Sensory interventions on motor function, activities of daily living, and spasticity of the upper limb in people with stroke: A randomized clinical trial.
Filed under Treatments, Uncategorized
Maryam, D., Parvin, R., Hossein, B., Jalili, M. & Hosein, T. (2020). Sensory interventions on motor function, activities of daily living, and spasticity of the upper limb in people with stroke: A randomised clinical trial. Journal of Hand Therapy, Jun 18;S0894-1130(20)30076-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jht.2020.03.028. Online ahead of print.
The Skinny:
- Stroke is the second cause of death, leading to sensory impairments and motor problems.
- The purpose of this study was to determine if proprioceptive and exteroceptive stimulation would improve outcomes for spasticity and activities of daily living (sensory stimulation activities for stroke patients) compared to traditional therapy in chronic stroke patients (hand therapy for stroke patients).
- Participants were randomly assigned to two groups
Intervention (Group 1):
- Exteroceptive exercises Included: Facilitatory or inhibitory techniques, fast brushing, stretch pressure, icing,
- Proprioceptive Stimulation: Weight-bearing, heavy joint compression, and stretch pressure
- Traditional therapy
Control (Group 2) :
- Traditional therapy
In the Weeds:
- A single-blinded clinical trial comparing the effect of exteroceptive and proprioceptive stimulations in people who have suffered from a stroke. Sixty patients who were are least 6 months post-stroke were divided into two groups intervention (group one) and control (group 2).
- Patients attend therapy 4 days per week for 45-minute sessions for 6 weeks.
- Outcome measures included the Modified Ashworth Scale, Fugl-Meyer assessment of Motor Recovery after Stroke, and Barthel Index. These were completed pre and post-study.
Bringing It Home:
- Patients in the intervention group showed improvements in motor function, activities of daily living, and improvement in spasticity compared to the control group. Adding proprioception and exteroceptive stimulation can improve motor function and ADLs even in chronic stroke patients. These can be added to your traditional therapy regimes.
Rating:
- 4/5
- Limitations: The article did not give a definition of traditional therapy. The sample size is fairly small in number. Long-term follow-up is unknown which would be helpful in determining if the interventions improved long terns outcomes.
More To Read
Hand Contractures from Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita
What is Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita?Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita (AMC) is a rare congenital condition that is characterized byan individual being born with multiple joint contractures, involving two or more areas of the body(Khurana et al., 2024). AMC is a general term that describes over 400 different medicalconditions that involve joint contractures, instead of just describing one…
Article Review: Best Edema Management Techniques in Hand Therapy
Miller, L. K., Jerosch-Herold, C., & Shepstone, L. (2017). Effectiveness of edema management techniques for subacute hand edema: a systematic review. Journal of Hand Therapy, 30(4), 432-446. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2017.05.011 By: Ammie Ingwaldson The Skinny Edema is something therapists deal with on a daily basis and often is apart of most treatments. Managing edema can be a challenge…
Dog Bites to the Hand: What Every Hand Therapist Should Know
What to Expect with a Dog Bite to the Hand for Hand Therapists By: Kathryn Harada Prevalence and Severity:One reason people seek hand therapy is for rehabilitation after an animal bites. In the US alone, 1% of emergency department visits are due to animal bites each year, resulting in 2 to 5 million animal bites…
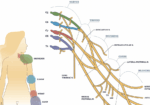
Comparison of Erb’s Palsy and Klumpke’s Palsy: Symptoms, Presentation, and Treatment Options
What is the brachial plexus? The brachial plexus is a group of nerves originating from the cervical and thoracic nerve roots (from C5 to T1). The brachial plexus forms 5 peripheral nerves of the upper extremity, consisting of the musculocutaneous, median, radial, ulnar, and axillary nerves. This group of nerves supplies motor and sensory innervation…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.