Crowley, J. S., Meunier, M., Lieber, R. L., & Abrams, R. A. (2020). The Lumbricals Are Not the Workhorse of Digital Extension and Do Not Relax Their Own Antagonist. The Journal of Hand Surgery.
The Skinny:
What do the lumbricals do?
There is a long-standing belief that the lumbricals act as a counterforce to the digital flexors enough to relax the digital flexors and act as primary digital extensors. This article works to update our understanding of the role of the lumbrical based on anatomy and innervation. They build off the work of Wang et al. to develop a better understanding of what the lumbricals function actually is in digit extension and balance of forces.
In The Weeds:
To review the anatomical line of the lumbricals, check out the picture below. Also, the lumbricals have several unique properties. They have the highest spindle fiber density of any UE muscle (a property of muscles intended for refined graded control, not power). They also have the highest fiber length-to-muscle length ratio. This means that the lumbricals are best at providing a low amount of force over a wide range of motion. These two aspects refute the idea that the lumbricals are strong enough to overpower counterbalance the much larger, conversely designed, FDP & FDS.
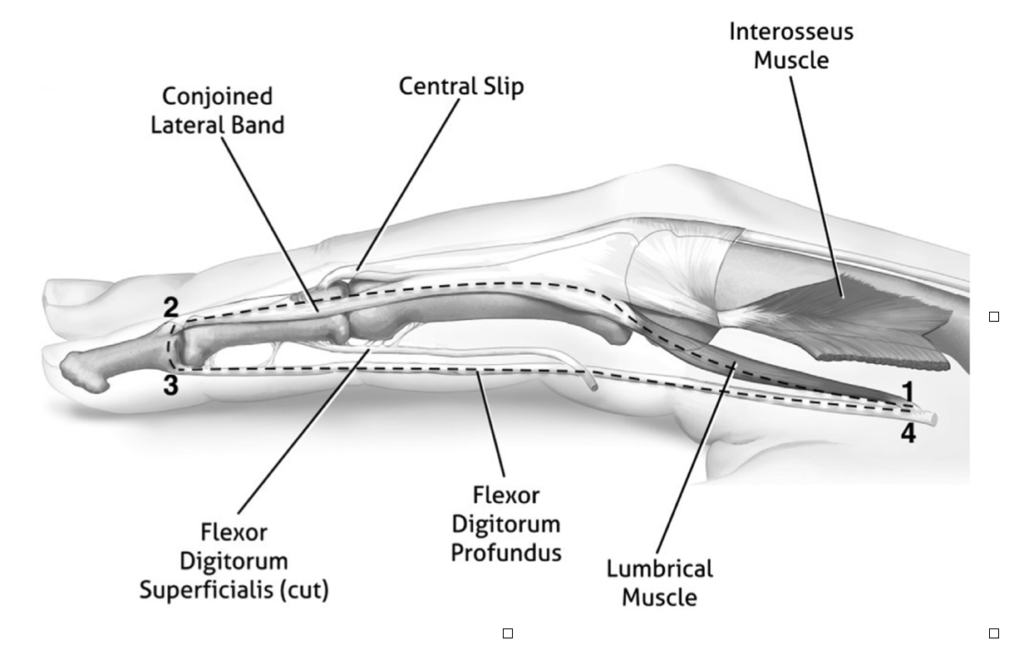
Crowley, J. S., Meunier, M., Lieber, R. L., & Abrams, R. A. (2020). The Lumbricals Are Not the Workhorse of Digital Extension and Do Not Relax Their Own Antagonist. The Journal of Hand Surgery.
Bringing It Home:
So what? What does that mean? Rather than the lumbricals being some powerhouse of IP extension, this article builds on the Wang articles proposal. Want et al. propose that the lumbricals are a tension monitoring device that allows for refined motor coordination to aid in coordinating the stronger extrinsic muscles. Crowley et al. add to that and suggest that the lumbricals also serve as a spring in a closed loop that helps to balance the 2nd and 3rd phalanx over the 1st, since the 1st phalanx has no tendon insertions to maintain its position. That makes the 1st phalanx an intercalated segment that needs delicately maintained tension to preserve its position. This is a significant shift in the idea that the lumbricals are a strong force in digital extension, counteracting the FDP & FDS.
Rating: 5/5
While not a research study, this article adds a lot of understanding and clarification of the anatomy and role of the lumbricals. Looking at muscle size, length, fiber type, and anatomical attachment can improve our awareness of a unique muscle like this is actually doing in the hand. It is always good to stay open-minded to alternative views of our sometimes dogmatically held opinions and beliefs. There are many more significant pieces of info in this article, and I highly recommend reading it if you have a chance.
Wang K, McGlinn EP, Chung KC. A biomechanical and evolutionary perspective on the function of the lumbrical muscle. J Hand Surg Am. 2014;39(1):149e155.
1 Comment
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Stretching Alone Can Change P1 Bone Shape in Patients with Camptodactyly
Woo Hong, S. Kim, J., Sang Kwon, O., Ho Lee, M., Sik Gong, H., Hyun Baek, G., (2019). Radiographic Remodeling of the Proximal Phalangeal Head Using a Stretching Exercise in Patients With Camptodactyly. J Hand Surg Am, 1.e1-1.e10 The Skinny – Camptodactyly is a congenital, nontraumatic flexion contracture of the PIP in fingers other than…
Intrinsic Hand Strengthening with Puttycise Tools
We are always looking for ways of the intrinsic hand strengthening. It is easy to overlook the importance of these small but mighty muscles. They are essential to performing functional grasps patterns. They can become weak in a short period of time due to their small size. So, How does intrinsic strengthening work?! The Basics…
6 of our Favorite Adaptive Equipment Tools for CMC Osteoarthritis
Individuals struggling with osteoarthritis of the 1st CMC joint usually have difficulty with daily activities and it can become very frustrating. Everyday tasks such as cutting food, opening containers, and donning a button up shirt can become painful and slow. The largest contributor to the overall function of our hand is the thumb. If the…
5 return-to-cooking activities (that don’t require a kitchen)
Hand therapy can and should be very occupation-based. Every week, we hear comments from patients that back that statement up: “I need to get back to work” “I just want to golf again” “I can’t even open a water bottle” “My spouse has to do all of the cooking” Although standard exercises are helpful, it’s…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.







Great explanation and illustration