Outcomes of Rigid Night Splinting and Activity Modification in the Treatment of Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
Filed under Treatments
Shah, C. M., Calfee, R. P., Gelberman, R. H., & Goldfarb, C. A. (2013). Outcomes of rigid night splinting and activity modification in the treatment of cubital tunnel syndrome (night splint for cubital tunnel syndrome). The Journal of Hand Surgery, 38(6), 1125–1130.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2013.02.039
By: Sophia Grimm
The Skinny:
The purpose of this study was to identify symptom improvement in patients with mild to moderate cubital tunnel syndrome treated with rigid night orthosis and activity modifications. The degree of ulnar nerve dysfunction was identified according to Dellon’s classification.
- Dellon 1: Limited to intermittent paresthesia and weakness
- Dellon 2: Intermittent paresthesia and notable weakness
- Dellon 3 Persistent paresthesia and significant weakness with or without intrinsic muscular atrophy
Current conservative treatment guidelines for cubital tunnel syndrome are nerve gliding exercises, activity modification, and orthotic use. It is also common to use the cubital tunnel syndrome splint.
In the Weeds:
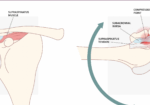
This study included 19 patients with Dellon’s 1 & 2 classification of cubital tunnel syndrome. All patients were treated with a rigid nighttime orthosis holding the elbow at a position of 45 degrees of flexion for 3 months and activity modifications to decrease irritation of the ulnar nerve. Patients were evaluated at enrollment, 6 weeks, 3 months, and 1 year with the QuickDASH, SF-12, grip and pinch strength measurement, presence or absence of Froment’s sign, and strength assessment of the first dorsal interosseous and flexor digitorum profundus to small finger. Researchers also used static 2-point discrimination of the 5th digit to assess for sensory changes, tinel’s at the elbow, evaluated ulnar nerve stability at the cubital tunnel, and assessed for a combined flexion with pressure provocation test by placing the patient’s elbow in maximum flexion and, while in this position, placing pressure on the ulnar nerve just proximal to the cubital tunnel. Electromyography and nerve conduction studies were also performed on all patients.
Bringing it Home:
The researchers found an 88% success rate for treating cubital tunnel syndrome in 21 out of 24 extremities with a rigid 45-degree nighttime orthosis and activity modifications. Both QuickDASH and SF-12 scores showed statistically and clinically significant improvement within 3 months of treatment. The improvements noted at 3 months were maintained at 1-year follow-up.

This study has promising clinical treatment findings for cubital tunnel syndrome. The sample size was small, and the study has not been replicated. All participants were treated with the same intervention and therefore no comparisons could be drawn. However, the subjective and objective data collected matched the findings of the study.
3 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Shoulder Pain: The Effectiveness of Conservative Treatment
Reference: Steuri, R., Sattelmayer, M., Elsig, S., Kolly, C., Tal, A., Taeymans, J., & Hilfiker, R. (2017). Effectiveness of conservative interventions including exercise, manual therapy and medical management in adults with shoulder impingement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs. British journal of sports medicine, 51(18), 1340–1347. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2016-096515 By: Tayler Roost The Skinny: This study…
3 Household Objects for 9 different Hand Therapy Activities
Do you struggle to develop new treatment ideas or even ideas for your virtual hand therapy visits? Thinking of unique ways to use objects your clients have in their homes can be half the battle. This blog post presents 3 different ways to use 3 everyday items. Item number 1: A tennis ball (hand therapy…
Stretching Alone Can Change P1 Bone Shape in Patients with Camptodactyly
Woo Hong, S. Kim, J., Sang Kwon, O., Ho Lee, M., Sik Gong, H., Hyun Baek, G., (2019). Radiographic Remodeling of the Proximal Phalangeal Head Using a Stretching Exercise in Patients With Camptodactyly. J Hand Surg Am, 1.e1-1.e10 The Skinny – Camptodactyly is a congenital, nontraumatic flexion contracture of the PIP in fingers other than…
What is Chronic Exertional Compartment Syndrome? Overview and Hand Therapy Treatment Ideas
Compartment syndrome is a condition characterized by increased pressure within a compartment of the body, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced tissue perfusion (Barkay et al., 2021; Buerba et al., 2019). It can be either acute or chronic (Barkay et al., 2021). Chronic exertional compartment syndrome (CECS) is a rare type, most commonly observed in…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.





Great article! Do you know why the splint is not positioned in full extension, why is it 45 degrees of flexion?
There is no mention of ulnar nerve gliding exercise (flossing) – is there are reason this was not included?
hello,
It was an article review focusing on orthosis fabrication therefore I don’t think it was a study objective of the authors
Miranda