Carpal Tunnel Treatment: Splinting Only vs Splinting & Conservative Treatment
Filed under Treatments
Short-term clinical outcome of orthosis alone vs combination of orthosis, nerve, and tendon gliding exercises and ultrasound therapy for treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome. Sim, Sze En et al. Journal of Hand Therapy, Volume 32, Issue 4, 411 – 416
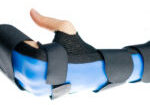
The Skinny- Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most common compression neuropathy. Compression of the Median nerve within the transverse carpal ligament causes tingling and numbness to areas distal to the compression and along the nerve distribution area. This can progress to pain and loss of muscle mass if left untreated. Treatment of CTS varies, but commonly includes use of an orthosis to decrease pressure to the carpal tunnel and preserve blood supply to the area. Modalities have also been used with success. These include, but are not limited to, nerve and tendon glides, ultrasound and manual therapy. This article sought to compare the success of orthosis use alone versus orthosis use combined with carpal tunnel syndrome conservative treatment methods.
In The Weeds- 41 total patients with 56 wrists were randomly allocated to the orthosis only (n=20) vs combined (n=21) groups. Pre and post assessments were conducted using the Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire (BCTQ). Post assessment occurred after 2 months, immediately at removal of orthosis protocol.
Orthoses were volar wrist cock up made custom from thermoplastic by a trained occupational therapist. Pt’s were to wear the orthoses for 8 weeks and only allowed to come out of carpal tunnel orthosis for 1 hour per day. Adjustments were made as needed based on discomfort. The Combined group used the same orthosis parameters but added in the use of weekly ultrasound for 5 minutes as well as nerve and tendon gliding exercises for 10 repetitions and 10 sessions per day.
Bring it Home- Analysis of the two groups showed statistically significant improvement in Symptom Severity Score (SSS) as well as Functional Status Score (FSS). There was not, however, a statistical significance on outcomes between groups. This is in contrast to other articles (Baysal et al) which demonstrate a significant difference between orthosis alone and orthosis and conservative therapy.
The outcomes contradict the hypothesis of the authors. They admit the limitations of their study include the use of exercises that did not replicate their model study as well as a lack of follow up at another interval after cessation of orthosis use at the 8 week mark. Symptom decrease with orthosis use only might not be sustainable without the conservative treatment to promote healthy motion moving forward. This would be identifiable with additional follow up after the 8 week mark.
It is also unclear if the participants in the Orthosis Only group had regular follow-ups during the 8 weeks for splint modification (splint for carpal tunnel occupational therapy) or compliance check-in. This return frequency would not necessarily directly replicate clinical application of an orthosis only treatment plan.
Baysal, O., Altay, Z., Ozcan, C., Ertem, K., Yologlu, S., & Kayhan, A. (2006). Comparison of three conservative treatment protocols in carpal tunnel syndrome. International journal of clinical practice, 60(7), 820-828.
More To Read
Sensitivity and Specificity in Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) Tests in Hand Therapy
By: Mikayla Murphy Sensitivity and Specificity in Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) Tests in Hand Therapy Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) describes the compression of nerves, arteries, and veins as they pass through the thoracic outlet. Compression can occur at the interscalene triangle, the costoclavicular triangle, and the subcoracoid space (Physiopedia, n.d.). There are three types of…
Factors that influence orthosis adherence in patients with acute traumatic tendon injuries to the hand
Savaş, S., & Aydoğan, Ç. (2020). Factors affecting orthosis adherence after acute traumatic hand tendon repairs: A prospective cohort study. Journal of Hand Therapy, S0894113020301848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2020.10.005 World Health Organization. (2003). Adherence to long-term therapies: evidence for action. World Health Organization. The Skinny Adherence to orthosis wear is vital for protecting healing tendons after a traumatic tendon…
Video-augmented mirror therapy for upper extremity rehabilitation after stroke
Kim, H., Kim, J., Jo, S., Lee, K., Kim, J., & Song, C. (2023). Video augmented mirror therapy for upper extremity rehabilitation after stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Neurology, 270(2), 831-842. Article Review: Shannon Skowbo The Skinny: This single-blind, randomized control trial aimed to assess the effects of mirror therapy for stroke patients…
Hand Therapy as a New Grad or Student
Tips for Getting Prepared for hand therapy as a new grad or a Level II Fieldwork Everything you need to know in hand therapy starts with the upper extremity anatomy. Here is a quick checklist to review and hopefully help get you started in your new hand therapy setting. By: Tristany Hightower I suggest, as…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.