Shoulder Pain: The Effectiveness of Conservative Treatment
Filed under Reviews
Reference:
Steuri, R., Sattelmayer, M., Elsig, S., Kolly, C., Tal, A., Taeymans, J., & Hilfiker, R. (2017). Effectiveness of conservative interventions including exercise, manual therapy and medical management in adults with shoulder impingement: a systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs. British journal of sports medicine, 51(18), 1340–1347. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2016-096515
By: Tayler Roost
The Skinny: This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis completed on the effectiveness of all relevant non-surgical interventions for shoulder pain and impingement.
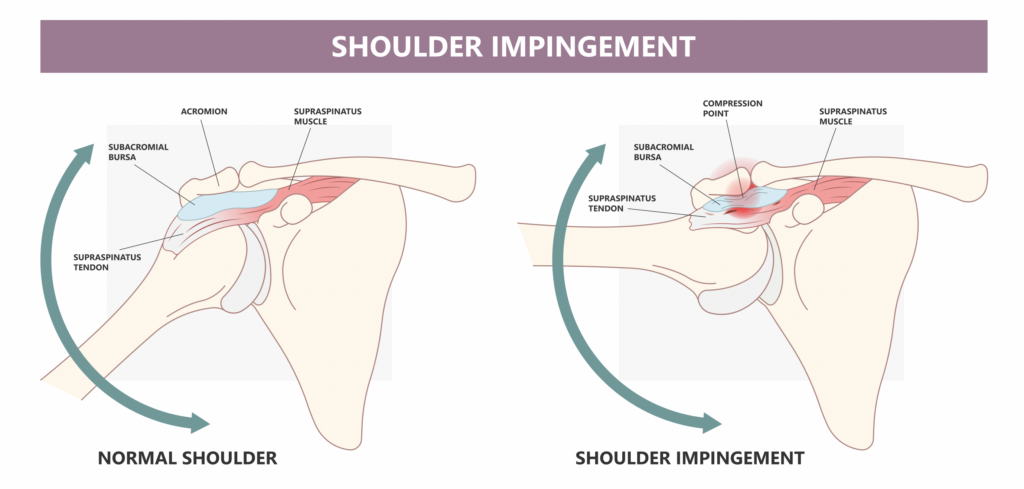
In the Weeds: 200 randomized controlled trials were analyzed to determine the most effective conservative interventions to treat shoulder pain and impingement. Patient inclusion criteria for each of the trials were as follows:
- 18 years or older
- Complaints of shoulder pain (pain arc between 40 degrees and 120 in abduction and flexion)
- Pain with active arm elevation
- Tenderness to palpation of rotator cuff tendons
- Resisted painful or weak shoulder external rotation and shoulder abduction
- Positive Neer, Hawkins-Kennedy, Speed, Jobe, or Empty can test
- At least one conservative intervention used
The considered parameters for each study encompassed pain, functionality, and the active range of motion.
Bringing it home: This analysis discovered that ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injections and targeted exercises addressing the rotator cuff musculature yielded the greatest benefits in pain relief and improved functionality. Additionally, the combination of manual therapy and exercise demonstrated effectiveness in pain alleviation, particularly showing more immediate effects during shorter follow-up appointments. Laser therapy was identified as effective in pain alleviation as well. Notably, active range of motion exercises exhibited superior effects compared to non-exercise therapy modalities.
Rating: 4/5
This review revealed that the overall quality of evidence for each modality was notably low, primarily due to a heightened risk of bias, imprecise data, inconsistent findings, and clinical heterogeneity (Steuri et al., 2017). While acknowledging the limited individual efficacy of these modalities, the study underscores the potential effectiveness of employing multiple approaches concurrently to address shoulder impingement. Despite the collective low quality, the study emphasizes that opting for conservative treatment is more advantageous than abstaining from any intervention. Furthermore, it advocates for tailoring the treatment approach to the specific needs of each patient.
More To Read
“Do joint mobilizations assist in the recovery of lateral elbow tendinopathy? A systematic review and meta-analysis”
By Sophia Grimm Lucado, A. M., Dale, R. B., Vincent, J., & Day, J. M. (2019). Do joint mobilizations assist in the recovery of lateral elbow tendinopathy? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of hand therapy : official journal of the American Society of Hand Therapists, 32(2), 262–276.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2018.01.010 The Skinny: The purpose of this study was…
Hand Therapy: How to Treat the Client with a New Distal Radius Fracture
A short blog post on the basics of treating a Distal Radius Fracture.
Soft Tissue Healing in Pediatrics
By: Chelsea Gonzalez Why do pediatric clients often not require as much hand therapy for soft tissue injuries when compared to adults? The simple answer: Kids have very elastic soft tissue, which can return to its original shape and position after stretch. This elasticity is lost with time as collagen fibers expand and their internal…
Top 5 DIP Flexion Exercises
By: Tori Rhodes Lately, we’ve had a handful of patients roll through our clinic with pretty significant limitations to DIP flexion. So, we’ve collected a selection of go-to exercises for these individuals. We’ve included a few of those here. From cat bites and fracture sites to mallet fingers and skin grafts, many individuals who are…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.






