Comparison of Interventions for Tennis Elbow aka Lateral Elbow Tendinopathy
Filed under Treatments, Uncategorized
Reference:
Lowdon, H., Chong, H. H., Dhingra, M., Gomaa, A.-R., Teece, L., Booth, S., Watts, A. C., & Singh, H. P. (2024). Comparison of interventions for lateral elbow tendinopathy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis for patient-rated tennis elbow evaluation pain outcome. The Journal of Hand Surgery, 49(7), 639–648. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2024.03.007
Brief Overview:
This Level 1 evidence article is a systematic review of treatments for tennis elbow also known as lateral epicondyle tendinopathy across various randomized controlled trials. The research aimed to identify which interventions provided the most benefits compared to any placebos for short-term (up to 6 weeks) and midterm (6 weeks up to 6 months) outcomes. In treating tennis elbow, a variety of interventions are typically used, including activity modification, physiotherapy, orthotics, medical treatments (including injection therapies), and surgery. The researchers of this study aimed to expand the evidence on this subject by comparing interventions to placebos and control groups.
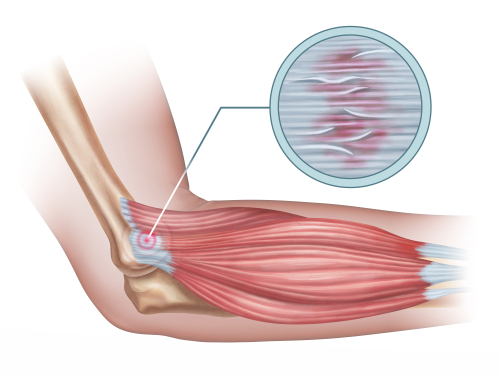
Methods:
The evidence was collected following the Cochrane Handbook standard systematic review protocol. The study included a total of 13 randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi-RCTs. Eligible criteria included adult patients aged at least 18 years, interventions (therapy, injection therapy, extracorporeal shockwave therapy [ECSWT], acupuncture/dry needling, and surgical release), control/placebo or other included intervention comparisons, PRTEE pain score, and sufficient data. The outcome measures were the Patient-Rated Tennis Elbow Evaluation (PRTEE) pain score, a validated 15-item questionnaire consisting of pain and function specific to lateral epicondyle tendinopathy.
Results and Conclusions:
Therapy and exercise showed improvement in the PRTEE pain score during midterm follow-up. The study showed that dry needling may yield potential short-term benefits, but individual response varied. Two injection therapies, autologous blood and steroid injections, improved PRTEE pain score at midterm follow-up. Orthotics, ECSWT, TENS, and surgery showed no statistically significant benefit according to the PRTEE pain score. Researchers concluded that the results should be interpreted with caution because of the limited amount of evidence that met the criteria. The optimal treatment for lateral epicondyle tendinopathy is still not concrete; however, physiotherapy or exercise is the intervention best supported by evidence.
Rating:
4/5 – This article is a Level 1 therapeutic evidence article, a high ranking of evidence. The authors considered the most common interventions and effectively discussed how the trials used supported their conclusions.
2 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Dorsal Wrist Pain?
Incorporating Emerging Evidence into Clinical Practice for Patients Experiencing Dorsal Wrist Pain During Weight-Bearing Activities By: Brittany Day Supporting Evidence A randomized control study recently published in the Journal of Hand Therapy found rigid carpal stabilizing taping (CST) to significantly increase passive range of motion, active range of motion, and decrease pain in patients experiencing…
Read MoreUltimate Guide to Continuing Education Credits for Occupational Therapists in 2025
Introduction to Continuing Education for Occupational Therapists In today’s fast-evolving healthcare landscape, continuing education credits for occupational therapists aren’t just a requirement—they’re a pathway to career advancement and improved patient care. Whether you’re renewing your license or specializing in a niche, staying current with the latest research, tools, and therapeutic techniques is vital. Continuing education…
Read MoreDoes Obesity or Smoking change the outcomes for Distal Radius Fractures
Hall, Matthew J., Ostergaard, P., Dowlatshahi, A., Harper, C., Earp, B. Rozental, T. (2019). The Impact of Obesity and Smoking on Outcomes After Volar Plate Fixation of Distal Radius Fractures. The Journal of Hand Surgery. In Press, Corrected Proof, Available online 31 October 2019. Doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2019.08.017 The Skinny- Distal radius fractures are one of the…
Read MoreSign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.



Any details on the therapy and exercise used?
The meta analysis did state specific exercises as it reviewed several articles all with different exercises.