Efficacy of Virtual Reality Rehabilitation after Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review
Filed under Treatments
De Araújo, A. V. L., Neiva, J. F. D. O., Monteiro, C. B. D. M., & Magalhães, F. H. (2019). Efficacy of virtual reality rehabilitation after spinal cord injury: A systematic review. BioMed Research International, 2019(1), 7106951. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7106951
Efficacy of Virtual Reality Rehabilitation after Spinal Cord Injury
Emilee Sanders, OTS
The Skinny:
Virtual reality (VR) rehabilitation may help individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI) improve motor function, motor skills, balance, and aerobic function and reduce pain either as a standalone intervention or in conjunction with rehabilitation therapies. This is a first systematic review of its kind concerning the effectiveness of VR and SCI in rehabilitation.

In the Weeds:
The systematic review includes 25 studies which contained randomized controlled trials, nonrandomized controlled trials, quasi experimental studies, and before and after studies.
Participant inclusion criteria: Male and Female participants aged 18-65 years with spinal cord injury (traumatic or nontraumatic) who participated in immersive or non immersive VR-based therapy.
Two reviewers extracted data based on participant characteristics, study characteristics, methodological details, VR effects, bias risk, size effects, statistical power, and limitations.
The reviewers used a p value of < 0.05 to assess whether the effects of VR-based rehabilitation were significant for the allotted category (motor function, aerobic function, pain, balance, or psychological aspects).
Bringing it home:
Studies showed a short-term improvement on motor function, aerobic performance, balance, pain, and psychological aspects. Long-term benefits were also shown for motor function, balance, and pain. Some subjective reports from participants included better mood, satisfaction improvements, and high enjoyment.
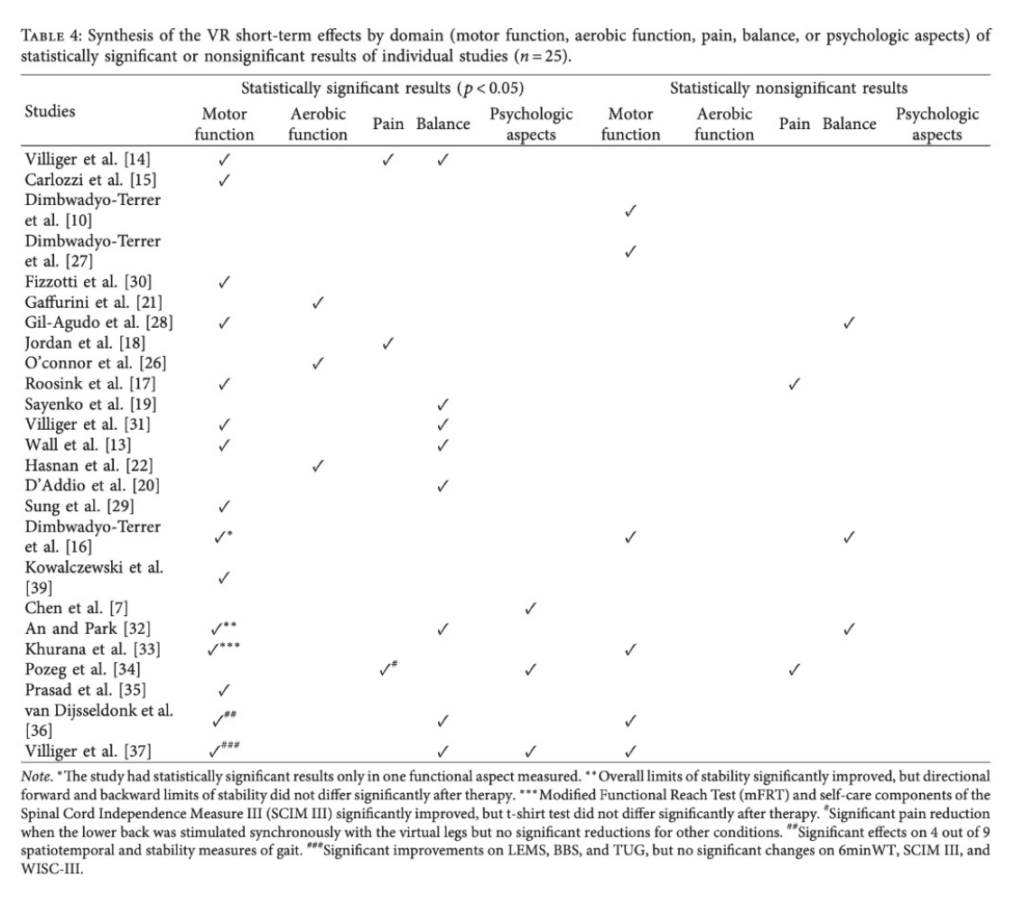
Note. From “Efficacy of Virtual Reality Rehabilitation after Spinal Cord Injury: A Systematic Review” by A. V. L. De Araújo, J. F. D. O. Neiva, C. B. D. M. Monteiro, & F. H. Magalhães, 2019, BioMed Research International, 2019(1), 7106951. (https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7106951). Copyright © 2019 Amanda Vito ́ria Lacerda de Arau ́jo et al.
Overall, the studies did not report any negative effects due to VR therapy. In the studies that did report adverse effects, a small number of participants had a short-lived muscle pain, physical fatigue, and difficulties with attention span, and one study reported a few participants having simulator sickness.
Rating (0-5 rating scale):
3/5 This study was well done for what was possible. They found that only 7/25 studies had high quality evidence. Furthermore, the exact protocols/ VR-interventions were not provided, so it is hard to ensure the specific activities and exercises did not affect the outcomes. It would also be important to note if certain VR-based activities were more therapeutically beneficial than others.
The study states that due to this limited evidence, they recommend that VR-rehabilitation be used in conjunction with conventional therapies, and I agree based on the present findings.
More To Read
6 of our Favorite Adaptive Equipment Tools for CMC Osteoarthritis
Individuals struggling with osteoarthritis of the 1st CMC joint usually have difficulty with daily activities and it can become very frustrating. Everyday tasks such as cutting food, opening containers, and donning a button up shirt can become painful and slow. The largest contributor to the overall function of our hand is the thumb. If the…
Title: Understanding De Quervain’s Pathology: A Comprehensive Exploration of Special Tests
Understanding De Quervain’s Pathology: A Comprehensive Exploration of Special Tests By: Miranda Materi De Quervain’s and Special Tests De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a condition characterized by inflammation of the tendons on the thumb side of the wrist, causing pain and discomfort. These tendons include Abductor Pollicis Longus (APL) and Extensor Pollicis Brevis as they pass through…
Creating an Action Plan for Addressing Mental Health in the Clinic
Blog By: Rachel Reed As hand therapists, our care for our patients must be driven by the goal of treating the whole person, not just their hand or injury (Hannah, 2011). Occupational therapy is a unique profession in which we are equipped to view our patients through a holistic lens. With this lens, we are…
Our Favorite Mallet Finger Splints
By: Josh MacDonald Fabricating a custom splint for a mallet finger injury is challenging. Fingers are tiny and they have small tolerances for errors and adjustments with custom splints. Making a splint for a mallet finger injury is probably the hardest type of finger splint for a therapist to make. Treatment recommendations vary, with some…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.