How much pain should a patient have during and after therapy?
Filed under Treatments
How much pain should a patient have during and after therapy?
As we all know pain is somewhat subjective. It can be hard to determine how much pain a patient should experience with the type of injury as well as the type of therapy intervention and hand pain treatment.
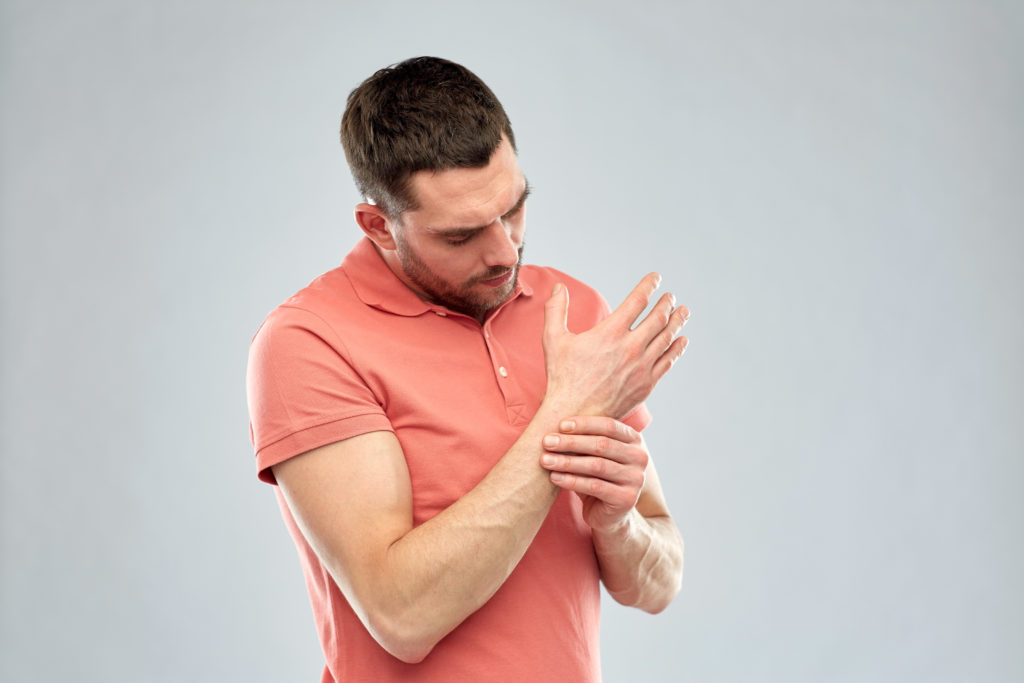

The saying of “no pain, no gain” is a common belief that patients have in a therapy setting. Many patients believe they have to experience pain in order to improve. This saying is simply not true and often times the goals of therapy are to improve range of motion and strength but also to minimize a patient’s pain response.
Pain is our bodies protective mechanism and it lets us know when something is just not right. Research supports manual therapy which includes stretching and other joint mobility techniques without increasing pain. It has actually been shown that in some cases aggressive manual therapy can actually make the joints stiffer and more problematic.
There are certain exceptions to this rule and most of the time they are due to surgical cases where increased stretching is needed to avoid adhesions and scar tissue buildup. In most of these cases the therapist and patient can work together to restore movement without prolonged periods of pain.
A common thing I will do with my patients is ask them how much pain they are having 10 minutes after the manual therapy session. If their pain is zero too minimal I know the manual therapy session was successful. If the exercise and manual therapy lead to a pain flare up or an increase in edema for a prolonged period of time I know the intervention was too aggressive.
Also I will remind my patient some of the manual techniques or provocative testing we do in the clinic may lead to an increase in pain but this can be helpful in guiding the decision making. It can guide us to what muscle groups may need to strengthened, what joints need mobilized and how we can better address the problem(s). If the joint or muscle structure has not been used in awhile I will remind the patient that muscle soreness may last for the next 24 hours and this is all a normal part of the process. Similar to going to they gym and working out.
There are some key words and questions that can be helpful in guiding your treatment.
Is there sharp pain? If so this is probably not a beneficial or helpful intervention
Is there throbbing? If it is at end range that is okay ask the patient to move through the pain free range and stop before you get to the point of throbbing.
As always keep in mind each patient is different and will have their own unique factors. It is important to manage these factors. I think it is always helpful to educate your patient on pain expectations and discuss the differences between good and bad pain!
2 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
When should you use a Static Progressive Splint in Hand Therapy?
Flowers, K. (2002). A proposed decision hierarchy for splinting the stiff joint, with an emphasis on force application parameters. Journal of Hand Therapy, 15, 158–162. The Skinny- The article proposes a decision hierarchy to determine when you should apply a static progressive or dynamic orthosis. The decision hierarchy uses a modified Weeks test (MWT). The…
Graded Motor Imagery in Hand Therapy
The 3 Stages of Graded Motor Imagery We’ve all heard of mirror box therapy, but do you know the details of how it works? There’s actually 3 stages involved that exercise the brain and take advantage of its plasticity. There is a great deal of evidence supporting these three stages and you can use them…
Hand Therapy: How to Treat the Client with a New Distal Radius Fracture
A short blog post on the basics of treating a Distal Radius Fracture.
What is the Effectiveness of IASTM?
Citation Kim, J., Sung, D. J., Lee, J. (2017). Therapeutic effectiveness of instrument-assisted soft tissue mobilization for soft tissue injury: Mechanisms and practical application. Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation, 13(1). doi: https://doi.org/10.12965/jer.1732824.412 The skinny IASTM is a relatively simple technique that uses the surface of an instrument to minimize the amount of pressure or force needed…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.






Excellent succinct post!
I’m shopping for assistive devices for my hands