Comparison of Erb’s Palsy and Klumpke’s Palsy: Symptoms, Presentation, and Treatment Options
Filed under Treatments
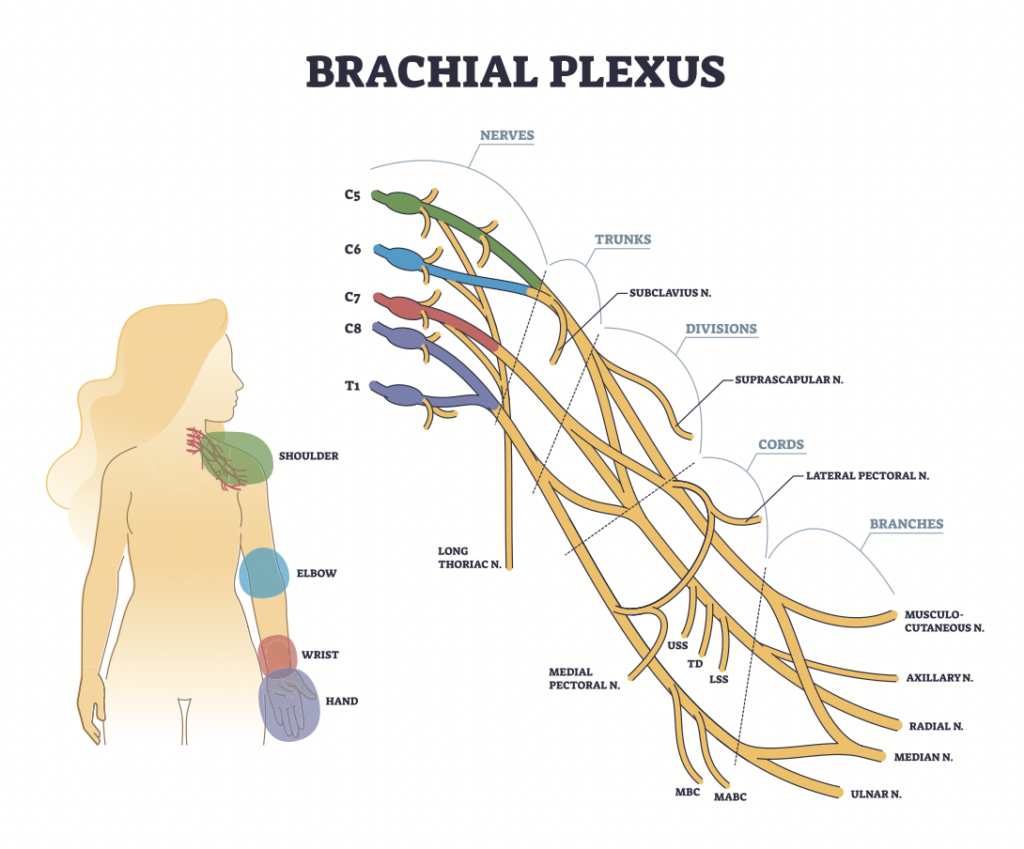
What is the brachial plexus?
The brachial plexus is a group of nerves originating from the cervical and thoracic nerve roots (from C5 to T1). The brachial plexus forms 5 peripheral nerves of the upper extremity, consisting of the musculocutaneous, median, radial, ulnar, and axillary nerves. This group of nerves supplies motor and sensory innervation to the entirety of the upper extremity.
How do injuries happen?
Brachial plexus injuries have multiple mechanisms of injury in infants. These injuries can be caused by compression, traction, stretching, rupture, or avulsion of the nerves of infants during childbirth. Larger infants are at a higher risk of brachial plexus injuries due to the risk of shoulder dystocia (the shoulder of the fetus gets stuck on the pelvis during childbirth). Injuries can also be caused by breech presentation at birth, uterine abnormalities such as uterine fibroids, or the fetus being in a transverse position for a prolonged period of time.
Erb’s palsy vs. Klumpke’s palsy
Erb’s palsy is an upper brachial plexus injury from C5-C6 (sometimes involving C7), while Klumpke’s palsy is a lower brachial plexus injury from C8-T1 (sometimes C7 is involved as well). Erb-Klumpke’s (total paralysis) can also occur if the entirety of the brachial plexus is involved with the injury (C5-T1).
Erb’s palsy causes weakness or paralysis of muscles of the upper arm and shoulder, presenting as the internal rotation of the forearm and flexion of the wrist and fingers with the arm hanging, also called waiter’s tip deformity. Klumpke’s palsy involves weakness or paralysis of the muscles of the forearm and hand, commonly presenting as a “claw hand” with the forearm in supination and flexion of the wrist and fingers.
How are they treated?
Many cases of brachial plexus injuries recover independently with time; however, nonsurgical and surgical treatments are available. Therapy is a common form of treatment that promotes passive range of motion of the shoulder, elbow, wrist, and hand to avoid stiffness of joints. Parents are educated on exercises they can practice with their children at home. Surgery is also an option to repair any rupture present or perform a nerve transfer from another muscle to restore the function of the affected muscles if no progress has been made through the conservative route.
References:
Benjamin, K. (2005). PART 1. Injuries to the brachial plexus. Advances in Neonatal Care, 5 (4), 181-189. doi: 10.1016/j.adnc.2005.03.004.
Brachial plexus injury. Johns Hopkins Medicine. (2022, December 22). https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/brachial-plexus-injuries
Erb’s palsy (brachial plexus birth palsy) – orthoinfo – AAOS. OrthoInfo. (n.d.). https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/erbs-palsy-brachial-plexus-birth-palsy/
Klumpke paralysis. Physiopedia. (n.d.). https://www.physio-pedia.com/Klumpke_Paralysis professional, C. C. medical. (n.d.). Shoulder dystocia: Signs, causes, prevention & complications. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22311-shoulder-dystocia
More To Read
The Influence of Psychological Factors on Outcomes Following Wrist and Hand Injuries: A Systematic Review
The Influence of Psychological Factors on Outcomes Following Wrist and Hand Injuries: A Systematic ReviewArticle: Minnucci, S., Fochi, F., Lerose, E., Scalise, V., & Brindisino, F. (2025). The influence ofpsychological factors on outcomes following wrist and hand musculoskeletal injuries: Asystematic review. Journal of Hand Therapy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2025.10.005 The Skinny:Wrist and hand injuries are common worldwide and…
“Do joint mobilizations assist in the recovery of lateral elbow tendinopathy? A systematic review and meta-analysis”
By Sophia Grimm Lucado, A. M., Dale, R. B., Vincent, J., & Day, J. M. (2019). Do joint mobilizations assist in the recovery of lateral elbow tendinopathy? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of hand therapy : official journal of the American Society of Hand Therapists, 32(2), 262–276.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2018.01.010 The Skinny: The purpose of this study was…
Sensory Kit for Hypersensitivity
Written by Melissa Miller Introduction After injury or surgery, nerves in the skin and surrounding the injured area can become overly sensitive. This can cause pain or an unpleasant sensation by stimuli that would not typically cause discomfort. For example, a light touch from a shirt or a certain material can feel like needles to…
Hand Therapy: How to Treat the Client with a New Distal Radius Fracture
A short blog post on the basics of treating a Distal Radius Fracture.
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.






