Mechanism of Interneural Edema in Carpal and Cubital Tunnel
Filed under Diagnoses
Mechanism of Interneural Edema
Over the last few weeks I have been learning about ultrasonic imaging and carpal tunnel syndrome. When reviewing carpal tunnel syndrome, I learned that intraneural edema is a common sign of compression injuries such as carpal tunnel and cubital tunnel. There are numerous causes of carpal tunnel syndrome, and every scenario ends with the reduction of available space within the carpal tunnel and the inevitable compression on the median nerve (carpal tunnel edema). What I did not know was that chronic compression on the nerve can disrupt and open the blood nerve barrier around the perineurial layer. This allows for blood to flow freely into the nerve causing swelling or interneural edema. Since the nervous system lacks lymphatic drainage in the endoneural space, swelling inevitably increases pressure and disrupts the flow of blood to the nerve resulting in a metabolic conduction block (Cooper, 2014). One animal study found that an increase in pressure as little as 30 grams of force (about the weight of an average lightbulb) over the course of 1 hour was enough to disrupt the blood nerve barrier around the median nerve and cause diffusion (Kobayashi et al., 2005).
Normal Nerve No Diffusion
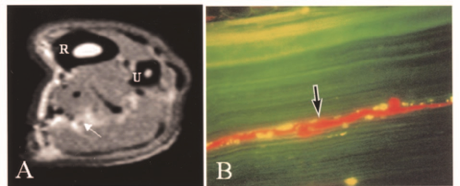
Nerve 30 Grams of Force with Diffusion
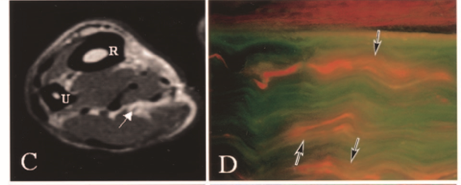
Nerve 90 Grams of Force Severe Diffusion
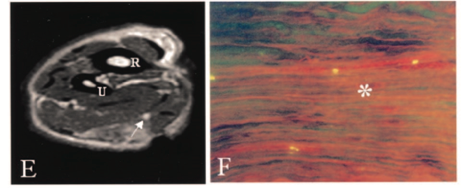
Chronic compression and decreased blood flow lead to impairment in nerve conduction. One source states that functional deficits are seen sequentially in the following order: motor, proprioception, touch, temperature, pain, and then sympathetic function (Cooper, 2014). Therapeutic activities such as nerve gliding exercises are hypothesized to increase nerve mobility and release the nerve from the sight of compression. Additionally, surgical decompression can help to alleviate symptoms, but the timeline for neural repair is largely based on the severity of nerve damage that has occurred. As neural edema subsides and blood flow to the nerve improves, the nerve begins to repair itself as long as the endoneurial tubes are intact. Patients are expected to regain sensation in the reverse order that they were initially lost (pain, temperature, proprioception).
Cooper, C. (20014). Fundamentals of hand therapy: Clinical reasoning and treatment guidelines for common diagnoses of the upper extremity [Second Edition]. Elsevier Mosby
Kobayashi, S., Meir, A., Baba, H., Uchida, K., and Hayakawa, K. (2005). Imaging of intraneural edema by using gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging: Experimental compression injury
2 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
How to Improve Fine Motor Translation Skills
By: Josh MacDonald The Basics – I lay a pile of small objects on the table and an open container for the client to put them into. What object I use depends on the client’s level. We’ll get to that later. Then, they use a 2-point pincer grasp to pick up one and shift it…
Splinting vs Stretching after a Stroke to treat Hand Spasticity
Splinting versus Stretching to improve hand function and reduce hand spasticity after stroke Reference: Ahmad Khan, M., & Singh, P. (2018, February). Effect of Hand Splinting versus Stretching Exercises for Reducing Spasticity and Improving Hand Function in Poststroke Hemiplegia: AComparative Interventional Study. Retrieved December 4, 2022, fromhttps://www.ijotonweb.org/article.asp?issn=0445 -7706;year=2018;volume=50;issue=4;spage=125;epage=129;aulast=Khan The Skinny: A comparative study by Khan…
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM hand)
By: Amalia Garcia Introduction After completing three weeks of my Level II hand therapy rotation, I have seen a wide variety of common upper extremity injuries such as carpal tunnel syndrome, distal radius fractures, mallet finger, flexor tendon lacerations, arthritis, and more. One condition that stood out to me was one that I hadn’t heard…
Flexor tendon rehabilitation in the 21st century: A systematic review
Neiduski, R. L. & Powell, R. K. (2019). Flexor tendon rehabilitation in the 21st century: A systematic review. Journal of Hand Therapy, 32, 165-174. The Skinny The objective of the study was to determine if there was evidence to support 1 type of exercise regimen. Exercise regimens reviewed include place and holds, early passive or…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.




The inter neural edema is fascinating.
Yes is is very interesting! I agree