Sensitivity and Specificity in Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) Tests in Hand Therapy
Filed under Treatments
By: Mikayla Murphy
Sensitivity and Specificity in Thoracic Outlet Syndrome (TOS) Tests in Hand Therapy
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) describes the compression of nerves, arteries, and veins as they pass through the thoracic outlet. Compression can occur at the interscalene triangle, the costoclavicular triangle, and the subcoracoid space (Physiopedia, n.d.). There are three types of TOS – neurogenic, venous, and arterial – each based on what structure is being compressed, with neurogenic TOS being by far the most common (Jones et al., 2019). Symptoms of thoracic outlet vary based on the type but can include paresthesia in the upper extremity, weakness, changes in color, and pain (National Institute for Neurological Disorders and Stroke, n.d.). TOS can have multiple causes, including differences in anatomy, trauma, and repetitive movement (Jones et al., 2019).
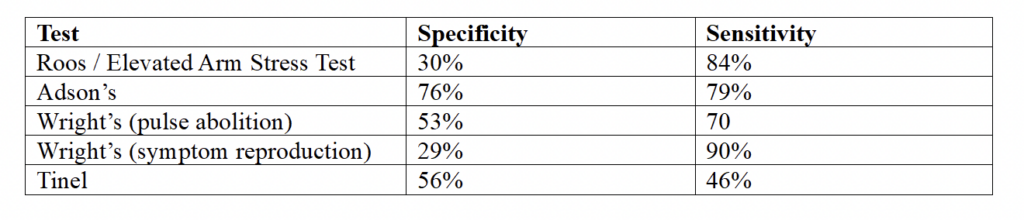
Special tests can help a therapist determine if a patient has possible thoracic outlet syndrome and can inform care. When looking at special tests, it is important to consider their specificity and sensitivity. Specificity refers to a test’s ability to correctly identify someone without the disease, while sensitivity refers to a test’s ability to correctly identify someone with the disease (New York State Department of Health, 1999). Gillard et al. (2001) lists the following sensitivity and specificities for several common TOS tests:
Test Specificity Sensitivity
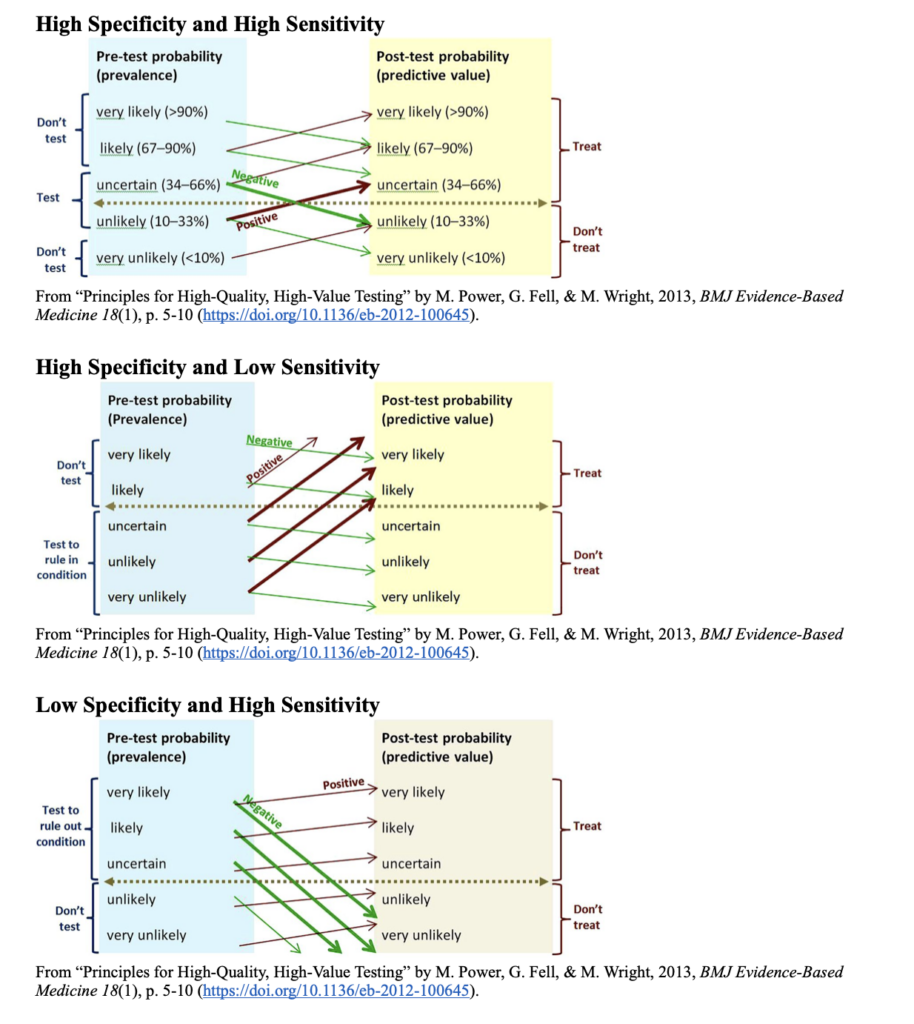
Power et al. (2013) offer three diagrams to assist with interpreting results of a test based on their pre-test probability, specificity, and sensitivity. Pre-test probability is a therapist’s estimate on whether or not a patient may have a condition based on the therapist’s clinical reasoning (The NNT Group, n.d.). In each of the diagrams, thicker lines mean the result is more likely to change how the condition is managed. Power et al. (2013) also suggest some pre-test probabilities should not be tested if testing will not change the way the condition is managed; however, their results are geared towards doctors whose testing may be more costly or invasive than simple provocative tests. Based on the pre-test probability, a therapist can use these diagrams to estimate the likelihood of a patient having a condition.
For example, Roos test has a low specificity and high sensitivity. If a therapist is uncertain whether a client has TOS, and the client has a positive result, it is still uncertain whether the client has TOS. However, if the client has a negative result, it is very unlikely the client has TOS. Using several tests in combination will provide more accurate results, such as Adson’s with Roos or Wright’s (Gillard et al., 2001; Power et al., 2013).
High Specificity and High Sensitivity
From “Principles for High-Quality, High-Value Testing” by M. Power, G. Fell, & M. Wright, 2013, BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine 18(1), p. 5-10 (https://doi.org/10.1136/eb-2012-100645).
High Specificity and Low Sensitivity
From “Principles for High-Quality, High-Value Testing” by M. Power, G. Fell, & M. Wright, 2013, BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine 18(1), p. 5-10 (https://doi.org/10.1136/eb-2012-100645).
Low Specificity and High Sensitivity
From “Principles for High-Quality, High-Value Testing” by M. Power, G. Fell, & M. Wright, 2013, BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine 18(1), p. 5-10 (https://doi.org/10.1136/eb-2012-100645).
References
Gillard, J., Pérez-Cousin, M., Hachulla, É., Remy, J., Hurtevent, J.F., Vinckier, L., Thévenon, A., & Duquesnoy, B. (2001). Diagnosing thoracic outlet syndrome: contribution of provocative tests, ultrasonography, electrophysiology, and helical computed tomography in 48 patients. Joint Bone Spine, 68(5), 416-424. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1297-319X(01)00298-6
Jones, M. R., Prabhakar, A., Viswanath, O., Urits, I., Green, J. B., Kendrick, J. B., Brunk, A. J., Eng, M. R., Orhurhu, V., Cornett, E. M., & Kaye, A. D. (2019). Thoracic outlet syndrome: A
comprehensive review of pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Pain and Therapy, 8(1), 5–18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40122-019-0124-2
National Institute for Neurological Disorders and Stroke. (n.d.). Thoracic outlet syndrome. https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/thoracic-outlet-syndrome
New York State Department of Health. (1999). Disease screening – Statistics teaching tools. https://www.health.ny.gov/diseases/chronic/discreen.htm
Power, M., Fell, G., & Wright, M. (2013). Principles for high-quality, high-value testing. BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine 18(1), 5-10. https://doi.org/10.1136/eb-2012-100645
Physiopedia. (n.d.). Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS). https://www.physio-pedia.com/Thoracic_Outlet_Syndrome_(TOS)
The NNT Group. (n.d.) Diagnostics and likelihood ratios, explained. theNNT. https://thennt.com/diagnostics-and-likelihood-ratios-explained/
More To Read
How to Improve HEP Adherence for Optimal Rehabilitation Outcomes
By Sophia Grimm A lack of adherence to home exercise programs in rehabilitation is a significant problem, with nonadherence estimates as high as 30-65% for general musculoskeletal conditions. This could have potentially detrimental effects on patients’ clinical rehabilitation outcomes as the success of certain medical interventions depends largely on patient adherence to advice and prescribed rehabilitation…
5+ Common Mallet Finger Splints
Finger orthoses can be tough, and the mallet finger orthosis is no exception. The protocol for 15 degrees of DIP extension with mallet fingers is tricky to manage while making a splint. Small splints on little fingers are also tricky to get sized just right and with strapping in the right places. Ask any experienced…
THUMB ABDUCTION IN PATIENTS WITH CMC ARTHRITIS? HOW DO YOU MEASURE?
Article Review THUMB ABDUCTION IN PATIENTS WITH CMC ARTHRITIS? HOW DO YOU MEASURE? Corey McGee PhD, OTR/L, CHT , Virginia O’Brien OTD, OTR/L, CHT , Jennifer Skye MS, OTR/L, CHT , Katherine Wall MOT, OTR/L , Thumb Carpometacarpal Palmar and CMC Radial Abduction in Adults with Thumb Carpometacarpal Joint Pain: Inter-rater Reliability and Precision of…
How to Strengthen the Intrinsics with Puttycise Tools:
How to strengthen the intrinsic with Puttycise tools
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.