Stretching Alone Can Change P1 Bone Shape in Patients with Camptodactyly
Filed under Reviews
Woo Hong, S. Kim, J., Sang Kwon, O., Ho Lee, M., Sik Gong, H., Hyun Baek, G., (2019). Radiographic Remodeling of the Proximal Phalangeal Head Using a Stretching Exercise in Patients With Camptodactyly. J Hand Surg Am, 1.e1-1.e10
The Skinny – Camptodactyly is a congenital, nontraumatic flexion contracture of the PIP in fingers other than the thumb. Type 1 Camptodactyly ( Isolated anomaly in children <36 months) also includes volarly angulated and beak-shaped flat proximal phalangeal head. This study investigated the impact of a stretching-only camptodactyly treatment plan on restoration of Proximal Phalangeal head angulation as well as joint contracture.
In The Weeds – In a retrospective cohort study using radiographic series, 48 digits in 20 patients <36 months with >12 months of follow up were studies. 2 indexes were created to measure Head Angle (HA) and Head Triangle Ratio, or head shape (HTR).
Camptodactyly Stretches: Parents conducted a minimum of 20 sessions/day of a minimum of 5 minutes/session on affected fingers. Wrist and MCP were held in extension to increase FDS and FDP tension while force was applied to DIP joint flexion crease. This was done for 12 months.

Results: “roundness and concentricity of the proximal phalangeal head was restored in all cases” with statistical significance. Flexion contracture of the PIP decreased from 34 degrees ± 13 to 6 degrees ±7.
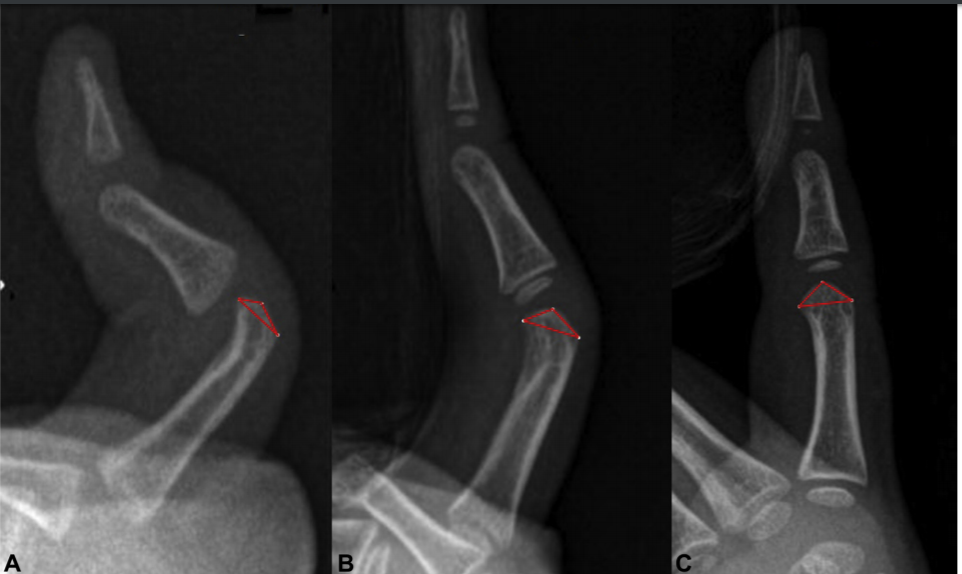
Bring it Home – Radiographic imaging indicates that stretching alone can restore the shape and angulation of the proximal phalangeal head and decrease flexion contracture. There was no correlation between contracture angle and boney shape throughout the study. This study had significant intra and inter-rater reliability for HA and HTR measures and control group illustrated that bone growth alone did not account for change in these parameters.
While other types (i.e. ages) of camptodactyly need to be studied, this study supports the strong value in stretching exercises for this diagnosis (camptodactyly exercises). Younger patients are particularly more receptive due to soft tissues being more extensile and the joint is more flexible. While the stretching protocol in this study is extensive, and may not be maintainable by many families, this approach is highly effective in achieving results non-surgically.
2 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
A Review on the Conservative Management of Trigger Finger
Lunsford, D., Valdes, K., & Hengy, S. (2017). Conservative management of trigger finger: A systematic review. Journal of Hand Therapy, 32(2), 212-221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2017.10.016 The Skinny The main purpose of the literature review was to determine the efficacy of conservative management of trigger finger (TF) through the use of an orthosis in addition to therapy. The review…
Is HEP Just as Good as Therapy for Metacarpal Fracture Rehab?
Gülke, J., Leopold, B., Grözinger, D., Drews, B., Paschke, S., & Wachter, N. J. (2018). Postoperative treatment of metacarpal fractures – Classical physical therapy compared with a home exercise program. Journal of Hand Therapy, 31(1), 20-28. The Skinny – Medicine is moving towards a model that encourages less direct intervention and a more DIY focus…
Article Review: Relative Motion for Extensor Tendon Repair zone V-VI? Is a night-time resting hand orthosis beneficial?
Hirth, M. J., Hunt, I., Briody, K., Milner, Z., Sleep, K., Chu, A., Donovan, E. & O’Brien, L. (2021). Comparison of two relative motion extension orthotic programs following surgical repair of finger extensor tendons in zones V-VI: A randomized equivalence trial. Journal of Hand Therapy-to be published. The Skinny: Following a zone V-VI tendon repair,…
Article Review: Trapeziectomy and LRTI: What can patients with CMC osteoarthritis expect 12 months after the procedure?
Janakiramanan, N., Miles, O., Collon, S., Crammond, B., McCombe, D., & Tham, S. K. (2021). Functional Recovery Following Trapeziectomy and Ligament Reconstruction and Tendon Interposition (Trapeziectomy and LRTI): A Prospective Longitudinal Study. The Journal of hand surgery, S0363-5023(21)00304-X. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2021.04.036 The skinny: Patients with trapeziometacarpal (TMC) osteoarthritis who are candidates for a trapeziectomy and…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.





Is it possible for me to obtain a copy of the full article?
We can’t distribute the article itself, but the reference is provided so you can still find it. If you have a connection at a local university they may be able to pull it for you. Or Google Scholar will often have articles available in full print for viewing.