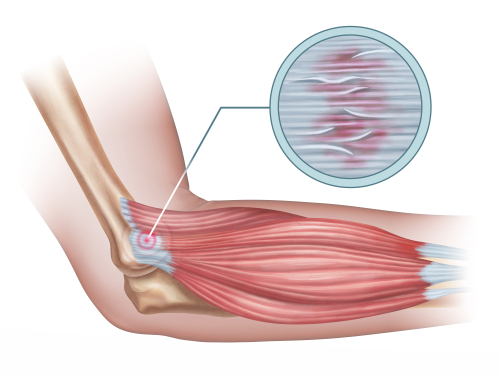
Comparison of Interventions for Tennis Elbow aka Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy
Filed under Treatments, Uncategorized
Reference:
Lowdon, H., Chong, H. H., Dhingra, M., Gomaa, A.-R., Teece, L., Booth, S., Watts, A. C., & Singh, H. P. (2024). Comparison of interventions for lateral elbow tendinopathy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis for patient-rated tennis elbow evaluation pain outcome. The Journal of Hand Surgery, 49(7), 639–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2024.03.007
Brief Overview:
This Level 1 evidence article is a systematic review of treatments for tennis elbow also known as lateral epicondyle tendinopathy across various randomized controlled trials. The research aimed to identify which interventions provided the most benefits compared to any placebos for short-term (up to 6 weeks) and midterm (6 weeks up to 6 months) outcomes. In treating tennis elbow, a variety of interventions are typically used, including activity modification, physiotherapy, orthotics, medical treatments (including injection therapies), and surgery. The researchers of this study aimed to expand the evidence on this subject by comparing interventions to placebos and control groups.
Methods:
The evidence was collected following the Cochrane Handbook standard systematic review protocol. The study included a total of 13 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi-RCTs. Eligible criteria included adult patients aged at least 18 years, interventions (therapy, injection therapy, extracorporeal shockwave therapy [ECSWT], acupuncture/dry needling, and surgical release), control/placebo or other included intervention comparisons, PRTEE pain score, and sufficient data. The outcome measures were the Patient-Rated Tennis Elbow Evaluation (PRTEE) pain score, a validated 15-item questionnaire consisting of pain and function specific to lateral epicondyle tendinopathy.
Results and Conclusions:
Therapy and exercise showed improvement in the PRTEE pain score during midterm follow-up. The study showed that dry needling may yield potential short-term benefits, but individual response varied. Two injection therapies, autologous blood and steroid injections, improved PRTEE pain score at midterm follow-up. Orthotics, ECSWT, TENS, and surgery showed no statistically significant benefit according to the PRTEE pain score. Researchers concluded that the results should be interpreted with caution because of the limited amount of evidence that met the criteria. The optimal treatment for lateral epicondyle tendinopathy is still not concrete; however, physiotherapy or exercise is the intervention best supported by evidence.
Rating:
4/5 – This article is a Level 1 therapeutic evidence article, a high ranking of evidence. The authors considered the most common interventions and effectively discussed how the trials used supported their conclusions.
2 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
3 Household Objects for 9 different Hand Therapy Activities
Do you struggle to develop new treatment ideas or even ideas for your virtual hand therapy visits? Thinking of unique ways to use objects your clients have in their homes can be half the battle. This blog post presents 3 different ways to use 3 everyday items. Item number 1: A tennis ball (hand therapy…
How to Improve Fine Motor Translation Skills
By: Josh MacDonald The Basics – I lay a pile of small objects on the table and an open container for the client to put them into. What object I use depends on the client’s level. We’ll get to that later. Then, they use a 2-point pincer grasp to pick up one and shift it…
Effectiveness of Conservative Therapy and Splinting for 1st CMC OA
Tsehaie, J., Sprekraijse, K., Wouters, R., Slijper, H., Feitz, R., Hovious, S., & Selles, R. (2018). Outcome of a Hand Orthosis and Hand Therapy for Carpometacarpal Osteoarthritis in Daily Practice: A Prospective Cohort Study. American Society for Surgery of the Hand, 1-11. The skinny: Non-surgical approaches (hand therapy & orthotics) are typically the go-to for…
Should we still be immobilizing the thumb in scaphoid fractures, or is a wrist-only cast just as effective?
Article:Harper, K. J., Rees, Y., Tan, N. X., Li, H., Fonseca, E. A., Quach, P. G., Lee, G. S., Brayshaw, J.R., & McGarry, S. (2025). Determining the success of clinical outcomes for thumbimmobilization compared to no thumb immobilization in adult non-displaced, non-surgically managed scaphoid fractures: A systematic review. Hong Kong journal ofoccupational therapy. The Skinny:This study…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.






Any details on the therapy and exercise used?
The meta analysis did state specific exercises as it reviewed several articles all with different exercises.