Teo, S. H., Ng D. C., Wong, Y.K.(2018). Effectiveness of proximal interphalangeal joint blocking orthosis vs metacarpophalangeal joint blocking orthosis in trigger digit: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Hand Therapy, 1-7.
The Skinny- This study compared PIP joint immobilization via an Oval-8TM with a custom MCP blocking orthosis in the treatment of trigger finger.
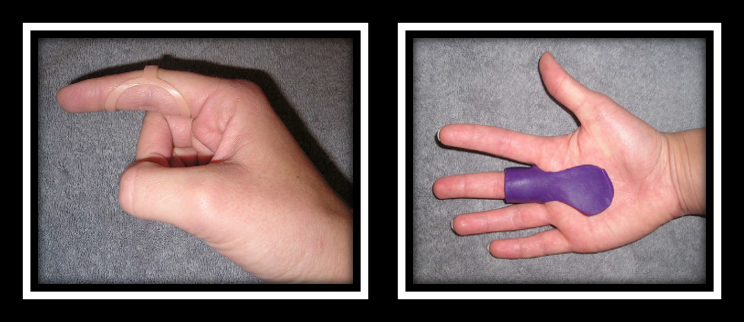
In the Weeds – Patient (n=35) with Trigger Finger (n=43) were analyzed. Twenty-three patients were allocated to the PIP joint splinting group and 20 patients were in the MCP splinting group. Patients wore the orthosis for eight weeks.
Pain reduction was observed in both groups, but pain reduction was greater with PIP joint splinting compared to the MCP joint splinting group (MCP joint splint). There was only significant improvement in QuickDASH for the PIP splinting Group. Patients wore the pip joint splint significantly longer during the day compared to the MCP splinting group (MCP splint), most likely due to improved comfort.
Bringing it Home- Findings suggest both orthoses are effective in reducing QuickDASH scores, reducing pain and improving overall trigger finger symptoms based on Green’s Classification. However, the pip joint immobilization splint was better for improved function and improved compliance.
The rationale for the rating. Small sample size. All patients with comorbidities were excluded limiting the generalizability of findings. Immobilizing the PIP joint compared to the MCP allows more function and improved compliance. When immobilizing the MCP you limit intrinsic grasp which is a necessity for function. The authors recommend wearing the orthosis for a 4-week duration of 24 hours in order to reduce triggering symptoms followed by night-time splint wear for another 3-4 weeks.
4 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Article Review: Relative Motion for Extensor Tendon Repair zone V-VI? Is a night-time resting hand orthosis beneficial?
Hirth, M. J., Hunt, I., Briody, K., Milner, Z., Sleep, K., Chu, A., Donovan, E. & O’Brien, L. (2021). Comparison of two relative motion extension orthotic programs following surgical repair of finger extensor tendons in zones V-VI: A randomized equivalence trial. Journal of Hand Therapy-to be published. The Skinny: Following a zone V-VI tendon repair,…
Hand Therapy Marketing 101
Marketing 101 – 5 Tips for Your Therapy Clinic Confession: I hate marketing. It’s my least favorite part of my job. It is so hard to open yourself up to that much rejection but still stay positive. It feels like the professional version of blind dating, except the other person probably already has a significant…
How to Strengthen the Intrinsics with Puttycise Tools:
How to strengthen the intrinsic with Puttycise tools
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: How does traditional hand therapy compare with neurodynamic therapy?
Hamzeh, H., Mohammad, M., Alghwiri, A., & Hawamdeh, Z. (2021). The long-term effect of neurodynamics vs. exercise therapy on pain and function in people with carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized parallel-group clinical trial. Journal of Hand Therapy, 34, 521-530. The Skinny: Carpal tunnel is the most common peripheral nerve compression problem. There is now some…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.






Trigger finger is easy to fix with surgery release. I’ve had it done. Piece of cake.
Have seen a pt lose a finger due to a freak release surgery accident. Have seen the scar tissue left behind following a surgical release replicate a trigger digit. Have seen conservative management effectively treat a trigger digit.
Even simple surgeries carry risks for pts, especially if there are preexisting conditions like diabetes or Raynaud’s. So maybe it is best to explore all aspects of treatment before throwing out a blanket statement, right?
why go to surgery before all conservative measures? Before surgery I would certainly consider CSI, which most times resolve the situation. another thing, is inflammation in the body due yo metabolic issues also need to be considered
What are some suggestions for pediatric trigger finger in the thumb?