Mirror therapy after a peripheral nerve repair in hand therapy
Filed under Reviews
Rapid Review
Paula, M. H., Barbosa, R. I., Marcolino, A. M., Elui, V. M., Rosén, B., & Fonseca, M. C. (2016). Early sensory re-education of the hand after a peripheral nerve repair based on mirror therapy: a randomized controlled trial. Brazilian journal of physical therapy, 20(1), 58–65. https://doi.org/10.1590/bjpt-rbf.2014.0130

The Skinny:
Therapy is often provided following an upper extremity peripheral nerve injury. As part of therapy, sensory and motor re-education programs are often utilized to preserve the cortical representation. This article compared traditional sensory re-education programs to mirror therapy combined with conventional rehabilitation.
In the traditional sensory re-education intervention group, therapy intervention did not occur until protective sensation had returned. The early re-education mirror therapy group began in the first post-operative visit. The authors hypothesized the early intervention group with mirror therapy following a nerve repair would yield better results. The study’s objective was to compare early re-education programs with mirror therapy compared to late sensory re-education with no mirror therapy for up to 6 months after a median and ulnar nerve repair in the upper extremity.
In the Weeds:
Early intervention group (mirror therapy group)
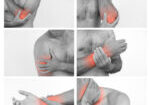
The intervention began at the first post-operative visit. A mirror was used and placed in front of the table to reflect the image as if it were the injured hand. While using the mirror and the uninjured hand, several textures and shapes were used, along with manipulating small objectives. Active range of motion exercises was performed for 30 minutes a day, three times a week, to give the brain the visual illusion of the injured hand. Once the cast was removed, this was performed with both hands. Mirror therapy was conducted as part of a home program for 30 minutes a day, every day.
Late intervention group (control group)
The control group performed classic sensory reduction three months after nerve repair and after protective sensation returned. This intervention was conducted the same as it was for the early intervention group without mirror therapy.
Both groups received an education booklet titled “Sensory re-education” after nerve repair by Birgitta Rosén. This guide provides information on stimulating hand function following a nerve repair and provided other education on hand injuries and trauma.
Outcome measures included the Disability of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (DASH) and the Rosen Score. The Rosen score is a valuable tool that combines grip strength, manual muscle testing, Semmes-Weinstein Monofilament testing, Shape-texture identification test, the Weber DiskCriminator test, and finger dexterity text. It also used a specific scale to assess hyperesthesia and cold intolerance. Therefore only 20 people completed the study.
Bringing it Home:
Thirty-two patients were eligible and agreed to the study, and sixteen were in each group. However, 12 dropped out of the study, and only 20 people completed the study.
In combination with traditional treatment, Mirror therapy was not more effective than conventional late therapy in terms of sensory education based on the DASH and Rosen Score.
Rating: 3/5. There were several limitations to this study and a very high dropout rate. Other restrictions included the study only took place for six months, and typical nerve regeneration takes several years, especially with discriminative touch. Caution should be utilized in the study’s generalizability due to the study’s significant limitations.
More To Read
What is the incidence of musculoskeletal complaints in the elbow, shoulder, and neck after hand and forearm injuries?
Winiarski, L. M., Livoni, J. D., Madsen, P. V., Rathleff, M. S., & Larsen, P. (2021). Concurrent musculoskeletal complaints in elbows, shoulders, and necks after common hand and forearm injuries or conditions: A cross-sectional study among 600 patients. Journal of hand therapy: official journal of the American Society of Hand Therapists, 34(4), 543–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2020.05.002 The Skinny: The…
Factors that influence orthosis adherence in patients with acute traumatic tendon injuries to the hand
Savaş, S., & Aydoğan, Ç. (2020). Factors affecting orthosis adherence after acute traumatic hand tendon repairs: A prospective cohort study. Journal of Hand Therapy, S0894113020301848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2020.10.005 World Health Organization. (2003). Adherence to long-term therapies: evidence for action. World Health Organization. The Skinny Adherence to orthosis wear is vital for protecting healing tendons after a traumatic tendon…
Extensor Tendon Repair Protocol (zone 4-7): Immediate Controlled Active Motion (ICAM)
Howell, J.W., Merritt, W. H., & Robinson, S. J. (2005). Immediate Controlled Active Motion Following Zone 4–7 Extensor Tendon Repair. Journal of hand therapy: 18, 182-90. The Skinny- For years immobilization was the standard procedure following extensor tendon injuries in zones 4-7. As expected immobilization caused lengthy rehabilitation times, stiff joints, and tendon adhesions often…
Outcomes of Rigid Night Splinting and Activity Modification in the Treatment of Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
Shah, C. M., Calfee, R. P., Gelberman, R. H., & Goldfarb, C. A. (2013). Outcomes of rigid night splinting and activity modification in the treatment of cubital tunnel syndrome (night splint for cubital tunnel syndrome). The Journal of Hand Surgery, 38(6), 1125–1130.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2013.02.039 By: Sophia Grimm The Skinny: The purpose of this study was to…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.