How many of us have practiced suture removal in occupational or physical therapy school?? NOT I!!

Often, hand surgeons will ask the therapist to remove sutures and sometimes the order will even say “remove sutures when ready”
SO NOW WHAT? How to remove continuous sutures? First, we can cover the basics of sutures!
There are two basic classifications for suture material, absorbable and non-absorbable. Absorbable sutures typically do not require manual removal, because the enzymes that live in the body’s tissue will digest them. Non-absorbable require a healthcare practitioner to remove them however sometimes they can be left in permanently for example sutures placed in tendons are typically never removed.
You may encounter patients with different types of sutures, or a different technique was utilized to place them.
The most common types of suture techniques you will see in the hand therapy setting is the interrupted suture techniques followed by the continuous sutures.
Interrupted Sutures:
After a stitch is made the material is cut and tied together. After this another stitch is placed and again cut and tied together, this step is typically repeated until the wound is closed. This technique usually takes a little longer than the continuous suture removal technique.
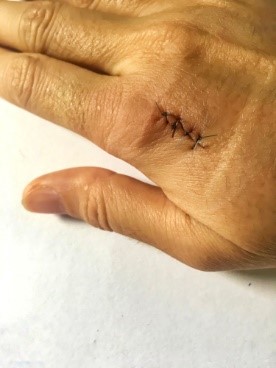
Continuous Sutures:
A series of stitches that use one single strand. This allows the tension to be distributed evenly. These are typically very easy to remove and can be placed quickly.
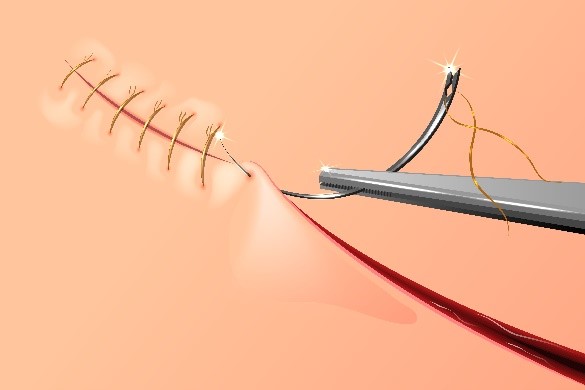
Buried Sutures: This is when the knot of the suture is found within the tissue. This suture is typically not removed.
Deep Sutures: These are placed in the layers of the skin and deeper tissues. These are either continuous or interrupted. Typically, these are used to close fascial layers.
Now for the Million Dollar Question? When should the sutures be removed?
This often will vary form patient to patient and may be dependent on how well the wound is healing. If the patient is diabetic and demonstrating poor wound healing or poor wound closure you may be inclined to leave the sutures in place a little longer compared the young kid whose incision is healing very well.
Guidelines for Suture Removal
Arms 7-10 days
Dorsal aspect of the Hand 10-14 days
Palms of Hand 14-21 days
When removing the sutures make sure you use a sterile suture removal kit. Pick up one end the suture and cut it, trying to stay as close to the skin as possible. After it is cut slowly pull the suture strand.
1 Comment
Leave a Comment
More To Read
How to Use Translation for Improving Fine Motor Skills after a Hand Injury:
I’m always looking for new therapy ideas. I want to keep my patients interested and engaged in therapy. I also want to keep things functional and task oriented. So much of what we do with our hands is about fine motor coordination and dexterity, and that is so hard to duplicate in a clinic setting.…
Scar Wars: Scar Management Techniques
We will briefly discuss Scar Management Options and Techniques
How to Improve HEP Adherence for Optimal Rehabilitation Outcomes
By Sophia Grimm A lack of adherence to home exercise programs in rehabilitation is a significant problem, with nonadherence estimates as high as 30-65% for general musculoskeletal conditions. This could have potentially detrimental effects on patients’ clinical rehabilitation outcomes as the success of certain medical interventions depends largely on patient adherence to advice and prescribed rehabilitation…
Therapeutic Interventions and Contraindications of Cupping
By Kaylen Kallander Cupping therapy is used to apply negative pressure to a localized area of muscular or neurological pain to relieve nerve pressure and increase blood flow to an affected area. This modality is commonly used for athletes, but is also a frequent treatment in physical therapy, occupational therapy, or hand therapy. While cupping…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.






Yourwebhoster.eu