Glenohumeral Joint Ligaments
The Glenohumeral (GH) joint is composed of the head of the humerus and the glenoid fossa. The fossa is relatively small compared to the humeral head, making the joint highly mobile, which also leads to an increased risk of instability.
The glenoid labrum is a fibrocartilagenous rim attached around the glenoid that helps deepen the glenoid fossa by 50%, providing increased stability of the GH joint.
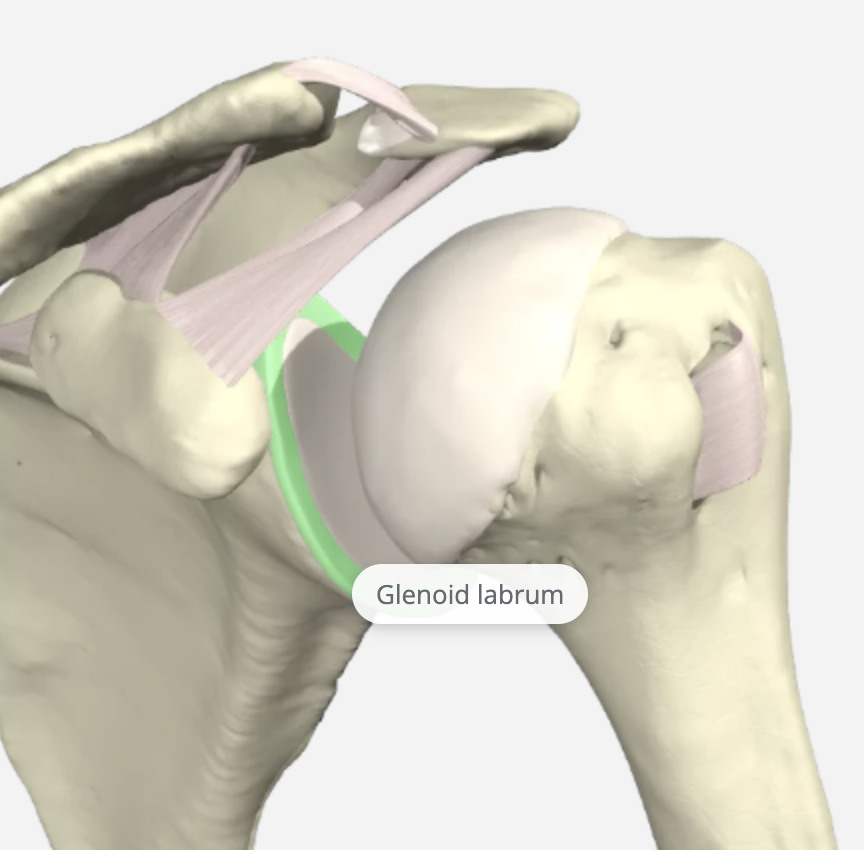
The GH joint relies heavily on the soft tissue structures for stability, and the GH ligaments are the primary static stabilizers of the joint. These include the Coracohumeral Ligament (CHL), Superior Glenohumeral Ligament (SGHL), Middle Glenohumeral Ligament (MGHL), Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament (IGHL), and the Posterior Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament (PIGHL).
Coracohumeral Ligament (CHL)
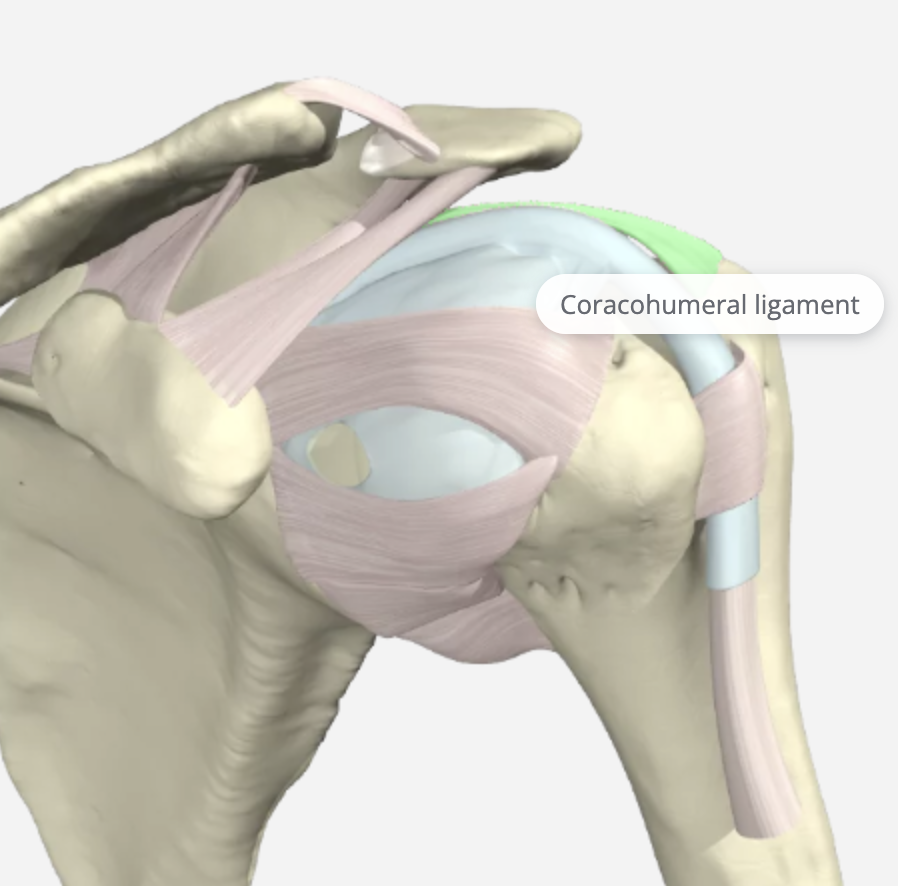
The CHL prevents superior dislocation and inferior displacement of the humerus. It is included in this review as it blends with the (SGHL). It is divided into two parts, the anterior and posterior bands. The Anterior Coracohumeral Ligament inserts on the lesser tuberosity and is tight in 30 degrees shoulder extension. The Posterior Coracohumeral Ligament inserts on the greater tuberosity and tight flexion at 60-70 degrees. It is also a secondary restraint in preventing the long head of the biceps from subluxing medially.
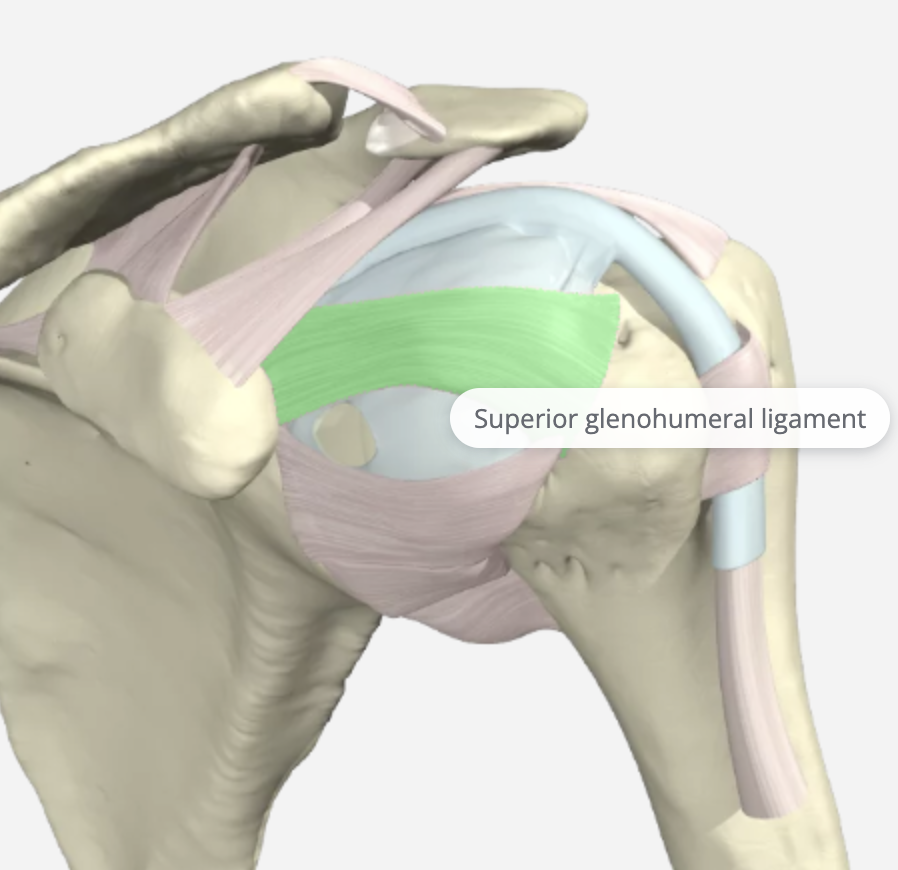
Superior Glenohumeral Ligament (SGL)
The SGHL is the smallest and least understood ligament in the GH capsule. Its origin is the upper part of the glenoid cavity and the base of the coracoid process. It attaches to the MGL, the biceps tendon, and the labrum. It is tight in adduction, the middle at 45 degrees of abduction, and when the shoulder is brought to 90 degrees of abduction with external rotation. It works with the CH ligament to prevent inferior translation of the humeral head.
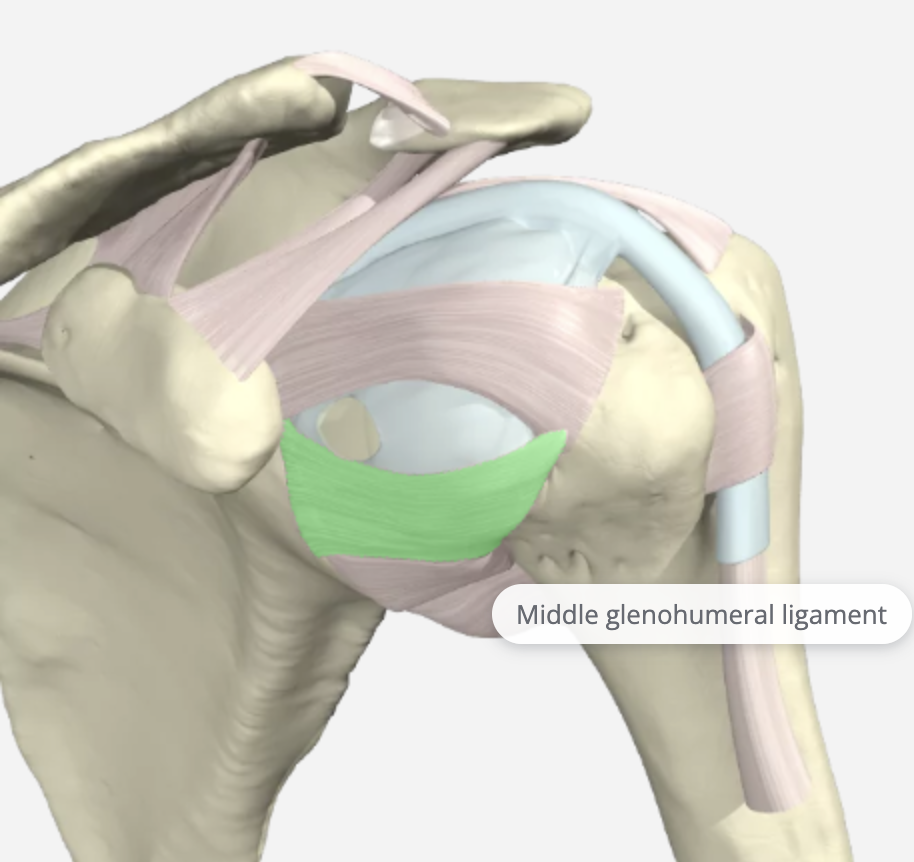
Middle Glenohumeral Ligament (MGHL)
The middle glenohumeral ligament (MGHL) attaches to the anterior aspect of the anatomic neck of the humerus, just medial to the lesser tuberosity. It arises from the glenoid by way of the labrum. Of the three glenohumeral ligaments, the MGL demonstrates the most significant variation in size. It is tight in the abduction and provides anterior stability at 45 degrees and 60 degrees abduction. Injuries to this area alone are very rare and are never isolated.
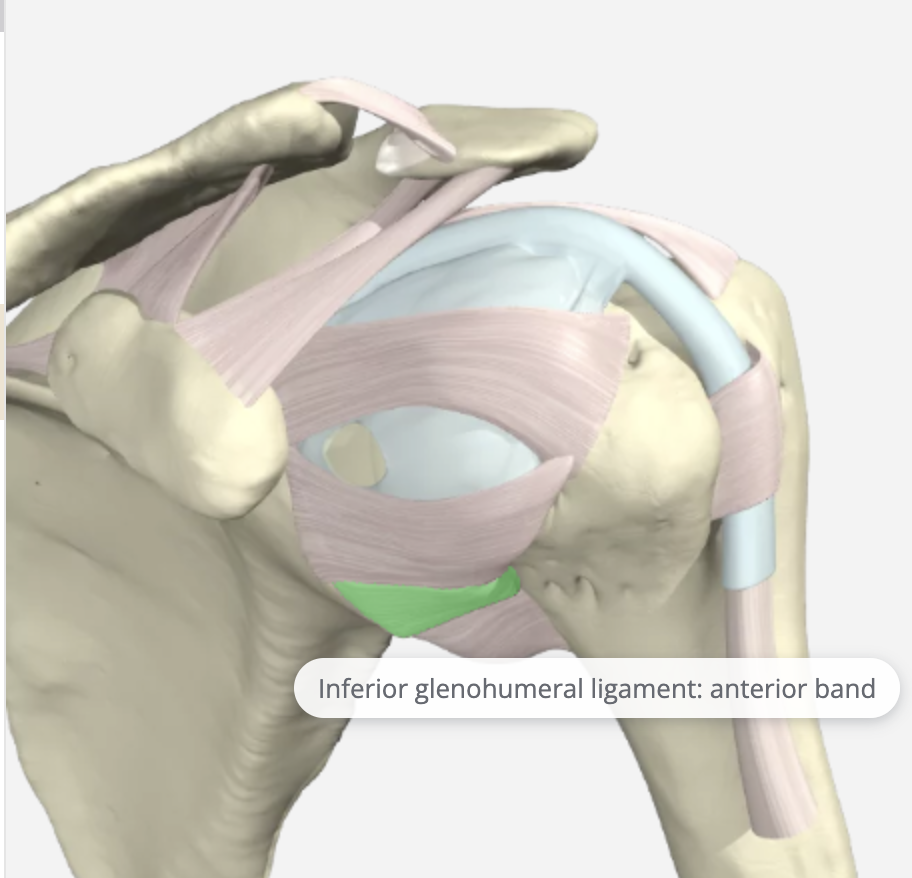
Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament (IGHL)
IGHL is tight in true abduction and slightly looser in the scapular plane of abduction. It originates from the glenoid labrum and inserts into the humeral neck. It is the most important stabilizer against anterior-inferior shoulder dislocation. Therefore this component is the most frequently injured and is most likely to tear when the arm is fully abducted. It is the strongest and most important soft tissue stabilizer. It can be avulsed from the glenoid side resulting in an anteroinferior labral tear.
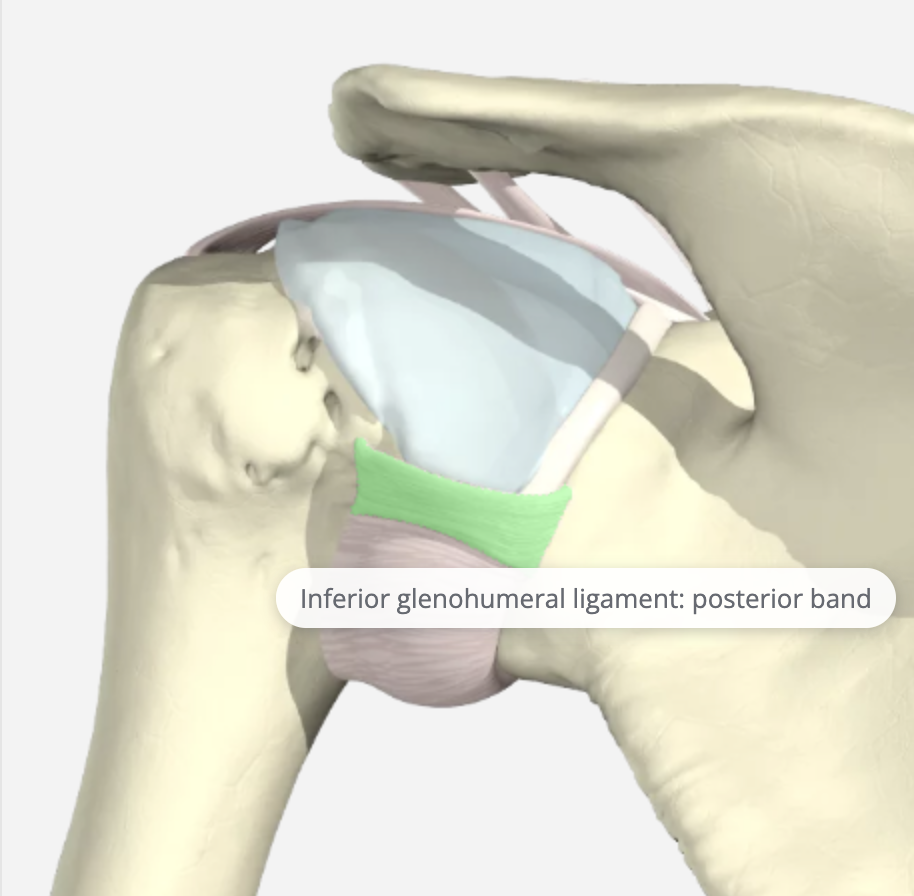
Posterior Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament (PIGHL)
PIGHL is not as robust as the anterior ligaments but is essential to balance the capsule. Laxity in this part of the capsule is considered normal. The posterior band of the IGLC is mainly responsible for capsuloligamentous restraint to posterior translation of humeral head in 90° of abduction.
Goetti, P., Denard, P. J., Collin, P., Ibrahim, M., Hoffmeyer, P., & Lädermann, A. (2020). Shoulder biomechanics in normal and selected pathological conditions. EFORT open reviews, 5(8), 508–518. https://doi.org/10.1302/2058-5241.5.200006
1 Comment
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Occupation Based Interventions in Hand Therapy
Keeping Occupation Based Interventions in Hand Therapy By: Tristany Hightower Are your treatments occupation based? Do you tailor your activity choices to fit the needs of each patient? As occupational therapists, we should be specialists in creating goals and interventions that are directed at returning our patients to meaningful occupations. Too often, hand therapy can…
Test for Distal Radial Ulnar Joint of the Wrist
Ballottment Test for Wrist DRUJ Reliability and Validity Analysis of the Distal Radioulnar Joint Ballottement Test Nagashima, M., Omokawa, S., Hasegawa, H., Nakanishi, Y., Kawamura, K., & Tanaka, Y. (2024). Reliability and validity analysis of the distal radioulnar joint ballottement test. The Journal of Hand Surgery, 49(1), 15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2023.10.006 The Skinny: Distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ)…
Mechanism of Interneural Edema in Carpal and Cubital Tunnel
Mechanism of Interneural Edema Over the last few weeks I have been learning about ultrasonic imaging and carpal tunnel syndrome. When reviewing carpal tunnel syndrome, I learned that intraneural edema is a common sign of compression injuries such as carpal tunnel and cubital tunnel. There are numerous causes of carpal tunnel syndrome, and every scenario…
Scapholunate Wrist Injuries in Hand Therapy
Scapholunate Wrist Injuries in Hand Therapy In outpatient hand therapy, we get a variety of referrals ranging from post-operative patients to those looking to avoid or prolong surgery. These referrals come from a variety of sources ranging from primary care doctors to experienced hand surgeons. The therapy orders can be vague to very specific. …
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.




Excellent!