Lateral Elbow Pain with Graded Exercise
Chronic tennis elbow with a supervised graded exercise protocol
Özdinçler, A. R., Baktır, Z. S., Mutlu, E. K., & Koçyiğit, A. (2023). Chronic lateral elbow tendinopathy with a supervised graded exercise protocol. Journal of Hand Therapy, 36(4), 913–922. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2022.11.005
The Skinny: This study looked at the effectiveness of an 8-week exercise program (4 weeks of a basic program and 4 weeks of an advanced program) for participants diagnosed with lateral epicondylalgia also known as tennis elbow without receiving treatment for at least one year. Pain was measured by the Visual Analog Scale, Pain Pressure Threshold, grip strength measurements using a Dynamometer, and the level of function determined with the Patient Rated Tennis Elbow Evaluation Questionnaire. All measurements were performed at baseline, after the 4-week basic program, and after the additional 4-week advanced exercise program.
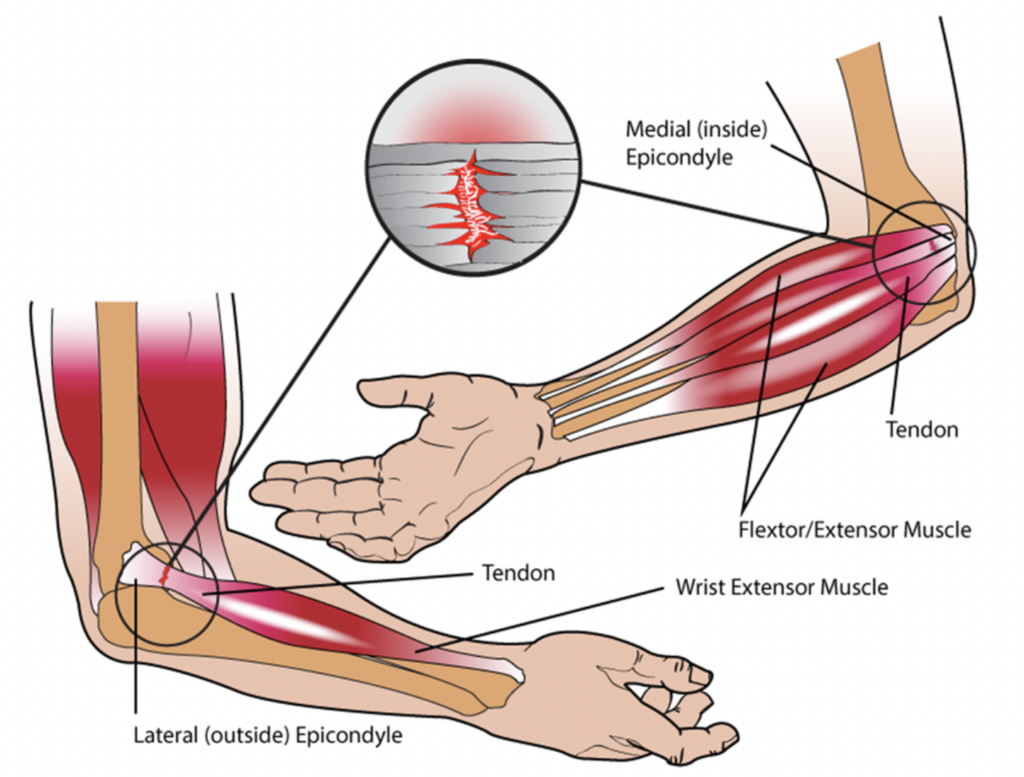
In the Weeds: This study included 30 participants between the ages of 30-50 and all had a previous lateral epicondylalgia diagnosis. Participants were divided into 7 different phases depending on their ROM, stiffness, pain, and level of function. All participants received a basic exercise program for four weeks, three times per week. All exercises utilized an elastic finger band, 1 kg weight, hand exercise ball, or a towel. Those who completed the basic exercise program then began an advanced exercise program where stretching exercises, isotonic strengthening, concentric movements, and eccentric movements were included. Exercises included in the two programs were: AROM wrist extension, AROM wrist circumduction, AROM wrist radial and ulnar deviation, AROM forearm pronation, AROM forearm supination, isometric wrist extension, PROM wrist extension, eccentric and concentric wrist extension and flexion, finger extension with rubber bands, gripping with a ball, and towel squeezing/twisting.
Bringing it Home: Both in the basic exercise group and in the advanced exercise group, participants saw an improvement in pain and function. The basic exercise program was shown to ease the symptoms, while the advanced exercise program further benefited function and grip strength. It was proven that although both exercise programs were beneficial, the advanced group contributed to better results, especially in terms of grip strength, pain, and function. In addition, the study found that adding isometric exercises to the program early on was more beneficial than adding it at the halfway point.
Rating: 4/5
This study had several limitations, including a small sample size of 30 participants aged 30-50; no long-term follow-up to determine the chronic benefits of exercise for tennis elbow patients; and the main focus being wrist exercises and not including scapular exercises. Future studies could look at the long-term implications, adding phase of scapular exercises, and having a larger sample size for reliability.
More To Read
Rapid Review: Is Finger Splinting Necessary after Flexor Tendon Repair?
Outcome of Flexor Tendon Repair Using Eight-Strand Core Stitch Without Postoperative Finger Splinting Reference: El-Gammal, T. A., Kotb, M. M., Ragheb, Y. F., El-Gammal, Y. T., & Anwar, M. M. (2024). Outcome of Flexor Tendon Repair Using Eight-Strand Core Stitch Without Postoperative Finger Splinting. HAND. https://doi.org/10.1177/15589447231220686 The Skinny: The purpose of this study was to…
Which orthosis design is better for zone 5-6 extensor tendon injuries, a relative motion orthosis compared to a dynamic extension orthosis?
M. Buhler, ˝ D. Gwynne-Jones, M. Chin et al., (2023) Are the outcomes of relative motion extension orthoses noninferior and cost-effective compared with dynamic extension orthoses for management of zones V-VI finger extensor tendon repairs: A randomizedcontrolledtrialJournalofHandTherapy. The Skinny: The aim of this study was to compare the data for two different types of orthoses…
“Do joint mobilizations assist in the recovery of lateral elbow tendinopathy? A systematic review and meta-analysis”
By Sophia Grimm Lucado, A. M., Dale, R. B., Vincent, J., & Day, J. M. (2019). Do joint mobilizations assist in the recovery of lateral elbow tendinopathy? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of hand therapy : official journal of the American Society of Hand Therapists, 32(2), 262–276.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2018.01.010 The Skinny: The purpose of this study was…
INTEROSSEOUS MUSCLE TIGHTNESS TESTING
May 2012 No. 19 INTEROSSEOUS MUSCLE TIGHTNESS TESTING Judy Colditz, OT/L, CHT, FAOTA INTEROSSEOUS MUSCLE TIGHTNESS TESTING – ARE YOU DOING IT CORRECTLY? The common term “Intrinsic Tightness Testing” is a misnomer as it describes a maneuver specifically designed to test tightness of the interosseous muscles. The interosseous muscles are small, short-fibered muscles contained within…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.