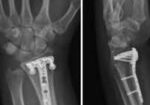
The Importance of Purposeful Activities Following Surgical Repair of a Distal RadiusFracture
Filed under Treatments
By: Kelsey Melton
Collis, J. M., Mayland, E. C., Wright-St Clair, V., Rashid, U., Kayes, N., & Signal, N.
(2022). An evaluation of wrist and forearm movement during purposeful activities and
range of movement exercises after surgical repair of a distal radius fracture: A randomized
crossover study. Journal of Hand Therapy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2022.07.009
The Skinny: This randomized crossover study aimed to determine the difference in
wrist ROM gains when using purposeful activities compared to the typical active range of motion
exercises in individuals with surgical treatment of a distal radius fracture. The authors state that
previous studies have found that purposeful activities produce functional wrist ROM and
a large quantity of movement required for rehabilitation in healthy individuals and patients
with neurological conditions. This may not be the case for injured patients, considering they are in the early healing stages of the injury and may be hesitant to perform functional activities due to pain, weakness, or fear.
In the Weeds: Inclusion criteria for this study required participants to be over the age of 18 and
were less than four weeks postoperative with a surgical repair of a distal radius fracture.
Participants also needed to have a stable fixation cleared for mobilization by a
surgeon, and they could not have any other condition or injury that impacted the regular use of the
affected limb. Data was collected in a single session within the participant’s home where they
took part in both purposeful activity and active ROM exercise interventions in a non-specific
order. The two interventions were separated by a 60-minute washout period of wrist
immobilization so that the first intervention did not influence the one that followed. Purposeful
activities had to be essential or enjoyed by the participant. Still, they also had to encourage and
challenge wrist movement. Active exercises were standard postoperative forearm, wrist, and
hand exercises typically given following this procedure. During interventions,
movement parameters measured included time-accumulation of position, maximum active end
ROM, number of repetitions, excursions beyond 75% of active ROM, and proportion
of active time.

Bringing it Home: After completing a statistical analysis of the outcomes mentioned above, the
authors found that range of motion exercises produced a higher volume of sustained joint
position, but that purposeful activity had a higher volume of continuous and variable
motion. The authors also found that the ranges of movement between the two interventions
were very similar. Qualitative data to determine participants’ perception of each intervention was
also collected and found that both purposeful activity and AROM exercises were equally
enjoyable to participants, but they appreciated the set AROM exercises because of the
clear parameters.
Rating: 4 out of 5. Overall, the authors were successful in determining the difference in wrist
ROM for this population highlights the importance of considering purposeful movement to
restore movement and function by obtaining real-world data. One limitation of the study to
assess was the lack of researcher blinding. Still, the authors stated this was mitigated by giving
all patients standard instructions without prompting during the activities and exercises. Future
studies may consider the qualitative data collected to explore the value of giving patients more
specific parameters for completing purposeful activities for rehabilitation.
More To Read
Does Obesity or Smoking change the outcomes for Distal Radius Fractures
Hall, Matthew J., Ostergaard, P., Dowlatshahi, A., Harper, C., Earp, B. Rozental, T. (2019). The Impact of Obesity and Smoking on Outcomes After Volar Plate Fixation of Distal Radius Fractures. The Journal of Hand Surgery. In Press, Corrected Proof, Available online 31 October 2019. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2019.08.017 The Skinny- Distal radius fractures are one of the…
Rapid Review: Is Finger Splinting Necessary after Flexor Tendon Repair?
Outcome of Flexor Tendon Repair Using Eight-Strand Core Stitch Without Postoperative Finger Splinting Reference: El-Gammal, T. A., Kotb, M. M., Ragheb, Y. F., El-Gammal, Y. T., & Anwar, M. M. (2024). Outcome of Flexor Tendon Repair Using Eight-Strand Core Stitch Without Postoperative Finger Splinting. HAND. https://doi.org/10.1177/15589447231220686 The Skinny: The purpose of this study was to…
Wound Healing Complications in Diabetic Patients who have undergone a Carpal Tunnel or Trigger Finger Release
By: Amalia Garcia Gundlach, B. K., Robbins, C. B., Lawton, J. N., & Lien, J. R. (2021). Wound Healing Complications in Diabetic Patients Undergoing Carpal Tunnel and Trigger Finger Releases: A Retrospective Cohort Study. The Journal of Hand Surgery, S0363502321003014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2021.05.009 The Skinny – carpal tunnel and diabetes In general, individuals with diabetes are more…
Thumbs up for treating thumb pain in the hand therapy clinic
What do “Mommy’s thumb,” “gamer’s thumb,” and “radial styloid tenosynovitis” have in common? They are all officially called de Quervain’s tenosynovitis De Quervain’s involves the tendons within the first dorsal compartment, abductor pollicis longus (APL) and extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) and arises when the tendons are inflamed and are not able to move through the…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.