What is the incidence of musculoskeletal complaints in the elbow, shoulder, and neck after hand and forearm injuries?
Filed under Reviews
Winiarski, L. M., Livoni, J. D., Madsen, P. V., Rathleff, M. S., & Larsen, P. (2021). Concurrent musculoskeletal complaints in elbows, shoulders, and necks after common hand and forearm injuries or conditions: A cross-sectional study among 600 patients. Journal of hand therapy: official journal of the American Society of Hand Therapists, 34(4), 543–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2020.05.002
The Skinny:
The authors looked to determine what the incidence of shoulder elbow and neck pain after sustaining a typical hand and forearm injury. Isolated hand injuries account for 20-29% of hand and forearm injuries in emergency rooms and orthopedic departments. Oftentimes pain associated in the upper quadrant beyond the injury is neglected and ignored. The authors hoped to bring awareness to these concurrent musculoskeletal issues.
In the Weeds:
The authors used a cross-sectional study. The study used patients that were referred to the shoulder elbow hand therapy department for an isolated hand or forearm injury. The patients were asked two basic questions.
1.) do you currently have pain and/or stiffness in the elbow, shoulder, or neck?
If yes then,
2.) did the symptoms develop before or after their hand and forearm injury?
If the patient answered yes to question 1 and stated the symptoms developed after the hand or forearm injury they were included in the study.
Bringing it Home:
The study took place for 15 months and a total of 600 patients met the eligibility requirements. The average age of patients was 49.1 years with the largest diagnostic group being distal radius and ulna fractures, ligament lesions in fingers (16%), finger fractures (14%). The common areas of concurrent pain were the shoulder (62%), elbow (49%), and the neck (32%”). Thirty-eight percent of patient reports multiple areas of musculoskeletal or stiffness in two or three regions of the upper quadrant and neck.
Rating 4/5.
The study brings attention to the continued need to address the entire upper quadrant when a patient sustains a hand, wrist, or forearm injury. In the future, it would be helpful to publish outcomes after addressing the musculoskeletal impairments to help justify the need for occupational and physical therapy services to prevent long-term pathologies.
2 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
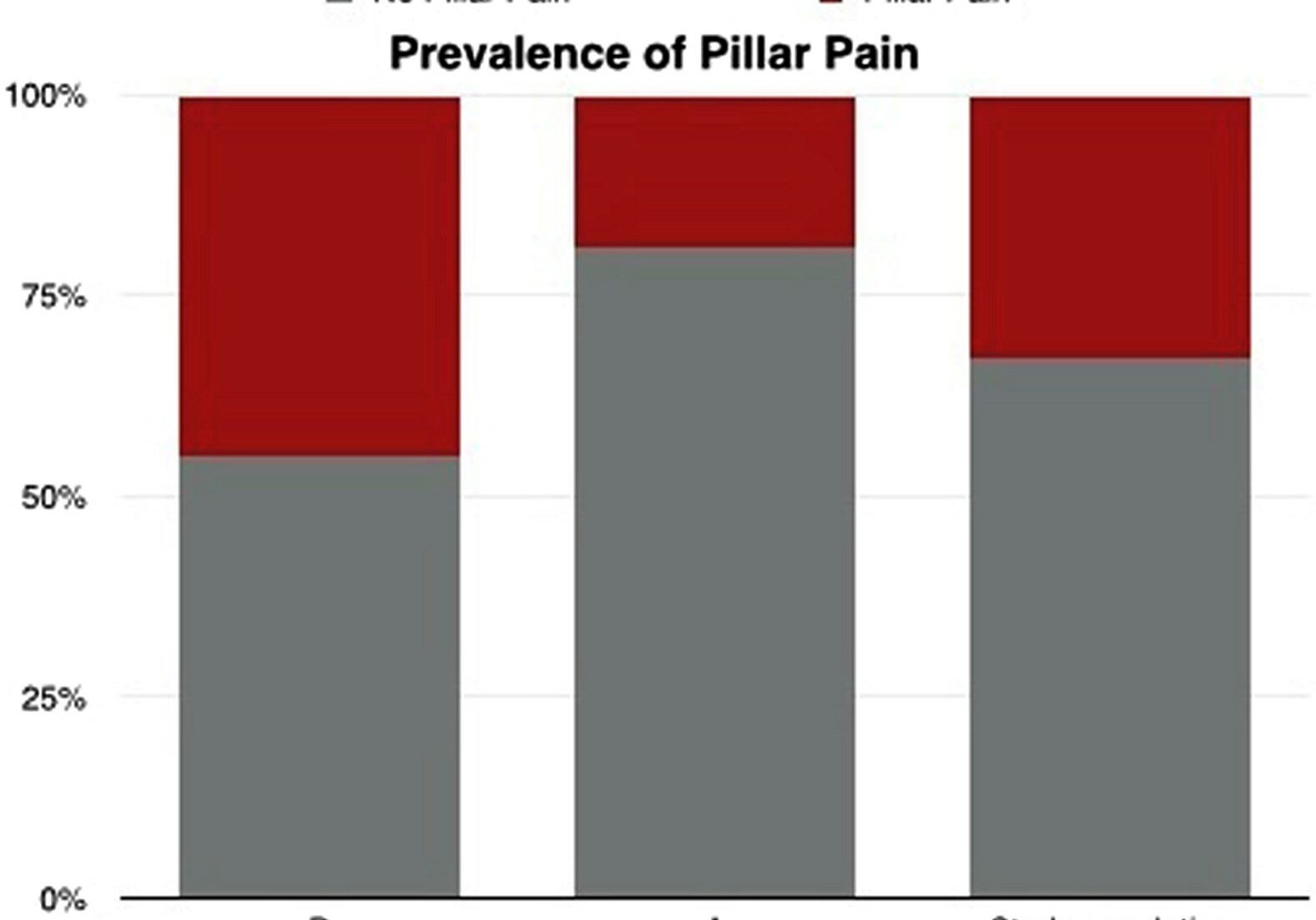
Taking Alpha-Lipoic Acid for 40 days after Carpal Tunnel Surgery can decrease the likelihood of developing Pillar Pain.
Filippo, B., Granchi, D., Roatti, G., Merlini, L., Sabattini, T., & Baldini, N. (2017). Alpha-lipoic acid after median nerve decompression at the carpal tunnel: A randomized controlled trial. The Journal of Hand Surgery, 4, 236–42. The Skinny – A double-blind, randomized controlled study was performed. Sixty-four patients were randomly assigned into two groups after median…
Read MoreHow to Strengthen the Intrinsics with Puttycise Tools:
How to strengthen the intrinsic with Puttycise tools
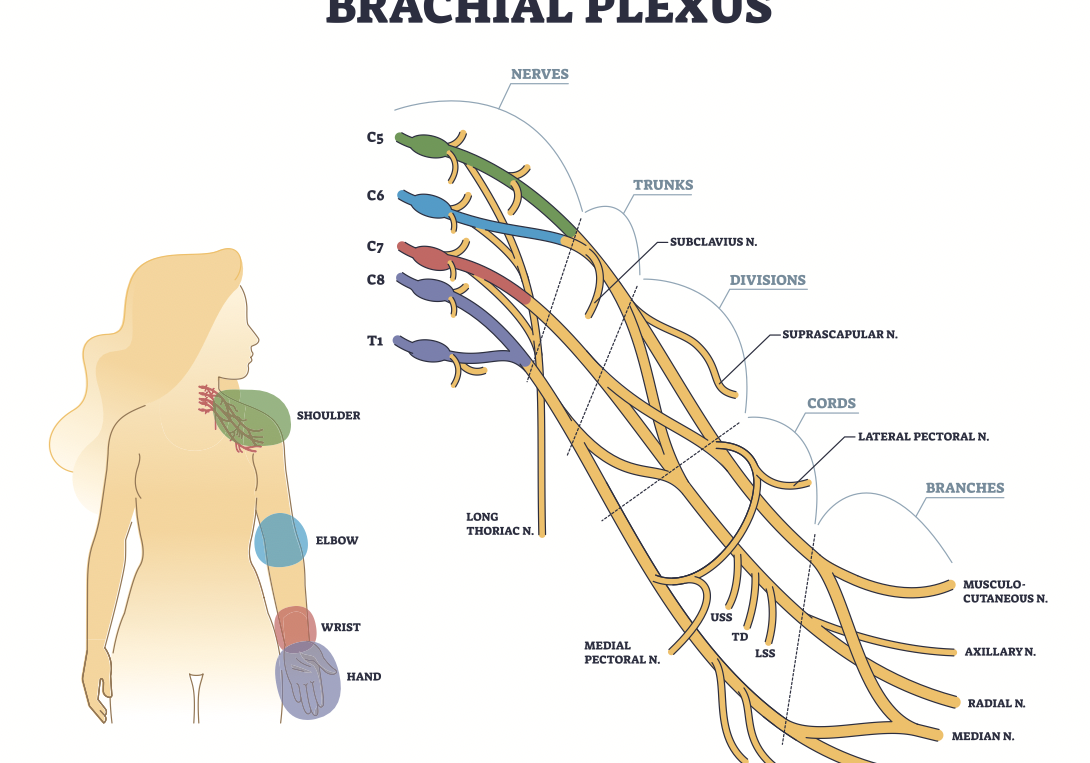
Read MoreComparison of Erb’s Palsy and Klumpke’s Palsy: Symptoms, Presentation, and Treatment Options
What is the brachial plexus? The brachial plexus is a group of nerves originating from the cervical and thoracic nerve roots (from C5 to T1). The brachial plexus forms 5 peripheral nerves of the upper extremity, consisting of the musculocutaneous, median, radial, ulnar, and axillary nerves. This group of nerves supplies motor and sensory innervation…
Read MoreSign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.




Thank you for this article. Trying to justify therapy beyond the specific joint a patient is brought in for can be frustrating. We need more research like this.
Great, good article.
At times patients are not necessarily believed and areas of discomfort are neglected. We forget there is fascia, and dermatomes that connect all structures, and will affect above or below the injured site.