Radial Nerve Palsy- Treatment
- Anatomy: The radial nerve comes off the posterior cord of the brachial plexus, travels down the back of the arm, passes anteriorly through the radial groove of the humerus to the lateral side of the elbow under the supinator muscles through the radial tunnel and runs along the outside of the forearm. As the radial nerve pass along the arm it is susceptible to different types of nerve injuries. Including radial nerve palsy, a paresis or paralysis affecting muscles innervated by the radial nerve. Wrist drop is a common indication of a radial nerve injury as the extensors of the wrist are all innervated by the radial nerve.
- What to look for as a patient comes in:
- Patients may present with the inability to extend the wrist and digits. They may also have paresthesia on the dorsal aspect of the forearm and hand numbness on the proximal dorsal side of digits 1-3 and half of 4. If the compression or injury is higher on the arm, elbow extension can also be lost.
- There are different compression sites of the radial nerve which can cause different presentations and limitations of movement and sensory input, however the treatment for radial nerve palsy in general is very similar
- What is the focus of treatment?
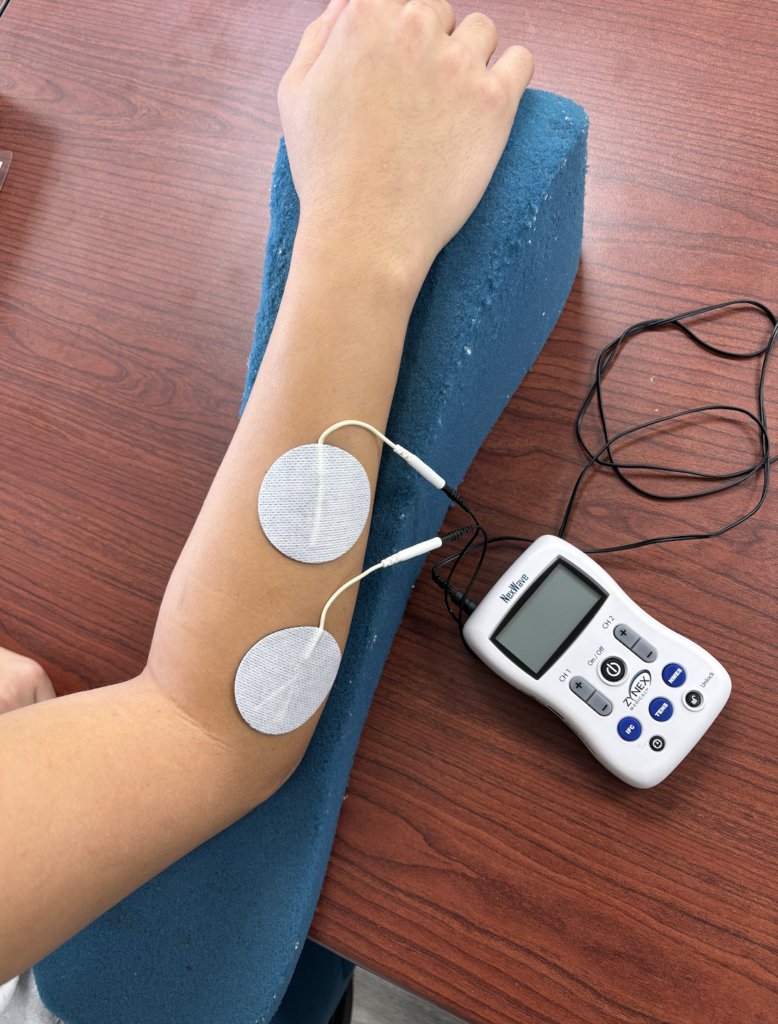
- Prevent Muscle Wasting: Because of the damaged nerve, the wrist (and possibly elbow) extensors are not able to fire. This can lead to muscle wasting. This is important for us to focus on in therapy to prevent any loss of muscle mass. One method for addressing atrophy is the use of NMES to the digit and wrist extensors. These help the muscle to remain active as we work to restore functional arm use.
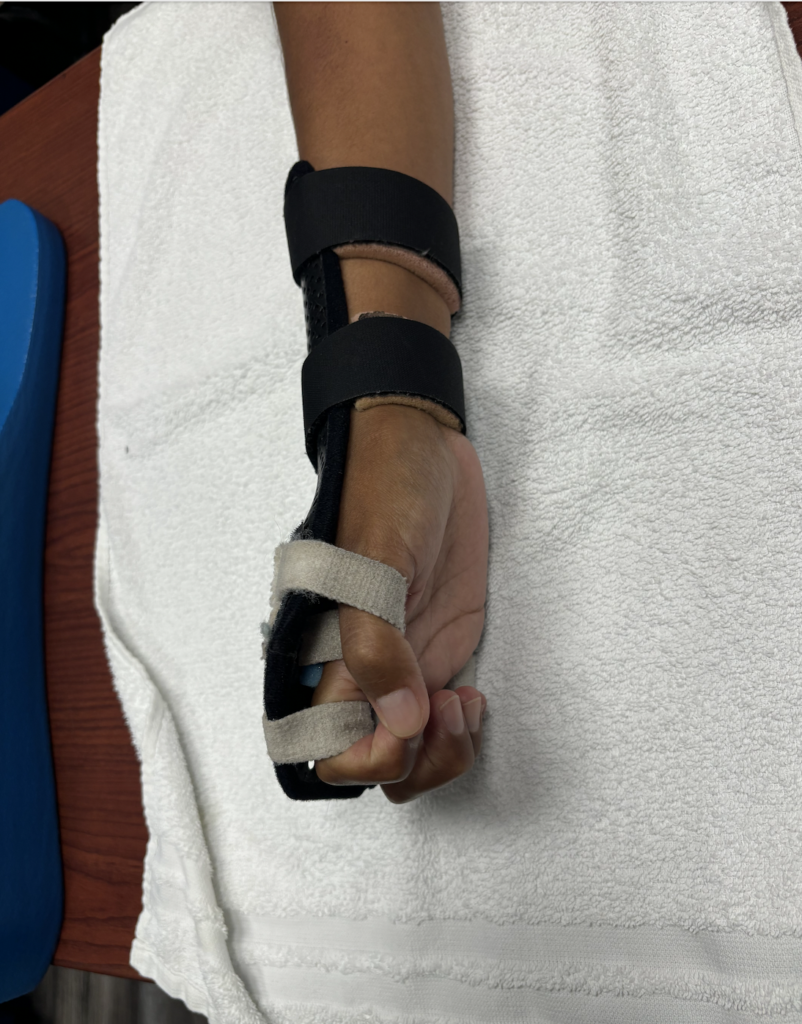
- Splinting: One option is a simple wrist cock up brace the second option is a “radial palsy” splint is made with elastic bands that wrap around the volar side of digits 2-5 at the first phalanx to help facilitate extension. But the elastic nature of the straps allow for active flexion of the digits.
- PROM to Prevent Contracture: Radial palsy weakens all of the wrist and digit extensors. With these affected, the wrist flexors begin to shorten without the counter force on the dorsal side of the forearm. This causes a contracture of the arm in a flexor pattern, making the hand less functional. To help prevent this, the therapist should include PROM extension of the wrist/fingers/elbow (depending on the compression site) during treatment.
- Functional Hand Use: Managing the function of the affected hand is crucial to improving occupational independence. Activities in therapy should be focused on grasp patterns, bilateral integration, ADLs and return to work tasks. Related tasks could include:
- Buttoning
- 2-handed coordination tasks (e.g. beading)
- In hand manipulation / translation tasks
- Big Arm Movements: Understanding that an injury such as radial palsy can play a role in the use of the affected arm, big arm movements can help facilitate gliding of the nerves and create fluid movement of the arm.
4 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
How To Do A Fast but Thorough Hand Therapy Assessment
We don’t get a lot of time. Sometimes new patients come in unexpectedly or someone comes at the wrong time and your 1-hour block for an eval is suddenly only 30 minutes. Do you know how to get the most out of your eval time with the patient? Do you know what things are the…
Scapholunate Wrist Injuries in Hand Therapy
Scapholunate Wrist Injuries in Hand Therapy In outpatient hand therapy, we get a variety of referrals ranging from post-operative patients to those looking to avoid or prolong surgery. These referrals come from a variety of sources ranging from primary care doctors to experienced hand surgeons. The therapy orders can be vague to very specific. …
Video-augmented mirror therapy for upper extremity rehabilitation after stroke
Kim, H., Kim, J., Jo, S., Lee, K., Kim, J., & Song, C. (2023). Video augmented mirror therapy for upper extremity rehabilitation after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Neurology, 270(2), 831-842. Article Review: Shannon Skowbo The Skinny: This single-blind, randomized control trial aimed to assess the effects of mirror therapy for stroke patients…
Top 5 Hand Therapy Toys for Kids
Many therapists in hand therapy clinics have a lot of tools for their adult patients, but may not have as many tools for the less common pediatric patient. With nearly 20 years experience in pediatrics, we’ve compiled a list of our top 5 picks for tools to use with pediatric patients in hand therapy. We…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.




Hi just a question…If the nerve has not regenerated yet to the wrist and digital extensor is it still a good idea to use NMES? I thought that it could damage the nerve?
NMES for sure if the nerve is allowing for some motor recruitment.
I am not aware of any researching citing that NMES can damage the nerve.
at what point is surgical intervention usually necessary?
Hello. Usually, they will determine this after they have confirmed the nerve is no longer healing. Surgical intervention for a radial nerve injury is usually considered based on cause, severity, and recovery timeline rather than a single time point. In general, conservative management (activity modification, splinting, therapy, and symptom management) is appropriate when the nerve is compressed or irritated, and there is evidence of clinical improvement over time. Many traction or compression-related radial nerve injuries recover spontaneously. Surgical intervention is more strongly considered when there is no meaningful motor or sensory recovery by ~3–6 months, depending on injury severity. There is progressive weakness, worsening sensory loss, or persistent pain despite appropriate conservative care. Imaging or EMG/NCS suggests nerve entrapment, laceration, or non-recovering axonal injury. The injury is associated with a fracture, mass, or structural lesion that will not resolve without decompression or repair