Exertional (Chronic) Compartment Syndrome of The Hand
Filed under Treatments
By: Tommi Long
What is it?
Chronic exertional compartment syndrome (CECS) is an exercise-induced condition affecting the muscles and nerves, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced muscle function due to increased pressure and restricted circulation. While most commonly, it impacts the arms and legs, it is rare to happen in the hand(s). CECS is most prevalent in young adult runners and athletes who participate in repetitive activities, although anyone can develop this condition.
Signs and Symptoms:
- Weakness
- Bludging around muscle
- Tightness
- Pain while completing stretches
- Numbness and tingling
- Aching, burning, or cramping pain in the affected muscle
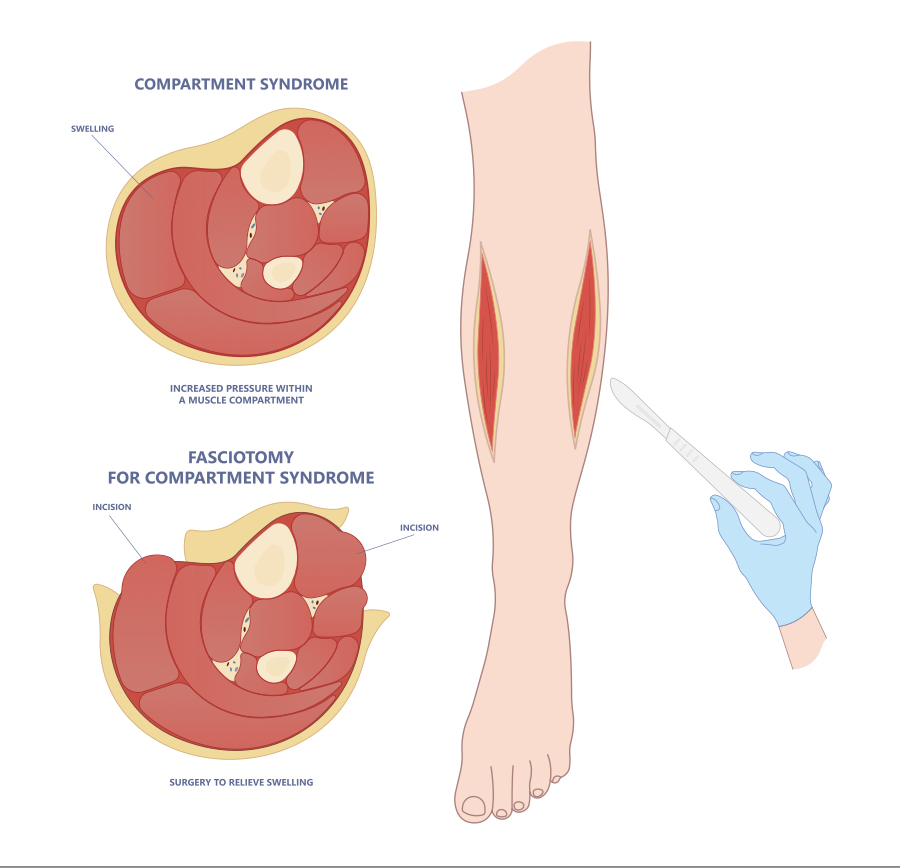
How is CECS diagnosed?
- X-ray to rule out any fractures or bone injuries
- MRI evaluates the compartments’ muscles and structures. Advanced MRIs can also assess the fluid volumes of each compartment during and after exercise.
- Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a newer technique for measuring the amount of oxygen in the blood and tissue of the affected limb. It is performed at rest and after exercise.
- Compartment pressure testing measures the pressure within your muscle compartments by inserting a needle into several different places. This test is the gold standard for diagnosing chronic exertional compartment syndrome.
Treatments:
Surgical and nonsurgical methods are available for this condition, although nonsurgical options must immediately stop or significantly limit activities that cause compartment syndrome. Nonsurgical options typically don’t have long-lasting effects for true CECS.
Nonsurgical options-
- Break from exercise or activity
- Medications for pain and anti-inflammatory
- Therapy (manual therapy, ergonomics, modified environment, strengthening, flexibility)
- Botulinum toxin A injections into affected muscles
- Orthosis
Surgical Options-
- Research suggests fasciotomies are the most effective treatment (Cutting open tissues encasing affected muscle compartments to relieve pressure) or (small incisions to reduce recovery time)
- Selective releases of the thenar and hypothenar compartments
References:
Dwyer, C. L., Soong, M. C., & Kasparyan, N. G. (2016). Chronic exertional compartment syndrome of the hand: Case report and literature review. HAND, 12(3). https://doi.org/10.1177/1558944716668826
Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research. (n.d.). Chronic exertional compartmentsyndrome. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/chronic-exertional-compartment-syndrome/symptoms-causes/syc-20350830
Phillips, J. H., Mackinnon, S. E., Murray, J. F., & McMurtry, R. Y. (1986). Exercise-inducedchronic compartment syndrome of the first dorsal interosseous muscle of the hand: A case report. The Journal of Hand Surgery, 11(1), 124–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0363-5023(86)80118-6
What are the main signs of compartment syndrome?. Cleveland Clinic. (2024, August 5).https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/15315-compartment-syndrome
More To Read
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) for Various Etiologies
What is it: Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is a medical treatment that uses a device to deliver electrical impulses to the vagus nerve, which runs on both sides of the body from the lower brain through the neck to the chest and stomach. The left vagus nerve is typically used for this procedure, as simulating…
Hand Therapy as a New Grad or Student
Tips for Getting Prepared for hand therapy as a new grad or a Level II Fieldwork Everything you need to know in hand therapy starts with the upper extremity anatomy. Here is a quick checklist to review and hopefully help get you started in your new hand therapy setting. By: Tristany Hightower I suggest, as…
What to Know as a Hand Therapist When Choosing Thermoplastic Orthosis Material
By: Kelsey Melton Thermoplastic materials can have a variety of properties. Each supplier has a different version of each combination of variables for the therapist to choose from. The most common brands used for orthosis fabrication are Orfit, NorthCoast Medical (NCM), and Raylan. These brands all have their versions of thermoplastic material that vary in…
Pediatric & Adolescent Shoulder Instability
Lin, K.M, James, E.W., Spitze, E. & Fabricant, P.D. (2018). Pediatric and adolescent anterior shoulder instability: Clinical management of first-time dislocators. Current opinion in pediatrics, 30, 49-56. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000000566. The Skinny: Shoulder instability for pediatric and adolescent patients is fairly common and is often complicated by a high re-dislocation rate. Shoulder instability typically occurs after…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.






