Comparing the Rates of Recovery Among Four Common Shoulder Surgeries
Filed under Reviews
Rapid Review By: Case Peters
Comparing the Rates of Recovery Among Four Common Shoulder Surgeries
Grubhofer, F., Martinez, A.R.M., Ernstbrunner, L., Haberli, J., Selig, M.E., & Warner, J.J. (2021) Speed of recovery of the most common performed shoulder surgeries. JSES International.5(4); 776-781. doi: 10.1016/j.jseint.2021.03.007
The Skinny:
Setting realistic expectations for the trajectory of recovery is an essential part of post-operative rehabilitation. In this retrospective cohort study, the authors compared the speed of recovery of four common shoulder surgeries over a 2-year timeframe. The authors hypothesized that patients undergoing shoulder arthroplasty would recover more quickly than those undergoing soft-tissue repair.
In the Weeds:
Patients and Procedures:
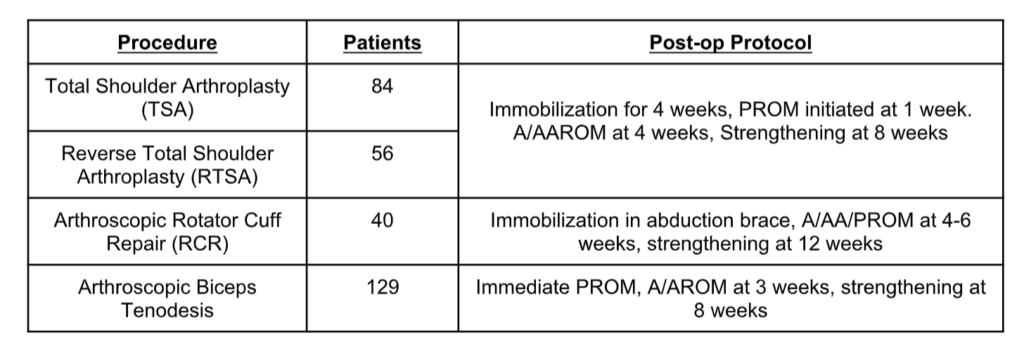
Outcome Measures:
Pain, measured using VAS at pre-op, 2 weeks, 6 weeks, 6 months, 12 months, 24 months
Function, measured using American Shoulder and Elbow score (ASES), and Single Assessment Numeric Evaluation (SANE) score at: pre-op, 6 months, 12 months, 24 months
Bringing it home:
Pre-operative pain tended to be higher in the RTSA and TSA groups. However, both the RTSA and TSA groups experienced significantly faster pain recovery from 0 – 6 weeks compared to the RCR and BT groups. At 3 months, the pain recovery was more similar, but still favored the arthroplasty group. At 6 months, the arthroplasty group’s average reported pain was 1.1 ± 1.7. The RCR and BT group’s average reported pain was 1.4 – 1.6 ± 1.8.
Pre-operative function varied between the two groups, but trended towards lower pre-operative function in the arthroplasty groups. The RTSA and TSA groups demonstrated faster and more substantial functional recovery from 0 – 6 months. At 6 months, the arthroplasty group demonstrated between 86 – 96% improvement in function. The RT and BT group demonstrated between 76 – 86% improvement in function.
Clinicians can refer to the original publication for specifics on reported pain and function at each timepoint. This paper is open access and can be found for free on PubMed.
Rating (0-5 rating scale):
Study rating: 3/5. As this is a retrospective cohort study (Level of Evidence: III), there was no randomization or control for confounding variables. There is limited detail on the post-operative therapy management. Furthermore, there is the potential for selection bias among those pursuing surgery, and recall bias over the long follow-up period. However, this was one of the first studies to compare the overall course of rehabilitation amongst these common procedures, demonstrating the interesting finding that recovery from shoulder arthroplasty is less strenuous than recovery from RCR and BT.
Furthermore, the results are generally in agreement with the findings of other cohort studies at different institutions. Cho et al. (2021) found that at 6 months, function was generally 75% improved compared to pre-op measures, and the average reported pain was 2.6/10 in patients undergoing RCR. Kurowicki et al. (2017) found that at 6 months, the function was generally 80% improved compared to pre-op measures, and the average reported pain was 2.0/10 (± 2.2).
The results stress the importance of ensuring that patients understand that recovery from soft-tissue repair in the shoulder is a lengthy process.
Additional References
Cho, C., Bae, K., & Kim, D. (2021) Patients who have undergone rotator cuff repair experience around 75% functional recovery at 6 months after surgery. Knee Surgery, Sports Traumatology, Arthroscopy. 29(7); 2220 – 2227. doi: 10.1007/s00167-020-06019-z
Kurowicki, J., Berglund, D.D., Momoh, E., Disla, S., Horn, B., Giveans, M.R., & Levy, J.C. (2017). Speed of recovery after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair. 26(7); 1271-1277. doi: 10.1016/j.jse.2016.11.002
More To Read
Radial Nerve Palsy: A Paralysis Causing Wrist Drop
Radial Nerve Palsy- Treatment
Mirror therapy after a peripheral nerve repair in hand therapy
Rapid Review Paula, M. H., Barbosa, R. I., Marcolino, A. M., Elui, V. M., Rosén, B., & Fonseca, M. C. (2016). Early sensory re-education of the hand after a peripheral nerve repair based on mirror therapy: a randomized controlled trial. Brazilian journal of physical therapy, 20(1), 58–65. https://doi.org/10.1590/bjpt-rbf.2014.0130 The Skinny: Therapy is often provided following an…
Carpal Fractures: A Brief Overview
Carpal fractures account for 8% of fractures in the upper extremity. The carpals are situated between the (distal radius and ulna) and the metacarpals. They make up the proximal row- Scaphoid, Lunate, Triquetrum, and Pisiform, the distal row- Trapezium, Trapezoid, Capitate, and Hamate. Here are some of the most common carpal bone fracture Scaphoid…
Article Review: Relative Motion for Extensor Tendon Repair zone V-VI? Is a night-time resting hand orthosis beneficial?
Hirth, M. J., Hunt, I., Briody, K., Milner, Z., Sleep, K., Chu, A., Donovan, E. & O’Brien, L. (2021). Comparison of two relative motion extension orthotic programs following surgical repair of finger extensor tendons in zones V-VI: A randomized equivalence trial. Journal of Hand Therapy-to be published. The Skinny: Following a zone V-VI tendon repair,…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.