This is for you… Hand Therapists!
Stenosing tenosynovitis, otherwise known as trigger finger, is a common condition affecting children and adults of all ages.
Fast Facts
- Trigger finger usually occurs at the A1 pulley
- It occurs with inflammation of the tendons and sheaths of fds and fdp
- The digit can lock in both flexion and extension… That’s right I said extension
- The risk for trigger finger is between 2-3% in the population and 10% in diabetics
- It can be associated with metabolic disorders such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, collagen disease and carpal tunnel syndrome
Trigger Finger Treatment How-To
There are three basic option for trigger finger treatment … as long as we are not talking about the THUMB
- Injection 60-65%
- Therapy (splinting) 60-65%
- Therapy (splinting) and injection together 80%
- Surgery almost always, around 98% of course there are complication and the risk of anesthesia.
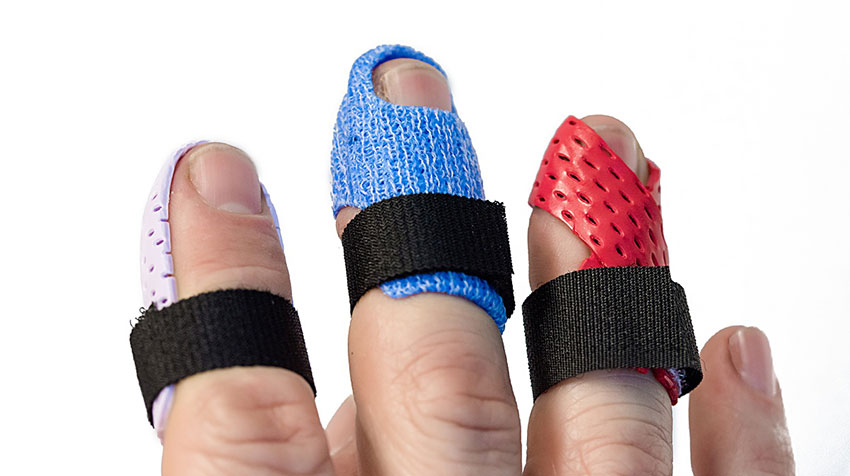
What Type of Splint Should You Use?
Any type of immobilization that limits the triggering will suffice. It could be a splint to immobilize the DIP, PIP or MCP. My personal favorite is an oval eight at the pip joint. I typically recommend wearing the splint for 3 weeks all of the time, than an additional 3 weeks night-time only, for a total of 6 weeks.
What About Trigger Thumb?
The triggering thumb typically does not resolve with conservative measures. Often times people with trigger thumb will need surgical intervention to resolve their symptoms.

What About the Doctor Who Does Not Believe in Splinting?
A lot of times physicians will tell you splinting doesn’t work. However, the research says otherwise! I often tell doctors there is no harm in trying therapy, it has very low risks and as therapist, we often are teaching our patients many more things that encourage good hand health! So I say why not!!
7 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Radial Nerve Palsy: A Paralysis Causing Wrist Drop
Radial Nerve Palsy- Treatment
3 Common Reasons for Ulnar-Sided Wrist Pain and Non-Surgical Hand Therapy Treatment Options
3 Common Reasons for Ulnar Sided Wrist Pain
Occupation Based Interventions in Hand Therapy
Keeping Occupation Based Interventions in Hand Therapy By: Tristany Hightower Are your treatments occupation based? Do you tailor your activity choices to fit the needs of each patient? As occupational therapists, we should be specialists in creating goals and interventions that are directed at returning our patients to meaningful occupations. Too often, hand therapy can…
Upper extremity weight-bearing tolerance
Barlow, S.J., Scholtz, J. & Medeiros (2020). Wrist weight-bearing tolerance in healthy adults. Journal of Hand Therapy, xxx currently in press. The Skinny Wrist pain and instability are common occurrences and can occur with acute or chronic injuries. This leads to significant dysfunction, including the inability to tolerate axial loading through the upper extremity. There is…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.




In the section “How is Trigger Finger Treated?” there are percentages listed next to each treatment, and I’m wondering what each percentage means?
It refers to the efficacy. Thanks for asking.
Can you put a photo of splint: “My personal favorite is an oval eight at the pip joint.” Thanks
I am a retired pediatric OT and experienced triggering in the DIP of my right thumb, dominant hand, mid-December. After one week of self-care, which was mainly rest and massage, I went to see a CHT. Her evaluation, treatment and home program of exercises was very helpful. I do the exercises every day. Now, about one month later, the “click” and triggering is almost gone, but I continue with the exercises and massage to maintain ROM and circulation. Some stiffness and weakness remains, especially in colder weather.
Do the percentages refer to efficacy?
I really want to know about the references? Could you indicate the articles about this findings? Tks.
Metacarpal/ phalengeal joint trigger in the digits???Have you used relative motion or yoke splint???