Carpal Tunnel Release: Outcomes of Pediatric and Adolescent
Filed under Diagnoses
Rapid Review. Outcomes of pediatric and adolescent carpal tunnel release based on etiology.
Velicki, K., Goldfarb, C. A., Roberts, S., & Wall, L. B. (2021). Outcomes of pediatric and adolescent carpal tunnel release. The Journal of Hand Surgery, 46(3), 178-186.
The Skinny: Less than 1% of pediatric carpal tunnel is idiopathic in nature, compared to adults where the majority of carpal tunnel is idiopathic. Limited studies have looked into the surgical outcomes of pediatric carpal tunnel release and there have been no studies comparing outcomes based on the etiology of symptoms.
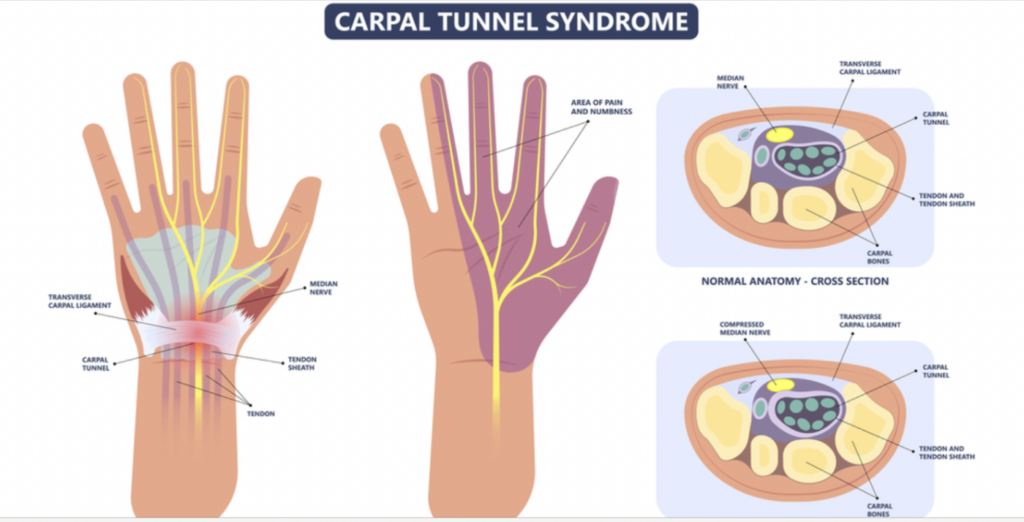
In the Weeds: Twenty-three patients with 26 surgeries were enrolled in the study and grouped based on the etiology: All of these patients had hand median nerve pain or other symptoms such as numbness and tingling indicating carpal tunnel syndrome.
| Etiology | Number of Hands |
| Lysosomal storage disease | 11 hands |
| Idiopathic | 6 hands |
| Acute traumatic | 7 hands |
| Delayed traumatic | 5 hands |
| Tumorous | 2 hands |
Outcome measures included the Boston Carpal Tunnel Questionnaire (BCTQ), and Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System (PROMIS) scores.
Bringing it Home: The median age for surgery was 12.7 years (range 2.5 – 23.3). All patients with tumorous etiology and acute trauma had resolution of symptoms. Those with delayed and idiopathic etiology experienced recurrent symptoms. Patients with lysosomal storage disease all experienced the gradual return of their symptoms with 2 of the patients undergoing revision carpal tunnel release.
In acute cases, carpal tunnel release was very successful in relieving median nerve pain in the pediatric population, but not always in the delayed traumatic. Approximately 50% with idiopathic carpal tunnel experienced resolution of symptoms. With lysosomal storage disease, the patient experienced relief for a few years.
Rating ⅘
There were multiple limitations in the study including a limited number of participants in each category. There was also some diagnostic uncertainty, as some of the diagnosis was based on the clinician’s judgment. Lastly, phone interviews and chart reviews were utilized to obtain outcomes data, so there were various means utilized to obtain the data, in which the interviewer could have influenced the outcomes.
More To Read
Hand Therapy Interventions for Distal Upper Extremity Injuries and Conditions
Takata, S.C., Wade, E.T., & Roll, S.C. (2019). Hand therapy interventions, outcomes, and diagnoses evaluated over the last 10 years: A mapping review linking research to practice. Journal of Hand Therapy, 32(1), 1–9. Written by Brittany Carrie The Skinny Approximately 26.9% of orthopedic injuries and disorders of the upper extremity occur worldwide. Injuries are most…
Read MoreTest for Distal Radial Ulnar Joint of the Wrist
Ballottment Test for Wrist DRUJ Reliability and Validity Analysis of the Distal Radioulnar Joint Ballottement Test Nagashima, M., Omokawa, S., Hasegawa, H., Nakanishi, Y., Kawamura, K., & Tanaka, Y. (2024). Reliability and validity analysis of the distal radioulnar joint ballottement test. The Journal of Hand Surgery, 49(1), 15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhsa.2023.10.006 The Skinny: Distal radioulnar joint (DRUJ)…
Read MoreFlexor tendon rehabilitation in the 21st century: A systematic review
Neiduski, R. L. & Powell, R. K. (2019). Flexor tendon rehabilitation in the 21st century: A systematic review. Journal of Hand Therapy, 32, 165-174. The Skinny The objective of the study was to determine if there was evidence to support 1 type of exercise regimen. Exercise regimens reviewed include place and holds, early passive or…
Read MoreSign-up to Get Updates Straight to Your Inbox!
Sign up with us and we will send you regular blog posts on everything hand therapy, notices every time we upload new videos and tutorials, along with handout, protocols, and other useful information.