Do you know the difference between an Electromyography (EMG) and a Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV) Study?
Filed under Diagnoses
Do you know the difference between EMG and NCV (an Electromyography and a Nerve Conduction Velocity Study?
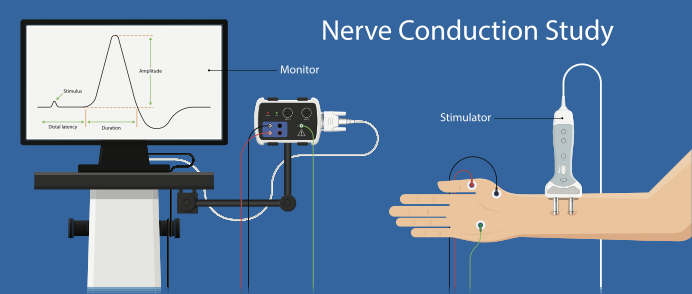
The term nerve test is usually a broad term that typically indicates both an Electromyography (EMG) and a Nerve Conduction Velocity (NCV) study (EMG vs NCV).
An EMG looks at the electrical signals your muscle makes when at rest and when they are being used. A Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) study is a test used to determine how fast and how well the body’s electrical signal travels down the path of the nerve.
These tests are usually performed simultaneously to determine if the issue is from a nerve disorder and/or a muscle disorder; as stated above NCV test help to determine if the problem is from the nerve versus an EMG, which looks at how a muscle is working based on stimulating the specific muscle. Together the test help determine the presence, location, and the extent of the problem.
Nerve Studies, including NCV and EMG (NCV test vs EMG), can help diagnose compression neuropathies, including many pathologies we treat as therapists. These tests can also help to measure how well your nerve is returning after an injury.
How is the testing application different?
With an EMG, the process is a little more involved than an NCV. With an EMG, a needle is placed into the muscle. The needle electrode has a mild current that is utilized to stimulate the muscle. This test can cause some pain and discomfort. It is used to measure the muscle while at rest and then when the muscle is contracted.
An NCV utilizes electrodes attached to the skin with a paste or tape; no needle is involved. There are typically two electrodes. One is a shock-emitting electrode, and the other is a recording electrode. The shock electrode is placed directly over the nerve, and the recording electrode is placed over the muscle controlled by that particular nerve. Several fast pulses are given to the nerve, and the time it takes for the muscle to contract in response to the pulses sent is measured.
Both tests can give critical insight and help the doctor determine which course of action is most appropriate for treatment, including physical and occupational therapy.
References
AAEM Quality Assurance Committee, Jablecki, C. K., Andary, C. M. T., So, Y. T., Wilkins, D. E., & Williams, F. H. (1993). Literature review of the usefulness of nerve conduction studies and electromyography for the evaluation of patients with carpal tunnel syndrome. Muscle & Nerve: Official Journal of the American Association of Electrodiagnostic Medicine, 16(12), 1392-1414.
Domkundwar, S., Autkar, G., Khadilkar, S.V. et al. Ultrasound and EMG–NCV study (electromyography and nerve conduction velocity) correlation in diagnosis of nerve pathologies. J Ultrasound 20, 111–122 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40477-016-0232-3
1 Comment
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Carpal Tunnel Treatment: Splinting Only vs Splinting & Conservative Treatment
Short-term clinical outcome of orthosis alone vs combination of orthosis, nerve, and tendon gliding exercises and ultrasound therapy for treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Sim, Sze En et al. Journal of Hand Therapy, Volume 32, Issue 4, 411 – 416 The Skinny- Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most common compression neuropathy. Compression of the…
Dorsal Scapular Nerve Entrapment and Thoracic Pain
Don’t Forget to Evaluate for Dorsal Scapular Nerve Entrapment By Delaney Wright If your patient presents with any upper thoracic pain, it is critical to take measures to evaluate for dorsal scapular nerve entrapment. In a study completed by Sultan et al. (2013), 55 patients with interscapular pain were evaluated clinically and via nerve conduction…
Distal radius fracture types seen in the hand therapy clinic
Distal radius fractures are one of the most common injuries seen in hand therapy. Several different distal radius fracture classification systems have been developed, and this blog post will focus on the more common types of distal radius fractures and their classification. Extra-articular fractures are either nondisplaced or displaced fractures. These fractures occur outside…
Scar Wars: Scar Management Techniques
We will briefly discuss Scar Management Options and Techniques
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.





My friend has been dealing with chronic pain for months, and it’s making her seriously contemplate undergoing an electromyography (EMG) test as part of her pain management plan. I think it’s become clear to her that finding the right solution to alleviate her discomfort has become a top priority for her. I just hope she’s aware that an EMG involves inserting a needle electrode into the muscle, which uses a little current to activate the muscle.