Pillar Pain After Carpal Tunnel Release Surgery
Carpal tunnel release (CTR) surgery is a common procedure, with the majority of patients experiencing satisfaction with its outcomes. However, for some individuals, a temporary complication known as “pillar pain” may arise, affecting approximately 13% of those undergoing CTR.
Pillar pain manifests in the thenar eminence and hypothenar eminence due to their proximity to the transverse carpal ligament. It is characterized by wrist pain that causes tenderness and discomfort upon touch, distinct from the incision pain typical of surgical recovery, which usually subsides within a few days to weeks.
Although pillar pain symptoms typically resolve within three months, they can persist longer, even up to 9-12 months. While the exact cause of pillar pain remains elusive, several theories have been proposed, including tender scar tissue, muscle alignment alterations, joint inflammation, injury to small nerve fiber branches, and nerve irritation. Notably, a neurogenic component is suggested, indicating that nerve tissue damage from carpal tunnel surgery may play a significant role.
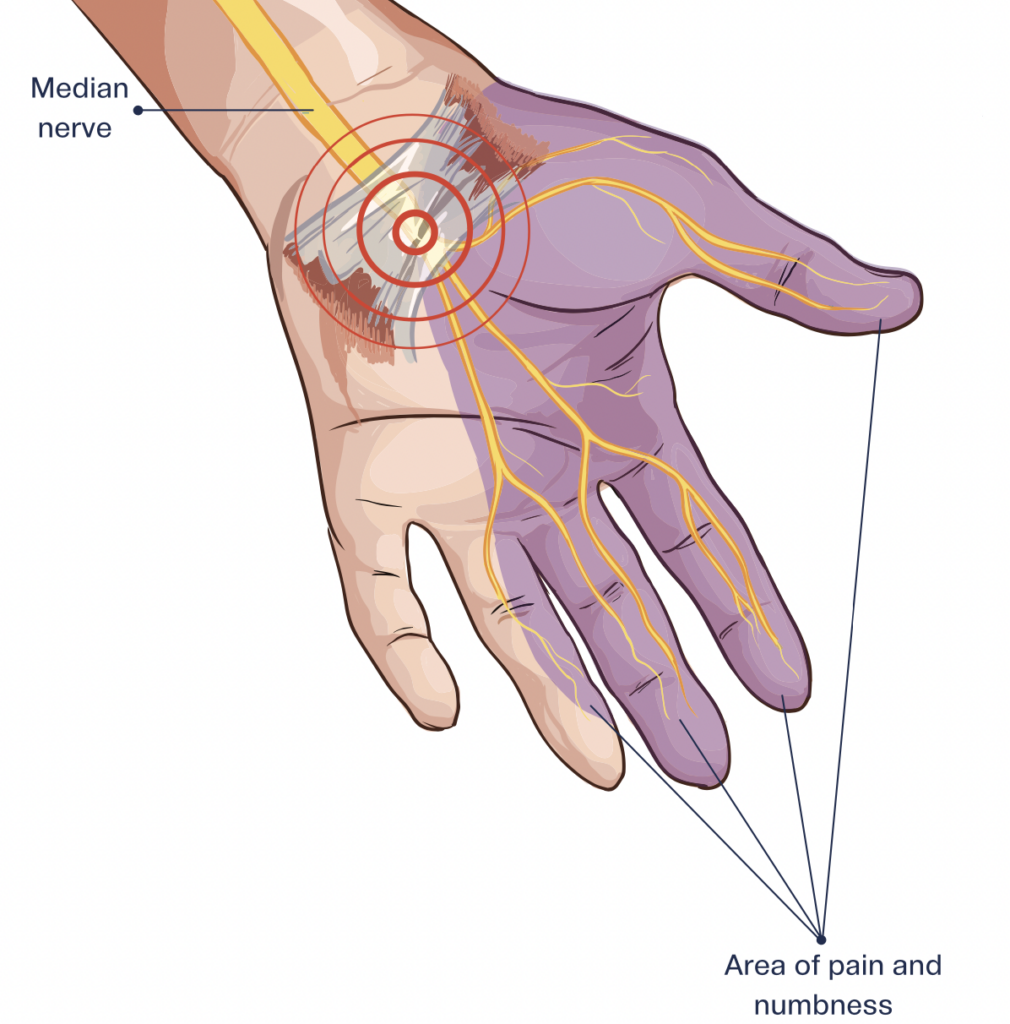
A theory posits that avoiding the “critical pillar rectangle” during surgery, which encompasses specific anatomical landmarks, could substantially reduce the likelihood of pillar pain occurrence.
Hand therapists offer various interventions for managing pillar pain, including:
- Stretching exercises such as the extrinsic stretching of wrist/hand flexor and tendon gliding exercises.
- Soft tissue mobilization targeted at the thenar and hypothenar eminences, gradually increasing pressure in sensitive areas.
- Desensitization techniques involve the use of different textures like cotton, wool, foam, soft Velcro, and others to rub over sensitive areas. Immersion of the affected area in substances like cotton balls, foam, rice, or beans can aid in desensitization.
- Median nerve glides to facilitate nerve flossing and restore median nerve mobility.
- Scar softening treatments such as paper tape or silicone gel pad.
By employing these strategies, individuals experiencing pillar pain can effectively manage their symptoms and facilitate recovery following carpal tunnel surgery.
Kumar, A., & Lawson-Smith, M. (2024). Pillar pain after minimally invasive and standard open carpal tunnel release: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Hand Surgery Global Online. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsg.2023.12.003
Ludlow, K., Merla, L., Cox, J., & Hurst, L. (1997a). Pillar pain as a postoperative complication of carpal tunnel release. Journal of Hand Therapy, 10(4), 277–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0894-1130(97)80042-7 .
2 Comments
Leave a Comment
More To Read
Orthotic Options for Hand Burns
By: Sophia Grimm Hand burns can be very challenging to treat, and successful rehabilitation begins early after acute injury. Following a burn injury, scar contractures are the primary reason for the deformity of the hand. Therefore, proper orthotic intervention is key to preventing joint and ligament contractures (Kelly, Berenz & Williams, 2019). Splinting goals following…
Top 6 treatments for Pinky Fractures
Clients who have experienced a fracture of the finger or hand often find it difficult to participate in meaningful occupations. Everyday tasks from grasping items, cutting food, taking lids off containers, turning keys, and many others can be very painful. Pinky fracture is particularly challenging and painful. This is typical because the largest contributor to…
Arthrodesis vs Arthroplasty in Thumb CMC OA
Piacenza A, Vittonetto D, Rossello MI, Testa M. Arthrodesis Versus Arthroplasty in Thumb Carpometacarpal Osteoarthritis: Impact on Maximal Voluntary Force, Endurance, and Accuracy of Pinch. J Hand Surg Am. 2021 May 24:S0363-5023(21)00199-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jhsa.2021.03.023. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34045112. The Skinny: This was a retrospective study based on a convenience sample of individuals who…
Top 5 DIP Flexion Exercises
By: Tori Rhodes Lately, we’ve had a handful of patients roll through our clinic with pretty significant limitations to DIP flexion. So, we’ve collected a selection of go-to exercises for these individuals. We’ve included a few of those here. From cat bites and fracture sites to mallet fingers and skin grafts, many individuals who are…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.






Thank you for all the info
Great information, thanks! 🙏🏻