Comparing Edema and Lymphedema: Understanding the Differences and Treatment Approaches in Hand Therapy
Filed under Treatments
Comparing Edema and Lymphedema: Understanding the Differences and Treatment Approaches in Hand Therapy
As hand therapists we often encounter patients presenting with swollen arms, hands, and/ or fingers, often attributing these symptoms to various conditions. Two commonly confused terms in this area are “edema” and “lymphedema.” While both involve swelling, they have distinct causes, presentations, and treatment strategies. Understanding these differences is important for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Understanding Edema
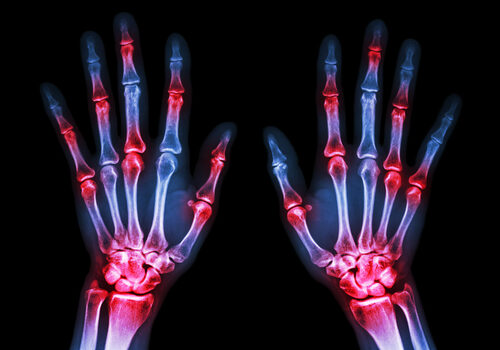
Edema is a broad term that refers to the swelling caused by excess fluid trapped in the body’s tissues. This condition can occur anywhere in the body but is most commonly observed in the limbs such as the hands, feet, and ankles.
Causes of Edema
- Injury/Trauma: This includes sprains, fracture, or any kind of trauma can lead to localized swelling.
- Inflammation: Conditions like arthritis or infections can cause inflammation and subsequent swelling.
- Venous Insufficiency: Poor circulation, often due to varicose veins, can result in fluid accumulation.
- Heart, Kidney, or Liver Disease: These conditions can lead to fluid imbalance and widespread edema.
- Medications: Certain drugs such as steroids and antihypertensives can cause fluid retention.
Symptoms of Edema
- Swelling or puffiness of the skin.
- Stretched or shiny skin.
- Increased size of the affected limb.
- Difficulty moving the joint near the swelling.
Treatment of Edema
Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying cause and reducing the swelling. Common approaches include:
- Elevation: Raising the affected limb above heart level.
- Compression: Using compression garments to reduce fluid buildup.
- Range of Motion: Gentle exercises such as tendon glides improve circulate and reduce swelling.
- Using a chip bag: the different densities of foam in a stockinette
- Massage: using retrograde edema massage can be helpful
- Medication: Diuretics may be prescribed to help the body expel excess fluid.
For more tips on managing edema check out this blog post https://www.handtherapyacademy.com/uncategorized/managing-ue-edema-in-hand-therapy/
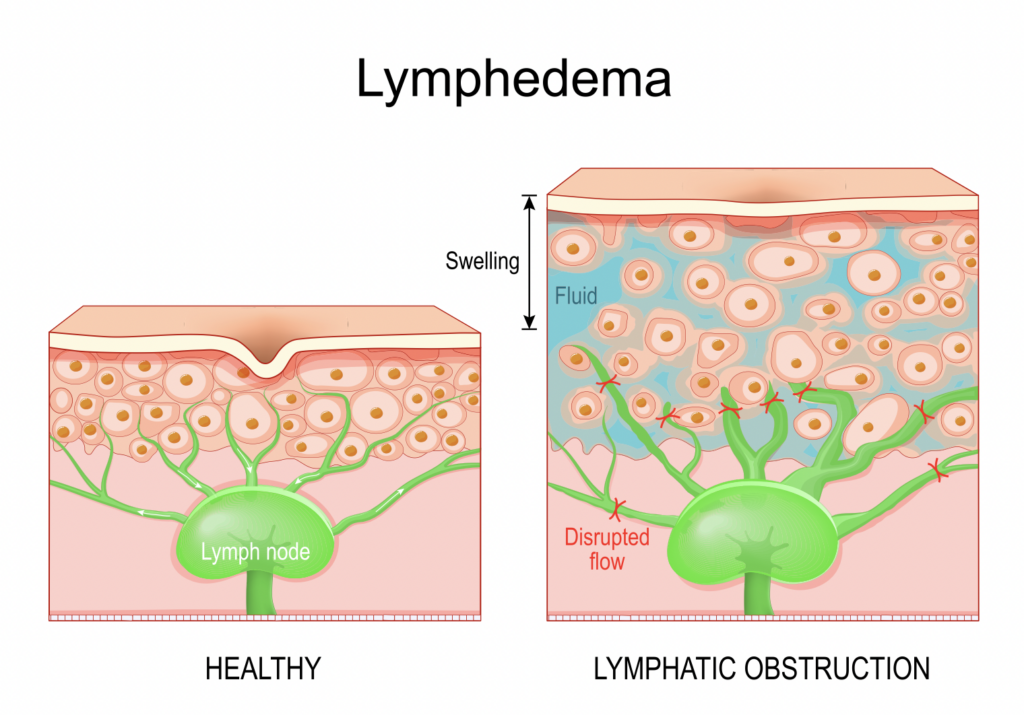
Understanding Lymphedema
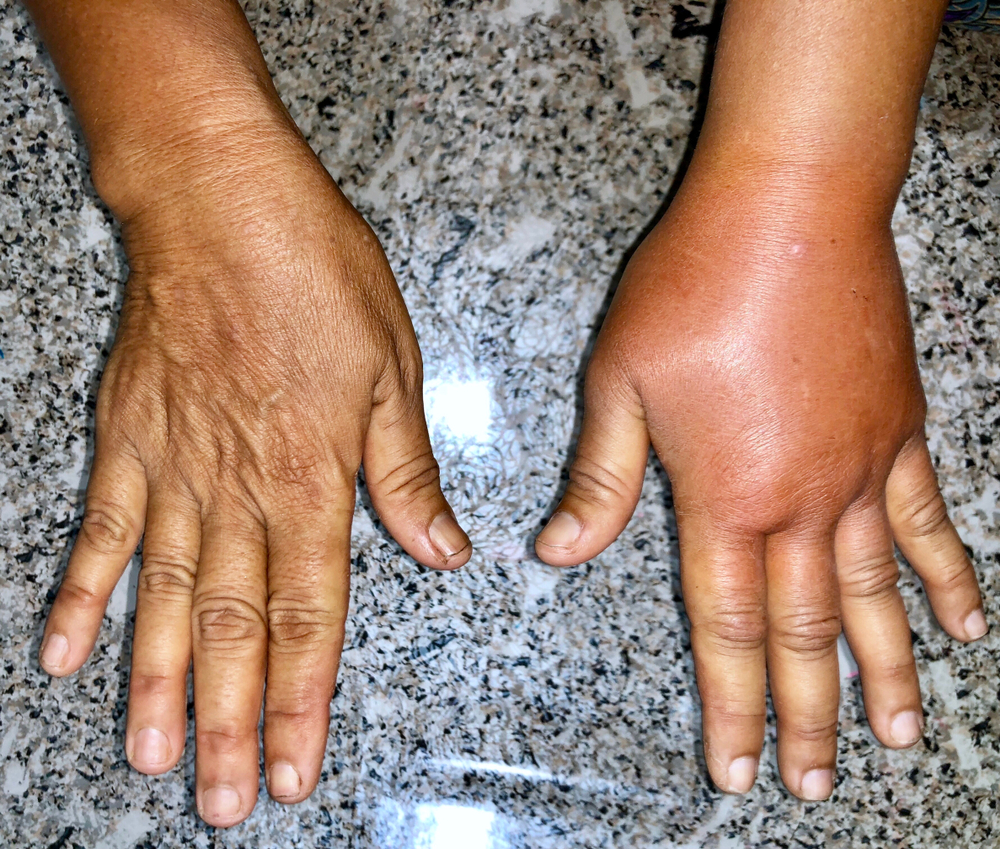
Lymphedema specifically refers to swelling that occurs due to a compromised lymphatic system, resulting in the accumulation of lymphatic fluid. It most commonly affects the arms or legs but can occur in other parts of the body.
Causes of Lymphedema
- Primary Lymphedema: A rare, inherited condition that causes problems with lymph vessel development.
- Secondary Lymphedema: More common and typically results from damage to the lymphatic system due to surgery, radiation therapy, infection, or trauma.
Symptoms of Lymphedema
- Persistent swelling, often in the arm or leg.
- A feeling of heaviness or tightness in the affected area.
- Restricted range of motion.
- Recurring infections.
- Hardening or thickening of the skin (fibrosis) in severe cases.
Treatment of Lymphedema
While lymphedema is a chronic condition with no cure, effective management strategies can help control the symptoms:
- Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD): A specialized massage technique to stimulate the movement of lymph fluid.
- Compression Therapy: Use of bandages or compression garments to support lymphatic drainage.
- Exercise: Tailored exercises to promote lymph fluid movement.
- Skin Care: Preventing infections through meticulous skin care.
- Surgical Options: In severe cases, surgical interventions like lymph node transfer or liposuction may be considered.
Key Differences Between Edema and Lymphedema
- Cause: Edema results from fluid leakage due to various reasons, while lymphedema is specifically due to lymphatic system impairment.
- Location and Presentation: Edema can be more generalized, while lymphedema often affects a specific limb or area and is usually unilateral.
- Chronicity: Edema may resolve with treatment of the underlying cause, whereas lymphedema is typically a lifelong condition requiring ongoing management.
Conclusion
Distinguishing between edema and lymphedema is essential for effective treatment and improving patient outcomes. As hand therapists, recognizing the unique characteristics and appropriate interventions for each condition ensures that patients receive the best possible care. By staying informed about the latest techniques and treatments, we can help our patients manage their symptoms and enhance their quality of life.
More To Read
Wound Healing in Hand Therapy
By: Maddie Mott Wound healing (healing hand therapy) involves a complex series of interactions between different cell types, cytokine mediators, and the extracellular matrix with its four basic stages including hemostasis, inflammation, proliferation, and remodeling (Mackay & Miller, 2003). Because successful wound healing requires adequate blood and nutrients to be supplied to the site of…
Read MoreConservative Therapy for OA in the Fingers: A Literature Review
Beasley, J., Ward, L., Knipper-Fisher, K., Hughes, K., Lunsford, D., & Leiras, C. (2018). Conservative therapeutic interventions for osteoarthritic finger joints: A systematic review. Journal of Hand Therapy, 32. 153-164. The Skinny – The article reviews the evidence on the effectiveness of conservative treatment for those who experience osteoarthritis in fingers and in their finger…
Read MoreTherapeutic Exercise vs Therapeutic Activity
What is the difference between therapeutic exercise vs therapeutic activity? Therapeutic exercise is billed as 97110 and Therapeutic activity is billed as 97530. Both are CPT codes that are commonly used in occupational and physical therapy billing. These codes are very similar and are often confused. So, when and what do you document for each…
Read MoreSign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.