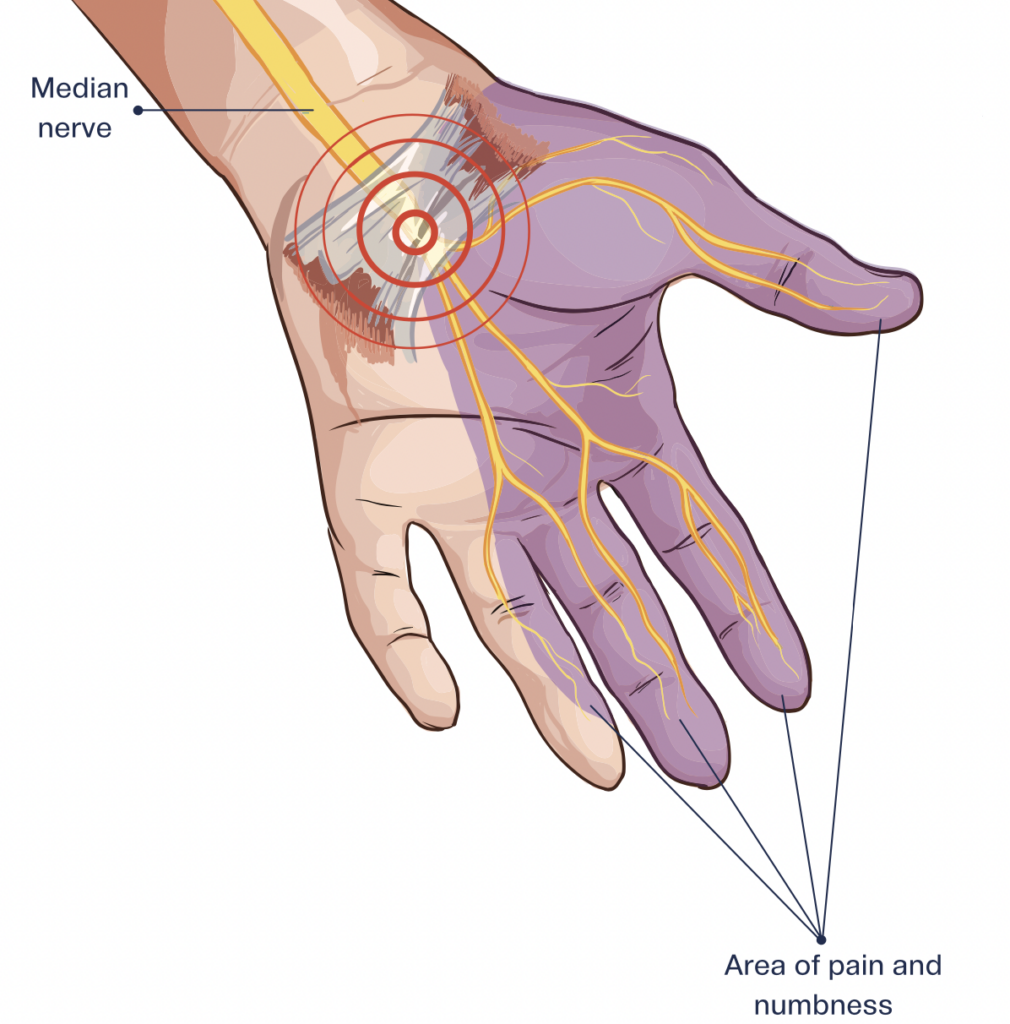
A theory posits that avoiding the “critical pillar rectangle” during surgery, which encompasses specific anatomical landmarks, could substantially reduce the likelihood of pillar pain occurrence.
Hand therapists offer various interventions for managing pillar pain, including:
- Stretching exercises such as the extrinsic stretching of wrist/hand flexor and tendon gliding exercises.
- Soft tissue mobilization targeted at the thenar and hypothenar eminences, gradually increasing pressure in sensitive areas.
- Desensitization techniques involve the use of different textures like cotton, wool, foam, soft Velcro, and others to rub over sensitive areas. Immersion of the affected area in substances like cotton balls, foam, rice, or beans can aid in desensitization.
- Median nerve glides to facilitate nerve flossing and restore median nerve mobility.
- Scar softening treatments such as paper tape or silicone gel pad.
By employing these strategies, individuals experiencing pillar pain can effectively manage their symptoms and facilitate recovery following carpal tunnel surgery.
Kumar, A., & Lawson-Smith, M. (2024). Pillar pain after minimally invasive and standard open carpal tunnel release: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Hand Surgery Global Online. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsg.2023.12.003
Ludlow, K., Merla, L., Cox, J., & Hurst, L. (1997a). Pillar pain as a postoperative complication of carpal tunnel release. Journal of Hand Therapy, 10(4), 277–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0894-1130(97)80042-7 .
1 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Scapholunate Wrist Injuries in Hand Therapy
Scapholunate Wrist Injuries in Hand Therapy In outpatient hand therapy, we get a variety of referrals ranging from post-operative patients to those looking to avoid or prolong surgery. These referrals come from a variety of sources ranging from primary care doctors to experienced hand surgeons. The therapy orders can be vague to very specific. …
Read MoreEfficacy of Virtual Reality Rehabilitation after Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review
De Araújo, A. V. L., Neiva, J. F. D. O., Monteiro, C. B. D. M., & Magalhães, F. H. (2019). Efficacy of virtual reality rehabilitation after spinal cord injury: A systematic review. BioMed Research International, 2019(1), 7106951. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7106951 Efficacy of Virtual Reality Rehabilitation after Spinal Cord Injury Emilee Sanders, OTS The Skinny: Virtual reality (VR)…
Read MoreOutcomes of Dorsal Bridging Plates
Outcomes of Dorsal Bridging Plates Fares, A. B., Childs, B. R., Polmear, M. M., Clark, D. M., Nesti, L. J., & Dunn, J. C. (2021). Dorsal Bridge Plate for Distal Radius Fractures: A Systematic Review. The Journal of Hand Surgery. https://doi-org.methodistlibrary.idm.oclc.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2020.11.026 The Skinny Distal radius fractures (DRF) are a common injury that we see in…
Read MoreSign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.




Thank you for all the info