Ilter, L., Dilek, B., Batmaz, I., Ulu, M.A., Sariyildiz, M.A., Nas, K., & Cevik, R. (2015). Efficacy of pulsed and continuous therapeutic ultrasound in myofascial pain syndrome: A randomized controlled study. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, 94(7), 547-554. https://doi.org/10.1097/PHM.0000000000000210
Review by: Megan Prather
The Skinny- Ultrasound hand therapy – ultrasound has been determined as an effective method for use in treatment of myofascial pain syndrome (MPS). Both continuous and pulsed ultrasound have been used with MPS but the two had not previously been compared in a controlled trial. Researchers in this study set out to compare the effects of continuous ultrasound, pulsed ultrasound, and a placebo in MPS to determine best practices for treatment and the use of ultrasound for hand therapy.
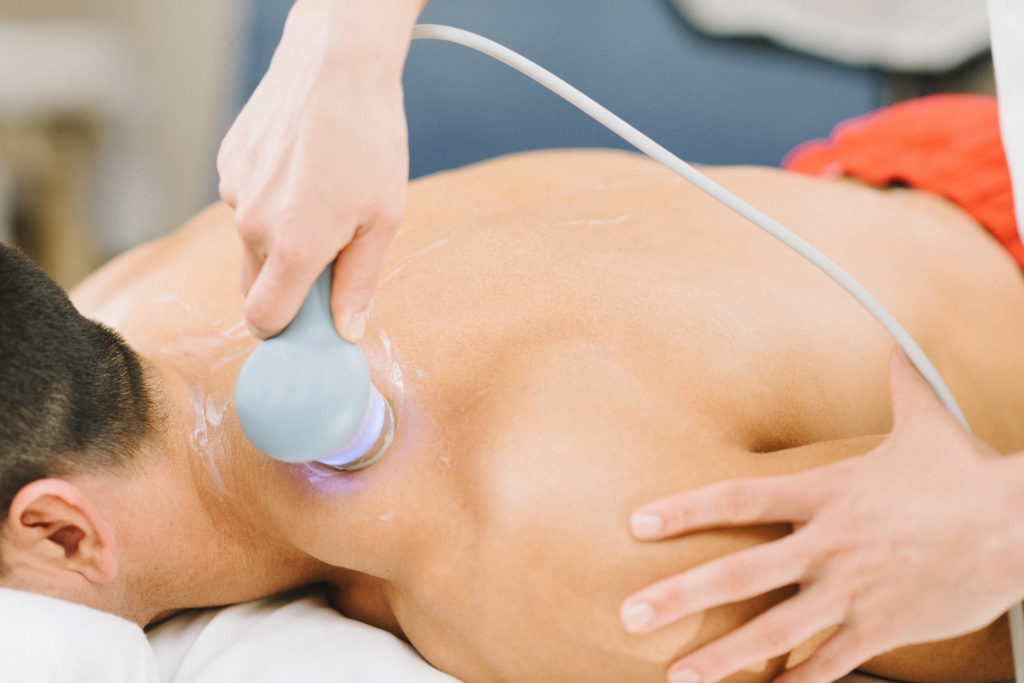
In The Weeds- This study was a placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized controlled trial looking at ultrasound in patients with a diagnosis of MPS with cervicoscapular myofascial pain based on Travell and Simons criteria. Researchers recruited 60 study participants between the ages of 18 and 60 with an active upper trapezius trigger point and pain for at least 1 month who consented to participate. Study participants were divided into one of three groups receiving continuous ultrasound (3 MHz, 1 W/cm2), pulsed ultrasound (3 MHz, 1 W/cm2), or sham ultrasound (machine not on) for 5 minutes 5 days a week for 2 weeks over the painful trigger point. All participants were also instructed in stretching and ROM exercises and received 10 minutes of hot pack treatment. The primary outcome measures for this study were pain at rest and pain with movement. Secondary outcome measures of muscle spasm palpation, psychological state, quality of life, function, and patient satisfaction were also used.
Bringing it Home- Researchers found statistically significant improvement in pain, degree of muscle spasm, neck function, and the Beck Depression Scale quality of life pain subparameter after therapy in all three groups at 6 weeks and 12 weeks after treatment (P<0.05). No significant improvement was found for patient satisfaction or the Beck Depression Scale quality of life social isolation subparameter in any of the groups. Further, in the placebo group no significant improvement was found for the Beck Depression Scale. The group receiving continuous ultrasound showed a statistically significant greater improvement in pain at rest than in either other group (P<0.05). Overall, this study found that continuous ultrasound is better for reducing pain at rest than pulsed ultrasound or placebo in patients with myofascial pain syndrome.

This study was well done and included randomization and blinding of participants into the three groups for clinical comparison. Outcome measures covered a wide range of patient factors and relevant conclusions can be drawn from the data. The smaller participant number and potentially inconsistent exercises done by participants may limit the results. However, these results can positively impact practice and methods used to treat patient pain.
More To Read
What is Chronic Exertional Compartment Syndrome? Overview and Hand Therapy Treatment Ideas
Compartment syndrome is a condition characterized by increased pressure within a compartment of the body, leading to pain, swelling, and reduced tissue perfusion (Barkay et al., 2021; Buerba et al., 2019). It can be either acute or chronic (Barkay et al., 2021). Chronic exertional compartment syndrome (CECS) is a rare type, most commonly observed in…
Common Median Nerve Injuries
Common Median Nerve Injuries By: Madison Mott Did you know!? Aside from the most common upper extremity nerve compression, carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), there are several additional median nerve injuries. Pronator SyndromeCompression of the median nerve between the two heads of pronator teres. Result of recurrent, forceful gripping, forearm rotation, or elbow flexion. Signs include…
Effectiveness of Conservative Therapy and Splinting for 1st CMC OA
Tsehaie, J., Sprekraijse, K., Wouters, R., Slijper, H., Feitz, R., Hovious, S., & Selles, R. (2018). Outcome of a Hand Orthosis and Hand Therapy for Carpometacarpal Osteoarthritis in Daily Practice: A Prospective Cohort Study. American Society for Surgery of the Hand, 1-11. The skinny: Non-surgical approaches (hand therapy & orthotics) are typically the go-to for…
Dart-throwing Angle in Hand Therapy for Scapholunate (SL) Ligament Injuries.
Does Object Height Affect the Dart Throwing Motion Angle During Seated Activities of Daily Living? Cohen, Y., Portnoy, S., Levanon, Y., Friedman, J. (2020). Does object height affect the dart throwers motion angle during seated activities of daily living. Journal of Motor Behavior, (52) 4. Article Review By: Rita Steffes The Skinny: Dart Throwers Motion…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.