The Effectiveness of Manual Therapy Versus Surgery in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Filed under Uncategorized
Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C., Cleland, J., Palacios-Ceña, M., Fuensalida-Novo, S., Pareja, J. A., & Alonso-Blanco, C. (2017). The effectiveness of manual therapy for carpal tunnel versus surgery on self-reported function, cervical range of motion, and pinch grip force in carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Orthopedic & Sports Physical Therapy, 47(3), 151–161. https://doi.org/10.2519/jospt.2017.7090
The Effectiveness of Manual Therapy Versus Surgery in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
The Skinny:
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), a painful condition associated with repetitive movements. It accounts for nearly 50% of all work-related injuries, and approximately 6% to 12% of the general population.
The typical mode of treatment for CTS is either conservative or surgical. Conservative management is often chosen as the first approach when symptoms are mild, while surgery is often chosen when symptoms are severe. Conservative interventions can include splinting, corticosteroid injections, and therapeutic interventions (carpal tunnel syndrome physiotherapy).
Recent evidence debates the most beneficial intervention for CTS. Some reviews argue that conservative management is only beneficial for short-term management, while others argue that surgery is only necessary as a last line of defense.
This study investigated the effectiveness of manual therapy for carpal tunnel versus surgery for improving self-reported function, cervical range of motion, and pinch-tip grip force in women with CTS.
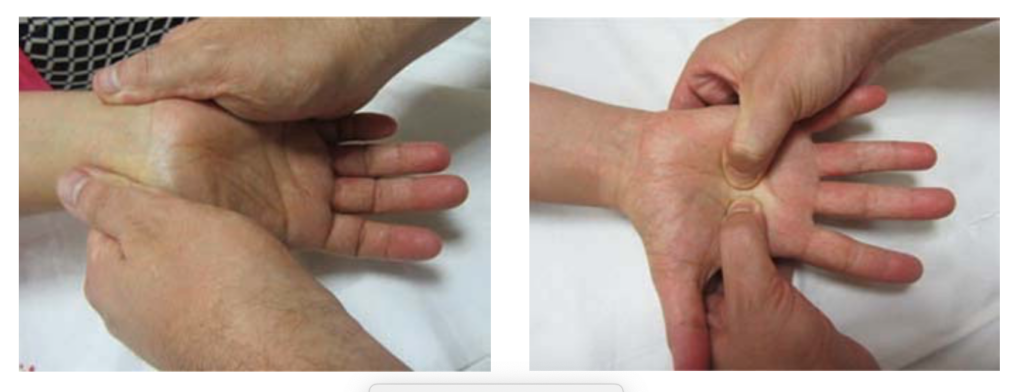
In the Weeds:
100 women with CTS were randomly split in half into a manual therapy group or a surgical group. The primary outcome was self-rated hand function, assessed with the Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire, while secondary outcomes included cervical range of motion, pinch-tip grip force, and the symptom severity subscale of the Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire. Each woman was assessed at month 3, 6, and 12.
At 12 months, 94 women completed the follow-up. Analyses showed statistically significant differences in favor of manual therapy at 1 month for self-reported function and pinch-tip grip force on the symptomatic side. Improvements in self-reported function and pinch grip force were similar between the groups at 3, 6, and 12 months. Both groups reported improvements in symptom severity that were not significantly different at all follow-up periods. No significant changes were observed in pinch-tip grip force on the less symptomatic side and in cervical range of motion in either group.
The manual therapy group intervention consisted of 3 sessions of manual therapy for carpal tunnel including intervention to treat the potential entrapment site. The manual treatment was performed for 30 minutes one time per week. These interventions included cervical spine, shoulder, elbow forearm, and wrist. Soft tissue interventions were targeted to the scalene muscles, costoclavicle space, pectorals minor, biceps brachii muscle, bicipital aponeurosis, pronator teres, transverse carpal ligament, palmar aponeurosis, and lumbrical muscles. These maneuvers are described within the article and the article is open access.
During the last treatment session, the manual group was provided instructions on how to perform the exercises at home, patients were instructed in work modifications and cervical spine exercises.
Taking it Home:
Manual therapy and surgery had similar effectiveness for improving self-reported function, symptom severity, and pinch-tip grip force on the symptomatic hand in women with CTS by 12 months. Manual therapy may be more beneficial during the first month of treatment intervention. Neither manual therapy nor surgery resulted in changes in cervical range of motion.
Rating: 4 out of 5
The ability to generalize the following results may be limited as only subjects from a single hospital were involved in the study. Outcome measures did not include a nerve conduction study which is arguably the gold standard for diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome. The study is classified as Level 1B, indicating a single high-quality randomized controlled trial with moderate level evidence.
Reference
Fernández-de-las-Peñas, C., Cleland, J., Palacios-Ceña, M., Fuensalida-Novo, S., Pareja, J. A., & Alonso-Blanco, C. (2017). The effectiveness of manual therapy versus surgery on self-reported function, cervical range of motion, and pinch grip force in carpal tunnel syndrome: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Orthopedic & Sports Physical Therapy, 47(3), 151–161. https://doi.org/10.2519/jospt.2017.7090
1 Comment
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM hand)
By: Amalia Garcia Introduction After completing three weeks of my Level II hand therapy rotation, I have seen a wide variety of common upper extremity injuries such as carpal tunnel syndrome, distal radius fractures, mallet finger, flexor tendon lacerations, arthritis, and more. One condition that stood out to me was one that I hadn’t heard…
Management of a TFCC Injury in Hand Therapy
By: Taylor Volentine The wrist is composed of very complex joints that assists with movement in individuals of all ages and abilities. For instance, an active individual who participates in sports such as tennis, football, or gymnastics may increase the probability for wrist complications and injury (Morrison, 2019). Individuals with repetitive trauma from work or…
Sensitivity and Specificity in Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) Tests in Hand Therapy
By: Mikayla Murphy Sensitivity and Specificity in Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) Tests in Hand Therapy Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) describes the compression of nerves, arteries, and veins as they pass through the thoracic outlet. Compression can occur at the interscalene triangle, the costoclavicular triangle, and the subcoracoid space (Physiopedia, n.d.). There are three types of…
Mirror Therapy
Mirror therapy has many implications for therapy and can be used to treat many diagnoses that commonly involve the upper extremity. These include some of the Neuro Conditions we highlighted last week including, Stroke and Focal Hand Dystonia. Btw, you can download a mirror therapy exercises pdf here for free. How long should the patient…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.





Good review!