By: Ammie Ingwaldson
Level 2 Fieldwork at a hand therapy clinic is a fast paced and continuous learning experience. The perfect example of this occurred last week while observing a therapist provide a client with their home CMC arthritis program. The therapist was educating the client on how to oppose their thumb to their small finger. While we watched them practice, she stated, “you have the Linburg sign!” She quickly turned to me and had me oppose my thumb to the base of my small finger, then confirmed that I had it as well. I began to become slightly concerned. We had not reviewed this sign or condition in school. I began to wonder if it was treatable and if it would affect me. My worries were put at bay when she then showed that she had it as well and provided an explanation of what it entailed.
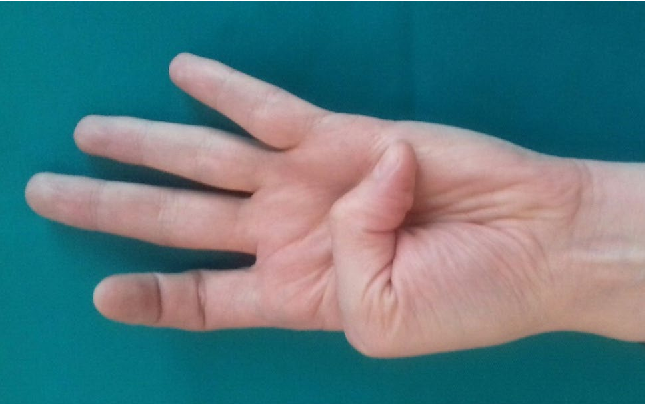
Linburg Comstock syndrome is an anatomical anomaly connecting the tendons of flexor digitorum profundus (FDP) of the index finger and flexor policis longus (FPL) (Puroshothaman & Powers, 2008). This connection of tendons leads to involuntary flexion of the index finger at the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joint with flexion of the interphalangeal (IP) joint of the thumb. The incidence of this anomaly is 37%, with higher distribution of unilateral sign than bilateral.
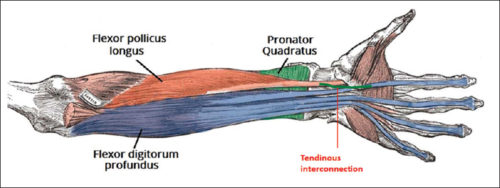
In most cases Linburg-Comstock syndrome is asymptomatic, but it can present as pain in the distal forearm, wrist, or hand. Median nerve symptoms, similar to carpal tunnel, can also be present due to tendon inflammation, presence of additional tendons, or synovitis with in the carpal tunnel (Puroshothaman & Powers, 2008). Individuals with repetitive thumb and finger movements, such as musicians, are more susceptible to pain or carpal tunnel like symptoms. Surgical release of the connection of FPL and FDP can be performed to relieve symptoms (Old, Rajaratnam & Allen, 2010).
References
Old, O., Rajaratnam, V., & Allen, G. (2010). Traumatic correction of Linburg-Comstock anomaly: a case report. Annals of the Royal College of Surgeons of England, 92(4), W1–W3. doi:10.1308/147870810X12659688852031
Puroshothaman, P., & Powers, D. (2008) A simple diagnostic test for symptomatic Linburg-Comstock anomaly (Linburg-Comstock test). The Internet Journal of Hand Surgery, 2(2), 1-3.
3 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Hand Therapy Article Review: The Radial Synergy Test, An Aid to Diagnose de Quervain’s Tenosynovitis
Chihua, L., Langford, P.N., Sullivan, G.E., Langford, M.A., Hogan, C.J., & Ruland, R.T. (2021) The radial synergy test: an aid to diagnose de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. HAND. epub ahead of print;1-6. doi: 10.1177/15589447211057297 Rapid Review By: Case Peters The Skinny: de Quervain’s tenosynovitis is a common pathology that involves swelling and thickening of the tendon sheaths…
Should we still be immobilizing the thumb in scaphoid fractures, or is a wrist-only cast just as effective?
Article:Harper, K. J., Rees, Y., Tan, N. X., Li, H., Fonseca, E. A., Quach, P. G., Lee, G. S., Brayshaw, J.R., & McGarry, S. (2025). Determining the success of clinical outcomes for thumbimmobilization compared to no thumb immobilization in adult non-displaced, non-surgically managed scaphoid fractures: A systematic review. Hong Kong journal ofoccupational therapy. The Skinny:This study…
Intrinsic Hand Strengthening with Puttycise Tools
We are always looking for ways of the intrinsic hand strengthening. It is easy to overlook the importance of these small but mighty muscles. They are essential to performing functional grasps patterns. They can become weak in a short period of time due to their small size. So, How does intrinsic strengthening work?! The Basics…
A Better De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis Test
J. F. Goubau, L. Goubau, A. Van Tongel, P. Van Hoonacker, D. Kerckhove, B. Berghs (2013).The wrist hyperflexion and abduction of the thumb (WHAT) test: a more specific and sensitive test to diagnose de Quervain tenosynovitis than the Eichhoff’s Test. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2014 Mar; 39(3): 286–292. Published online 2013 Jan 22. doi:…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.



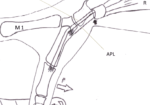

I love that great fun fact with a quick explanation, great visual representation of the UE possible problems, and treatment options that are available.
Thanks.
I have this issue but not just one or two fingers is every finger in both hands. if i bend thumb even my little finger goes with it. Just wondering how rare it is for that to happen?
Thanks for sharing! Funny enough, I also found out I had this anomaly during my level 1 OT fieldwork rotation at a hand therapy clinic! Actually, I realized I had this involuntary flexion of the index finger when I was young, in girl scouts, and I was unable to do the girl scout hand sign without my pointer finger bending. I forgot about it until my fieldwork rotation, where I found out the name of what it was and why it occurs! So, I guess another clinical test option could be to have the client try to do the girl scout hand sign 😂