All about kinesiology taping for upper extremity injuries and conditions!
Filed under Treatments
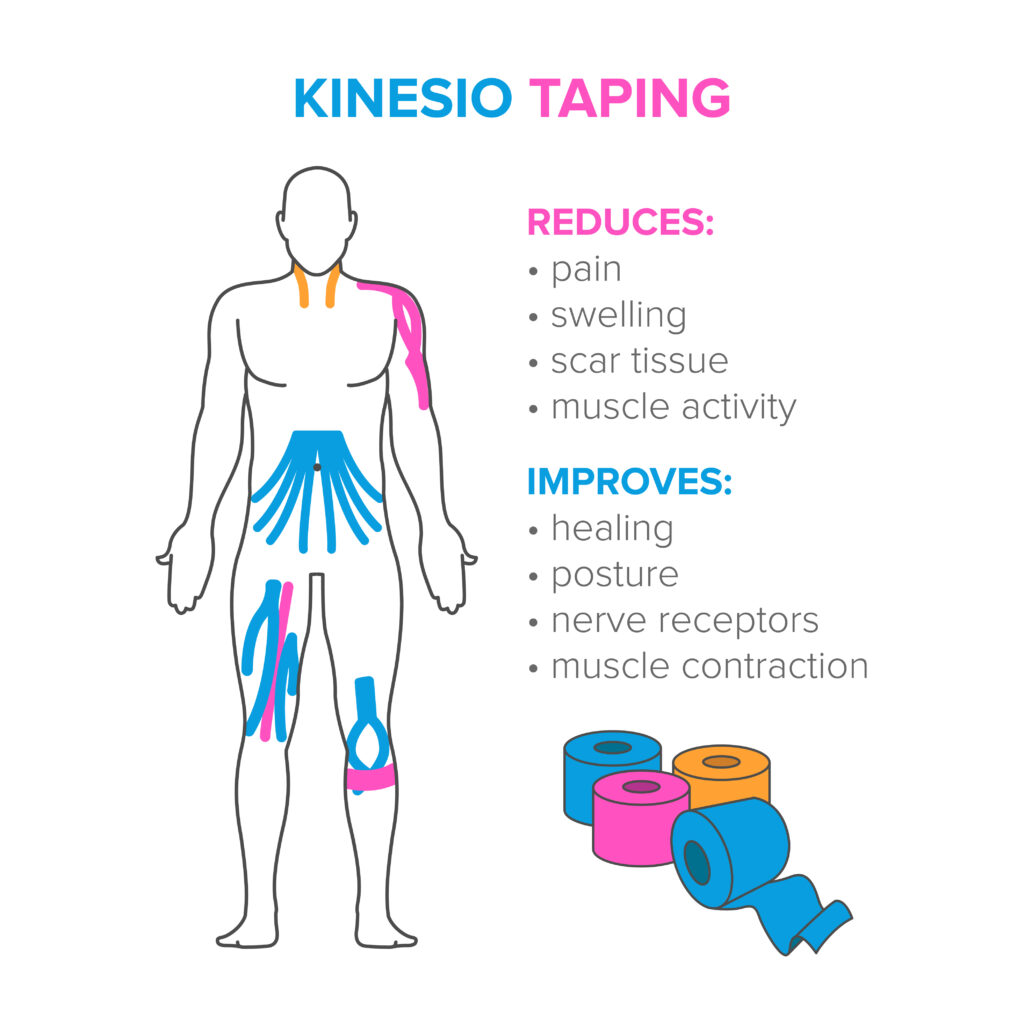
All about kinesiology taping!
Elastic is also known as k-tape, Kinesio-tape, and kinesiology taping. Elastic tape is all over the marketplace and is often seen on professional athletes. It can be found in most therapy clinics and is used to treat both orthopedic and neurological conditions. There are limited studies supporting the use of elastic tape, but there is strong anecdotal evidence of its effectiveness.
Elastic tape is another modality for pain management, soft tissue trauma, edema, joint subluxation, and nerve compression.

What is the theory behind elastic taping?
Skin Lifting: The elastic properties behind taping allow it to stretch. When the stretch tape is applied, it helps lift the skin microscopically, allowing for more movement and circulation. When muscles are inflamed and painful, this causes a lack of space; therefore, the lifting properties can be helpful.
Pain Theory or Gate Control Theory: Similar to how we rub our arm when it gets injured. Just rubbing the injury site disrupts the pain signal or the perception of pain, providing some pain relief. So theoretically, applying the tape would close the gate pain.

Provide Muscle Support: Unlike athletic tape, elastic tape is more of a facilitatory tape and aids in supporting the muscle. If taped properly, taping can improve the muscle’s ability to contract. It also still allows for the full range of motion while providing support.
The terminology behind applying k-tape?
Commonly used terms for kinesiology taping include anchor, stretch, and flex. Anchor is the term used to describe the end of the tape, typically the last two inches. This part of the tape should never be stretched or applied with tension.
The stretch is how far you extend the tape. The amount the tape is stretched is usually based on percentages. So if there is no stretch, this is referred to at 0% or paper off. If the tape were to be fully stretched, this would be 100% stretch, if it were between 0-100, it would be 50%.
A few of the basics
Never apply tape to damaged or broken skin. If the individual has sensitive skin, try a small piece of tape on the skin to ensure no skin irritation develops. There are brands of kinesiology tape that are made for sensitive skin.
Make sure the skin is clean and dry before applying the tape. Avoid applying lotions or oils before tape application.
Rond tape edges, so they adhere better.

Once the tape is stuck down, rub it to activate the adhesive, so it adheres better.
Remember not to apply tension at the anchors or ends of the tape.
More To Read
A Review on the Conservative Management of Trigger Finger
Lunsford, D., Valdes, K., & Hengy, S. (2017). Conservative management of trigger finger: A systematic review. Journal of Hand Therapy, 32(2), 212-221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jht.2017.10.016 The Skinny The main purpose of the literature review was to determine the efficacy of conservative management of trigger finger (TF) through the use of an orthosis in addition to therapy. The review…
Dart-throwing Angle in Hand Therapy for Scapholunate (SL) Ligament Injuries.
Does Object Height Affect the Dart Throwing Motion Angle During Seated Activities of Daily Living? Cohen, Y., Portnoy, S., Levanon, Y., Friedman, J. (2020). Does object height affect the dart throwers motion angle during seated activities of daily living. Journal of Motor Behavior, (52) 4. Article Review By: Rita Steffes The Skinny: Dart Throwers Motion…
A randomized clinical trial comparing early active motion programs: Earlier hand function, TAM, and orthotic satisfaction with a relative motion extension program for zones V and VI extensor tendon repairs
By Brittany Day Collocott SJ, Kelly E, Foster M, Myhr H, Wang A, Ellis RF. A randomized clinical trial comparing early active motion programs: Earlier hand function, TAM, and orthotic satisfaction with a relative motion extension program for zones V and VI extensor tendon repairs. Journal of Hand Therapy. 2019. doi:10.1016/j.jht.2018.10.003 The Skinny- This is…
Changes in ROM of the MCP after Trapeziometacarpal Arthrodesis
Rapid Review: Changes in ROM of the MCP after Trapeziometacarpal Arthrodesis Hayashi, M., Kato, H., Komatsu, M., Yamazaki, H., Uchiyama, S., & Takahashi, J. (2021). Changes in the Functional Range of Motion of the Thumb Metacarpophalangeal Joint After Trapeziometacarpal Arthrodesis for Patients With Advanced Trapeziometacarpal Osteoarthritis. The Journal of hand surgery, S0363-5023(21)00613-4. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2021.09.018. The Skinny: Several published…
Sign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.